Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Abdelmalak M, Pendse A. Hepatocellular adenoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/livertumorhepatocellularadenoma.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Benign neoplasm of hepatocellular origin arising in the noncirrhotic liver
- Majority are solitary; adenomatosis when > 10 lesions
- Rare cases associated with glycogen storage disease (type 1a), maturity onset diabetes of the young type 3 and Fanconi anemia
- 5 main subtypes based on gene mutations
Essential features
- Arises in noncirrhotic liver
- Female > male, strong association with oral contraceptive exposure
- Unpaired arteries with absence of interlobular bile ducts
Terminology
- Also known as hepatic adenoma and liver cell adenoma
- 5 main subtypes:
- HNF1A mutated hepatocellular adenoma (HA-H, ~35%)
- Beta catenin mutated hepatocellular adenoma (HA-B, ~10%)
- Inflammatory hepatocellular adenoma (HA-I, ~35%)
- Sonic hedgehog (SHH) hepatocellular adenoma (HA-sh, ~5%)
- Hepatocellular adenoma, not otherwise specified (HA-U, ~7%)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D13.4 - benign neoplasm of liver
Epidemiology
- F > M
- Annual incidence: 1 - 1.5 cases per million population with significantly higher incidence in women taking oral contraceptive pills, approximately 3 per 100,000 (N Engl J Med 1976;294:470)
- Additional risk factors include anabolic steroids, noncontraceptive estrogen supplements, obesity and metabolic syndrome
- Mean age = 37 - 41 years
- Rare in pediatric patients
Sites
- Liver
Pathophysiology
- Based on specific subtypes:
- HNF1A mutated hepatocellular adenoma (HA-H): somatic mutations of TCF1 (HNF1A) gene and rare (< 5%) heterozygous germline mutations of CYP1B1 gene; resultant increase in lipogenesis by promotion of fatty acid synthesis and by downregulation of liver type fatty acid binding protein (LFABP) (Nat Genet 2002;32:312)
- Beta catenin mutated hepatocellular adenoma (HA-B): beta catenin gene activating mutations (exon 7 - 8 and exon 3), resultant stabilization of beta catenin protein and increased or nontransient activation of Wnt / beta catenin signaling pathway (Hepatology 2006;43:515)
- Inflammatory hepatocellular adenoma (HA-I): gain of function mutations of the IL6ST gene, activation of STAT3 signaling pathway and acute phase inflammatory response (Nature 2009;457:200)
- Sonic hedgehog (SHH) hepatocellular adenoma (HA-sh): activation of sonic hedgehog pathway via fusion of promoter of INHBE with GLI1; also upregulation of argininosuccinate synthase 1, which may indicate increased risk of hemorrhage (Gastroenterology 2017;152:880, Hepatology 2017;66:2016, Hepatology 2018;68:964)
Clinical features
- May be asymptomatic and incidentally diagnosed due to imaging performed for an unrelated indication
- Symptomatic lesions present with abdominal pain or hemorrhage
- Risk of hemorrhage increases with size
Diagnosis
- Unpaired arteries are characteristic; interlobular bile ducts are absent
- Cytologic atypia is unusual
- Thin or mildly thickened hepatocyte cell plates
Laboratory
- Liver function tests tend to be normal
- Mild elevation in alpha fetoprotein in some cases
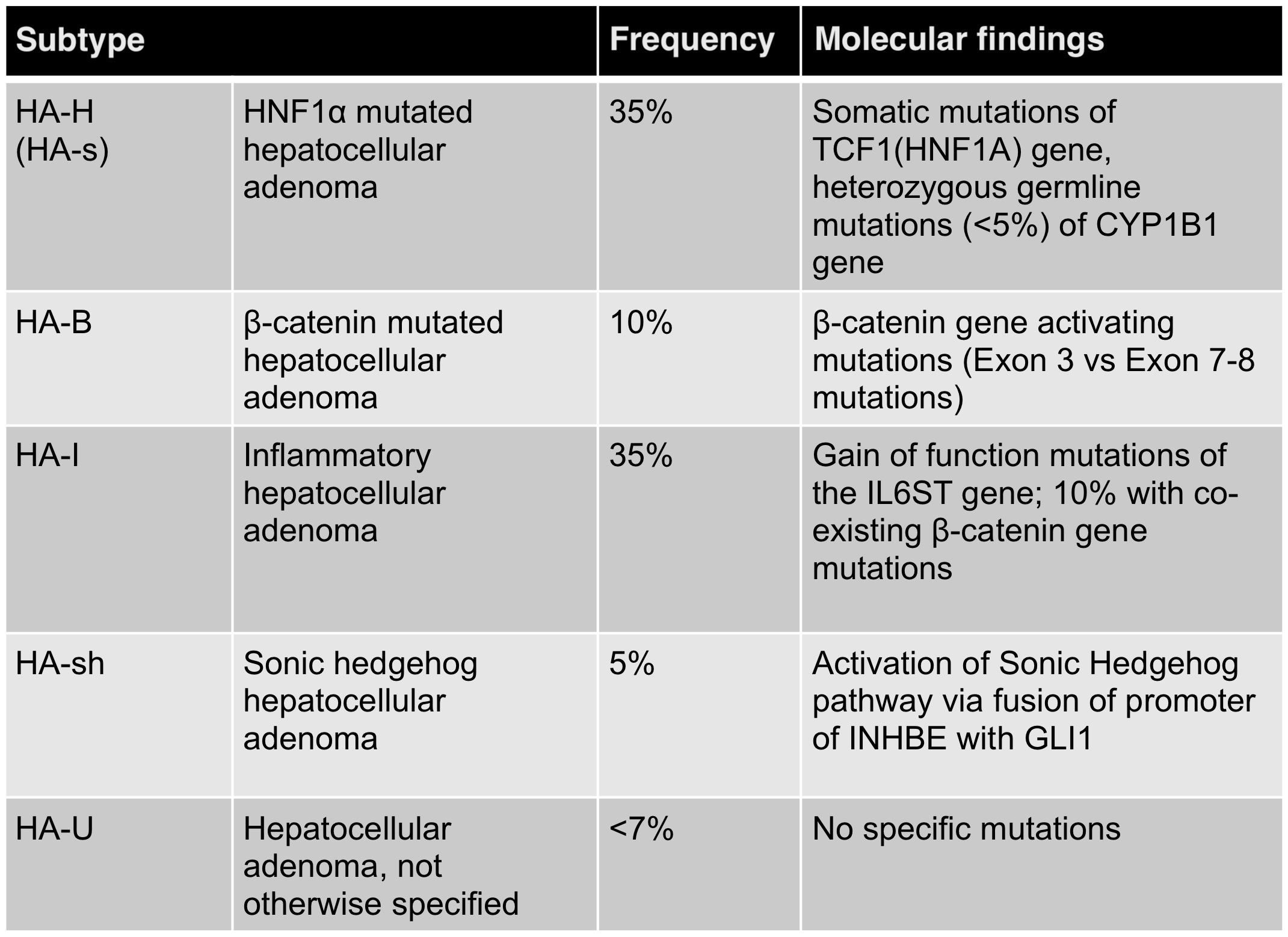
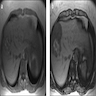
Radiology description
- MRI is the most optimal imaging modality
- Features characteristic of a hepatocellular adenoma over focal nodular hyperplasia include strong hyperintensity on T2 weighting, hyperintensity on T1 weighting, cystic areas, hemorrhagic areas and diffuse intralesional steatosis (Diagn Interv Radiol 2014;20:193)
- Specific features for some subtypes:
- HNF1A mutated hepatocellular adenoma (HA-H): homogeneous dropout of signal on T1 weighted out of phase sequence
- Inflammatory hepatocellular adenoma (HA-I): marked hyperintensity on T2 weighted sequences, hyperintense rim on T2 weighted sequence which corresponds to sinusoidal dilatation, also known as atoll sign
Prognostic factors
- Risk of malignant transformation is higher in
- Men
- Beta catenin mutated hepatocellular adenoma (HA-B)
- Larger tumors
- Reference: Hepatology 2006;43:515
Case reports
- 6 day old boy with multiple adenomas and microvillus inclusion disease (Dig Dis Sci 2013;58:2784)
- 20 year old man with malignant transformation of beta catenin mutated adenoma (Oncology 2017;92:16)
- 23 year old woman with diabetes and malignant transformation of HNF1A mutated adenoma (Semin Liver Dis 2015;35:444)
- 31 year old woman with recurrent adenoma requiring liver transplant (Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2014;106:494)
- 36 year old woman with hematoma following remote trauma (World J Gastroenterol 2013;19:4422)
- 11 cases of malignant transformation of adenoma (Mod Pathol 2014;27:1499)
Treatment
- Male patients: surgical excision irrespective of size
- Female patients: surgical excision if > 5 cm in size and with beta catenin activating mutations (Therap Adv Gastroenterol 2016;9:898)
- Nonsurgical cases: suspension of oral contraceptive pills (if applicable) and imaging follow up
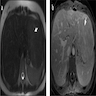
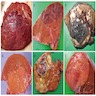
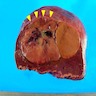
Gross description
- Majority are solitary and well circumscribed
- Uncapsulated or develop ill defined pseudocapsule
- Lighter in color compared with surrounding liver
- Foci of necrosis, hemorrhage and bile staining
- Usually lack significant fibrosis (including central scar) and nodularity
- Reference: Burt: MacSween's Pathology of the Liver, 7th Edition, 2017
Gross images
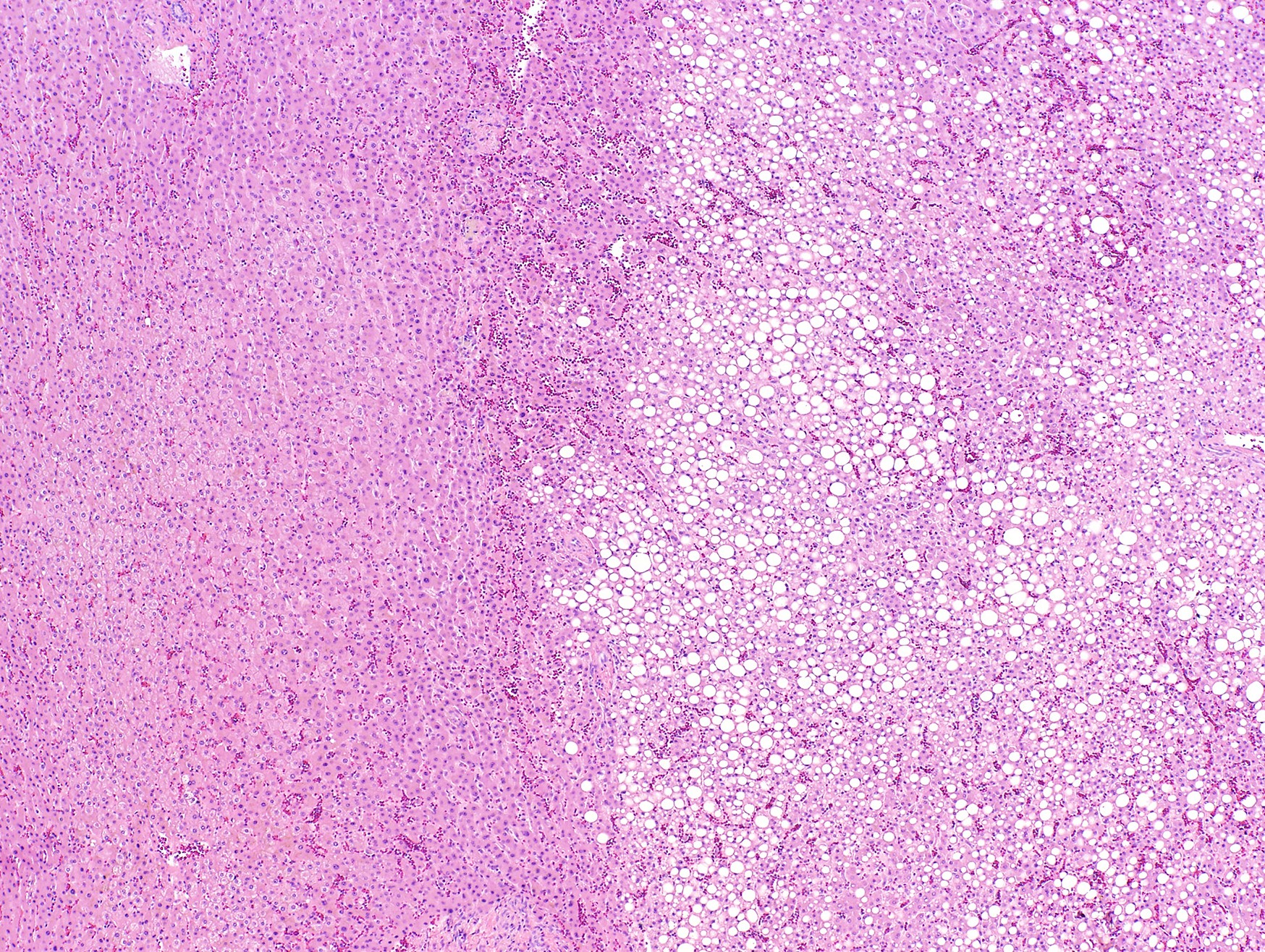
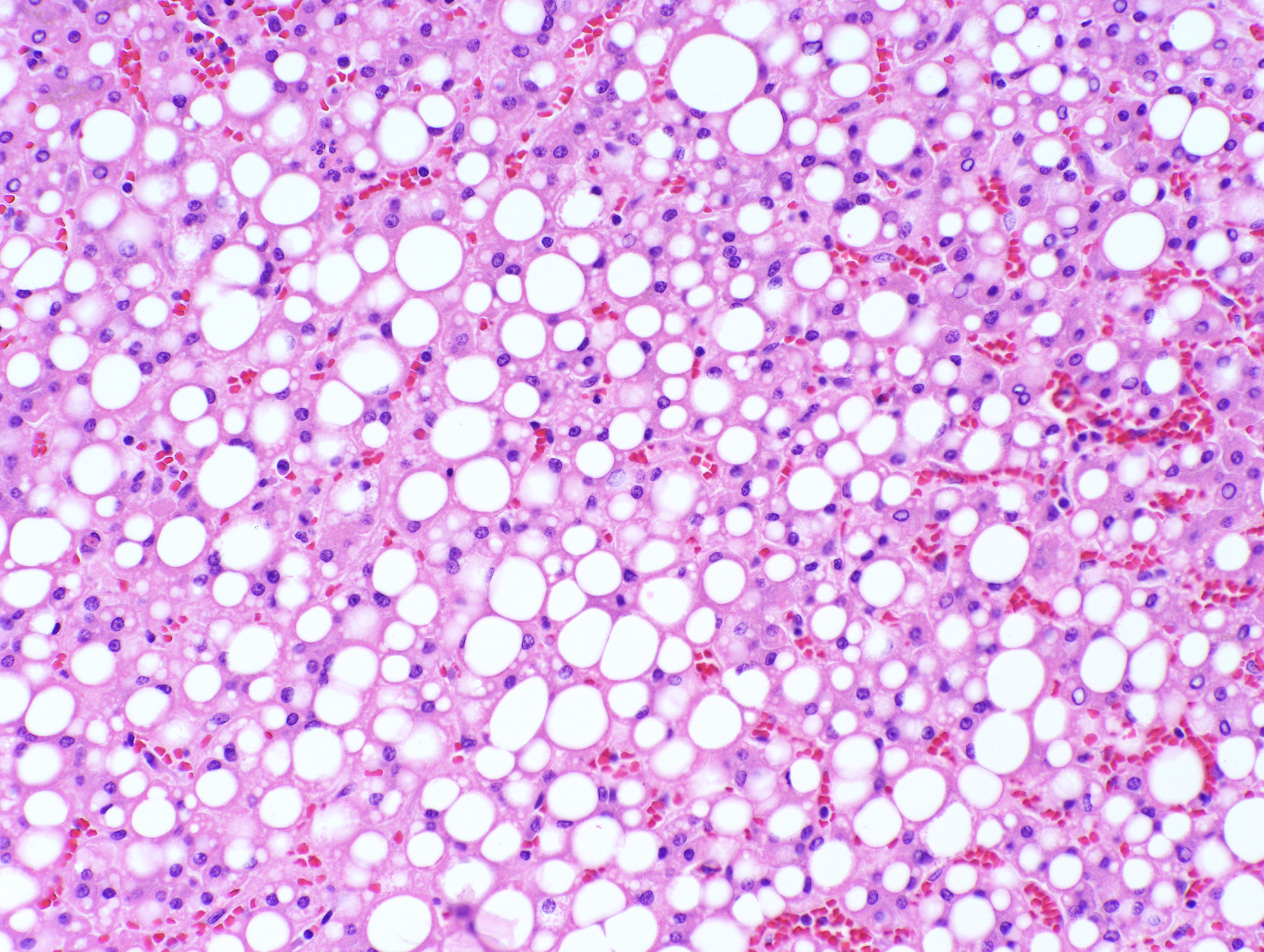
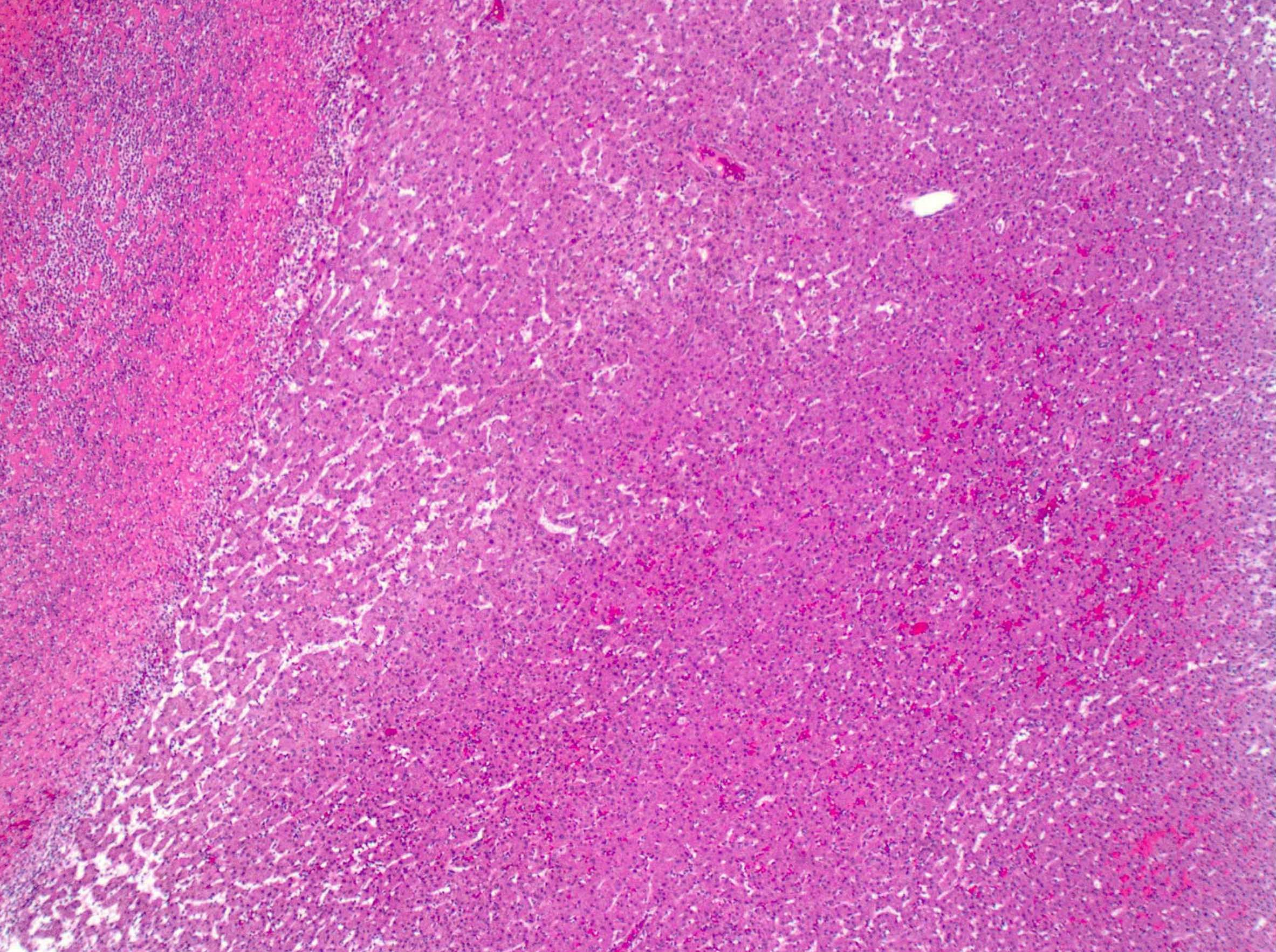
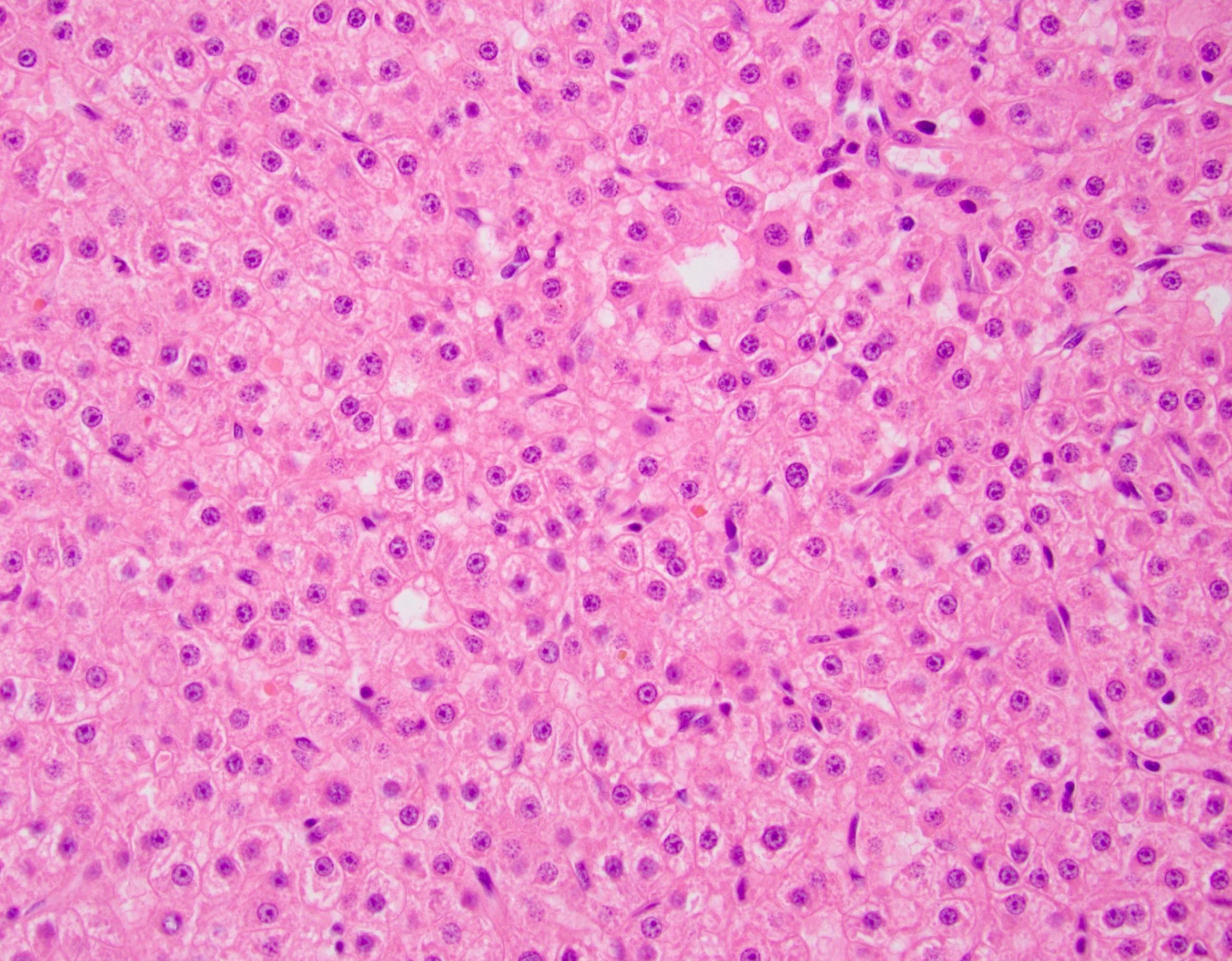
Microscopic (histologic) description
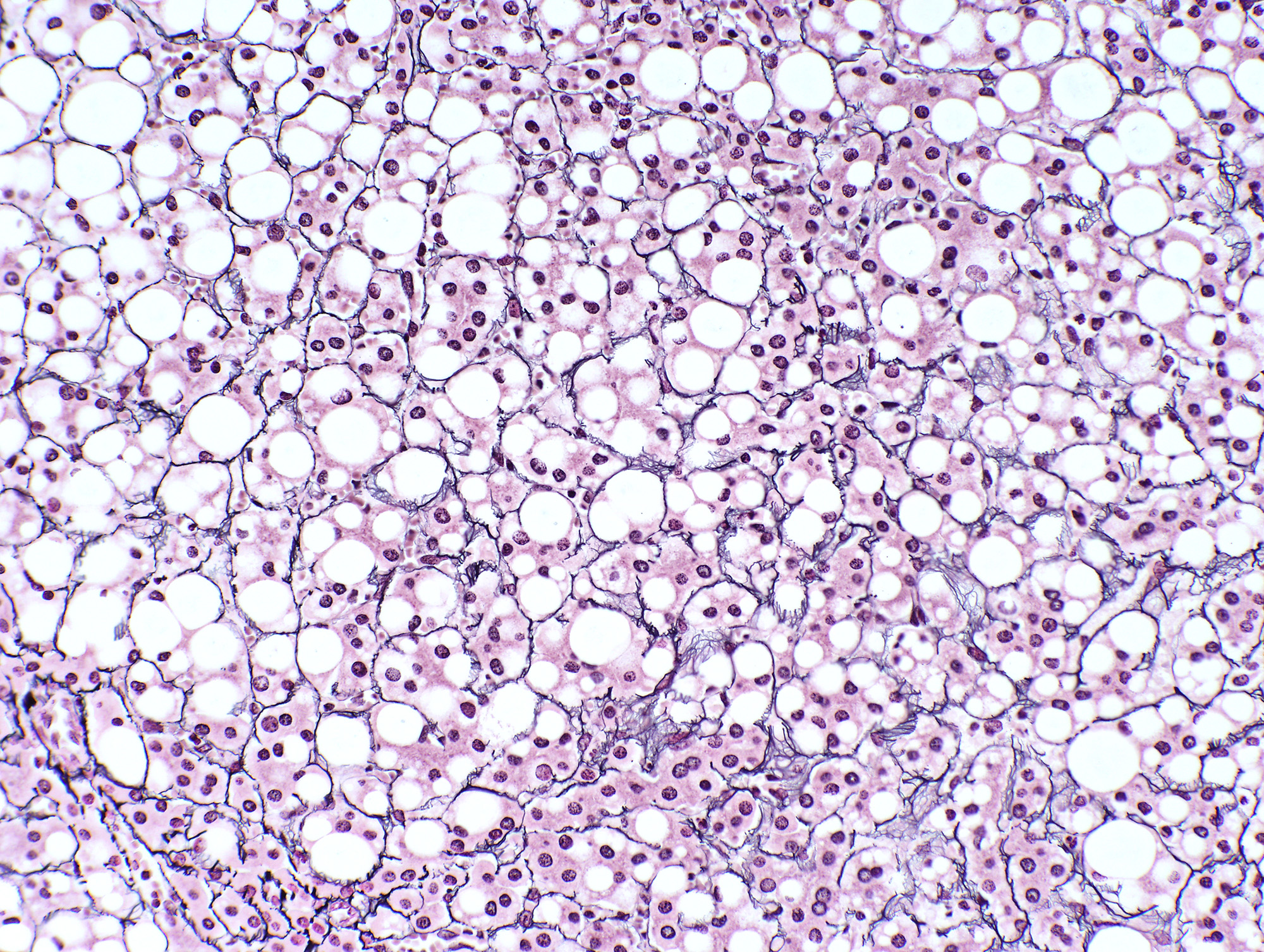
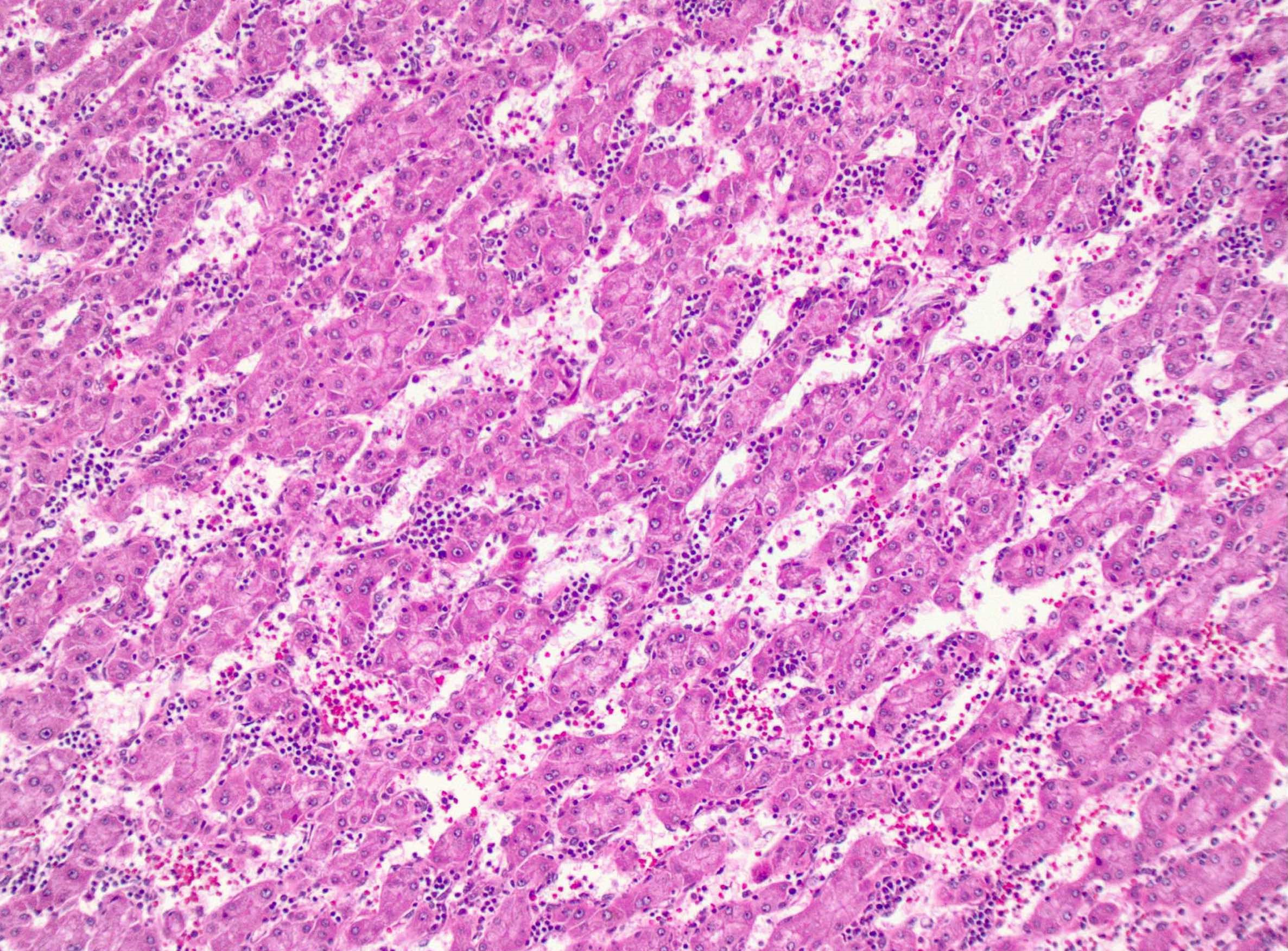
- Well defined border between the lesion and background liver
- Composed of hepatocytes with no significant cytologic atypia
- Arranged as thin or only mildly thickened cell plates, 1 - 2 cells thick
- May have pseudoacinar arrangement and steatotic foci
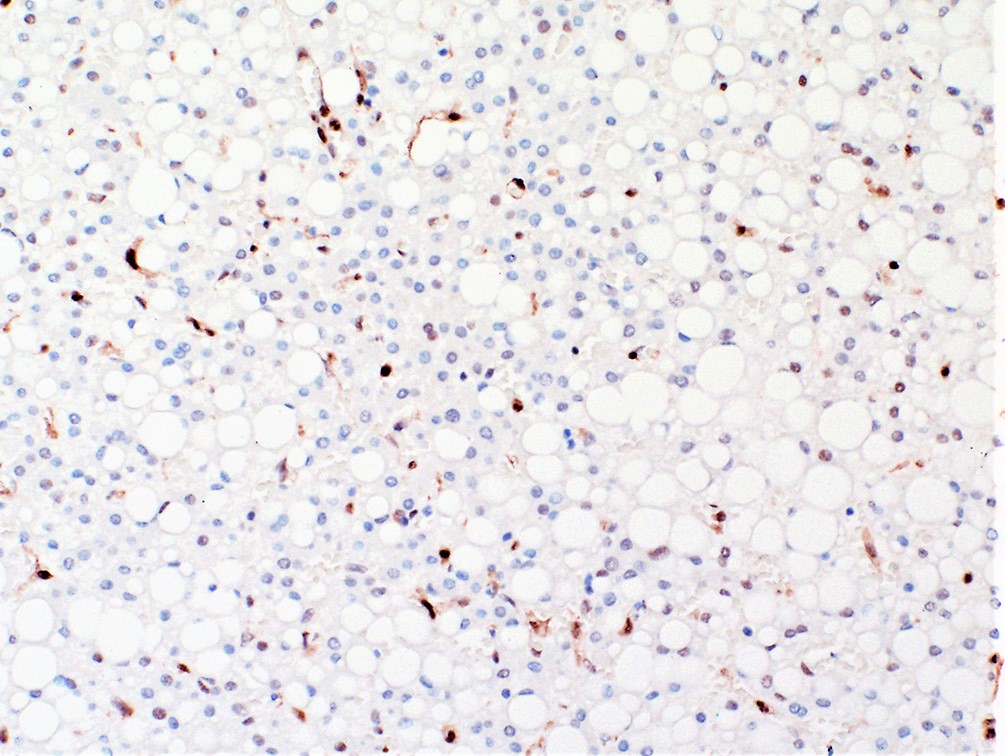
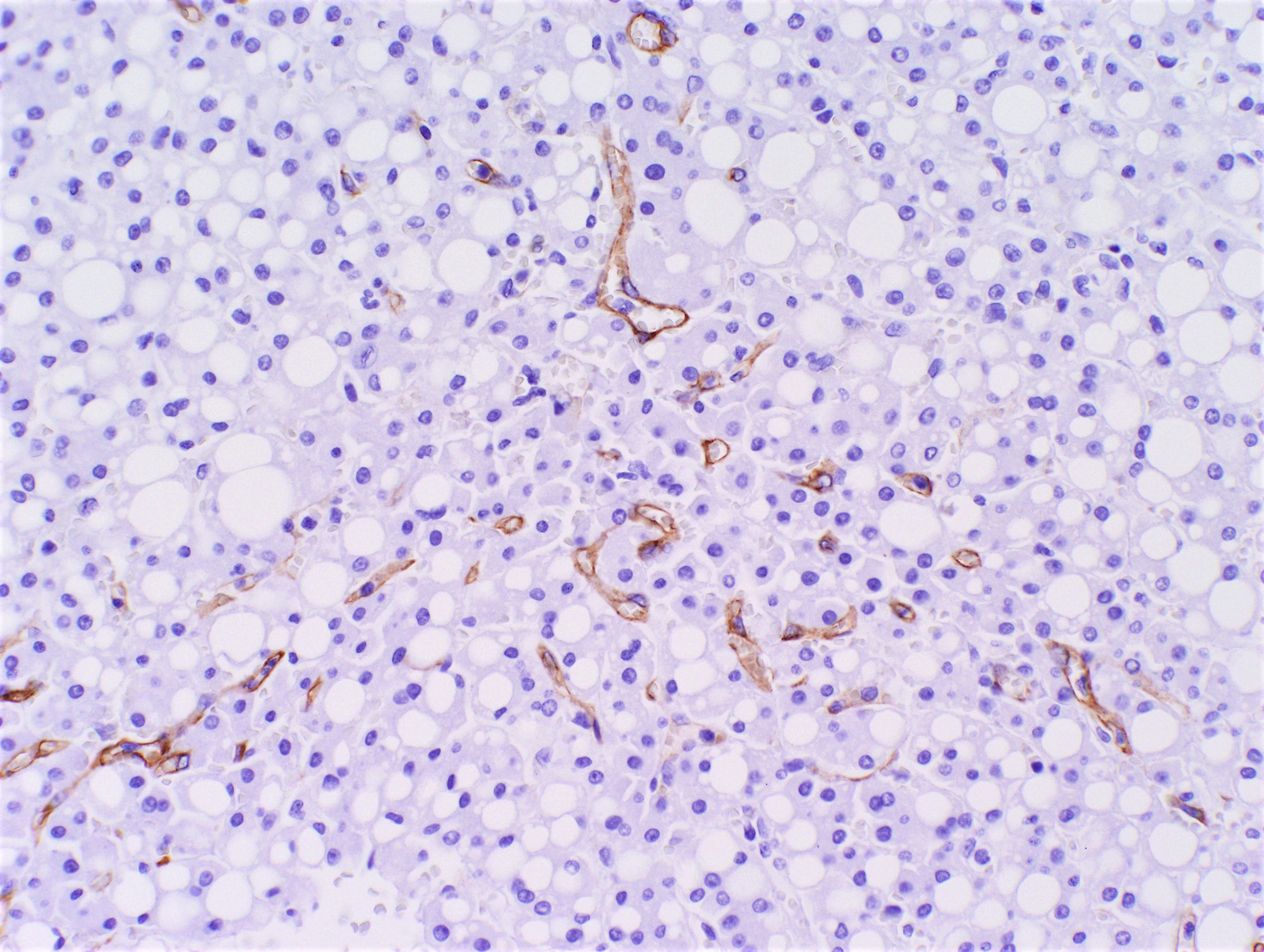
- Characterized by unpaired arteries; interlobular bile ducts are absent, some cases show bile ductules
- Foci of hemorrhage, ischemic changes and necrosis
- No cytologic atypia, atypical mitoses and portal / parenchymal invasion
- Reticulin stain helpful to establish near normal hepatocyte plate thickness with only focal loss, particularly in the steatotic areas
- Microscopic features of specific subtypes include:
- HNF1A mutated hepatocellular adenoma (HA-H): characterized by steatosis (fat accumulation in lesional hepatocytes), reticulin staining is mostly intact, some cases / areas show "packeting" (i.e. prominent pericellular staining or almost complete circling of small groups of hepatocytes by reticulin fibers)
- Beta catenin mutated hepatocellular adenoma (HA-B): pseudoacinar arrangement; cytologic abnormalities including nuclear pleomorphism and atypia, multinucleation, prominent nucleoli; steatosis is rare, no significant inflammation
- Inflammatory hepatocellular adenoma (HA-I): may have irregular, poorly circumscribed borders; inflammatory infiltrates and sinusoidal dilatation; may have pseudoportal tracts, which are islands of thick walled arteries with no definite bile ducts but associated ductular reaction
- Hepatocellular adenoma, not otherwise specified (HA-U): morphology characteristic of adenoma but no specific characteristics of the individual subtypes; lesions with extensive hemorrhage and necrosis are currently grouped into this subtype
- References: Burt: MacSween's Pathology of the Liver, 7th Edition, 2017, Diagn Pathol 2016;11:27, Clin Mol Hepatol 2016;22:199, Hepatology 2006;43:515, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2014;138:1090, Front Med (Lausanne) 2017;4:10
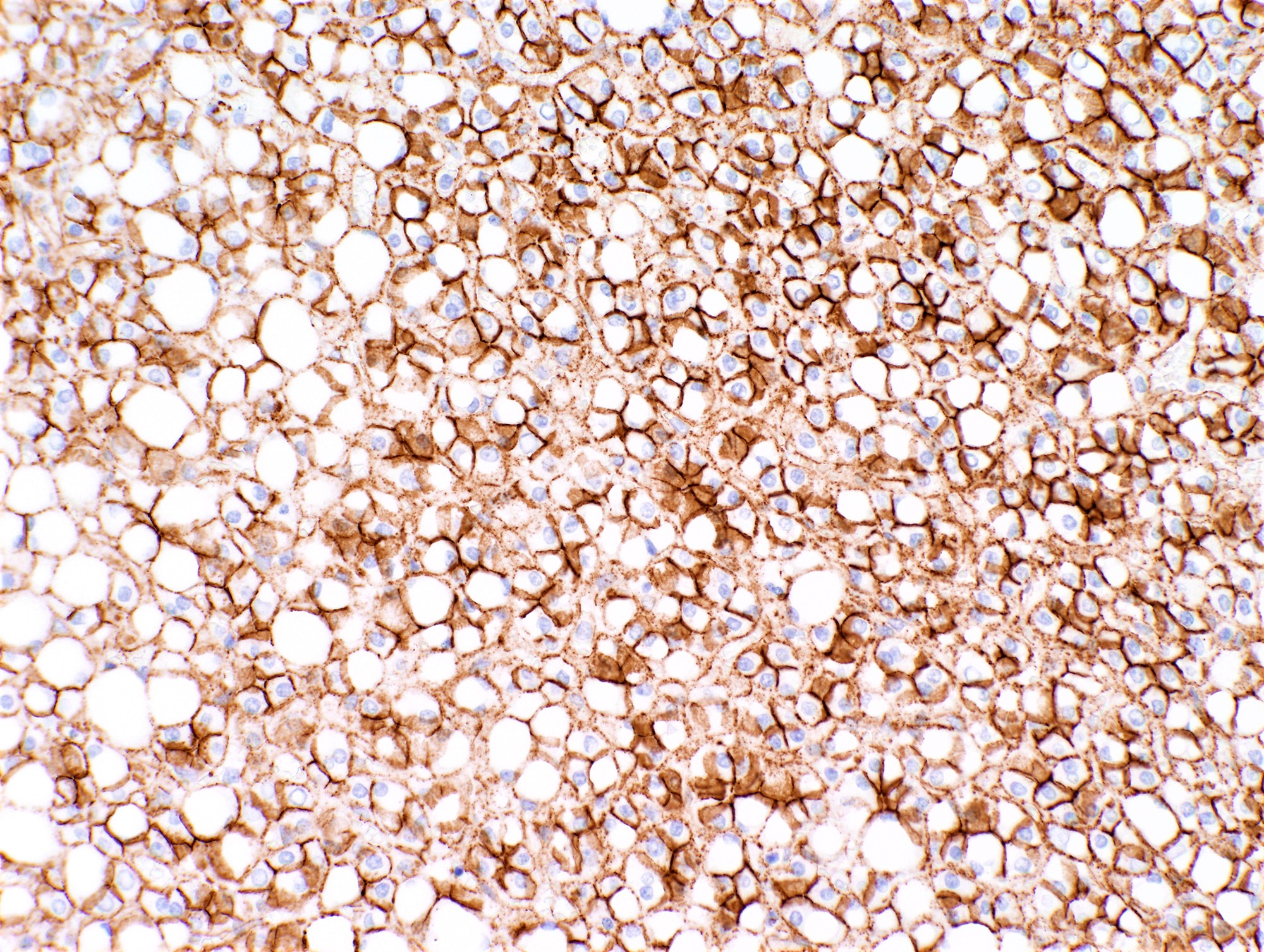
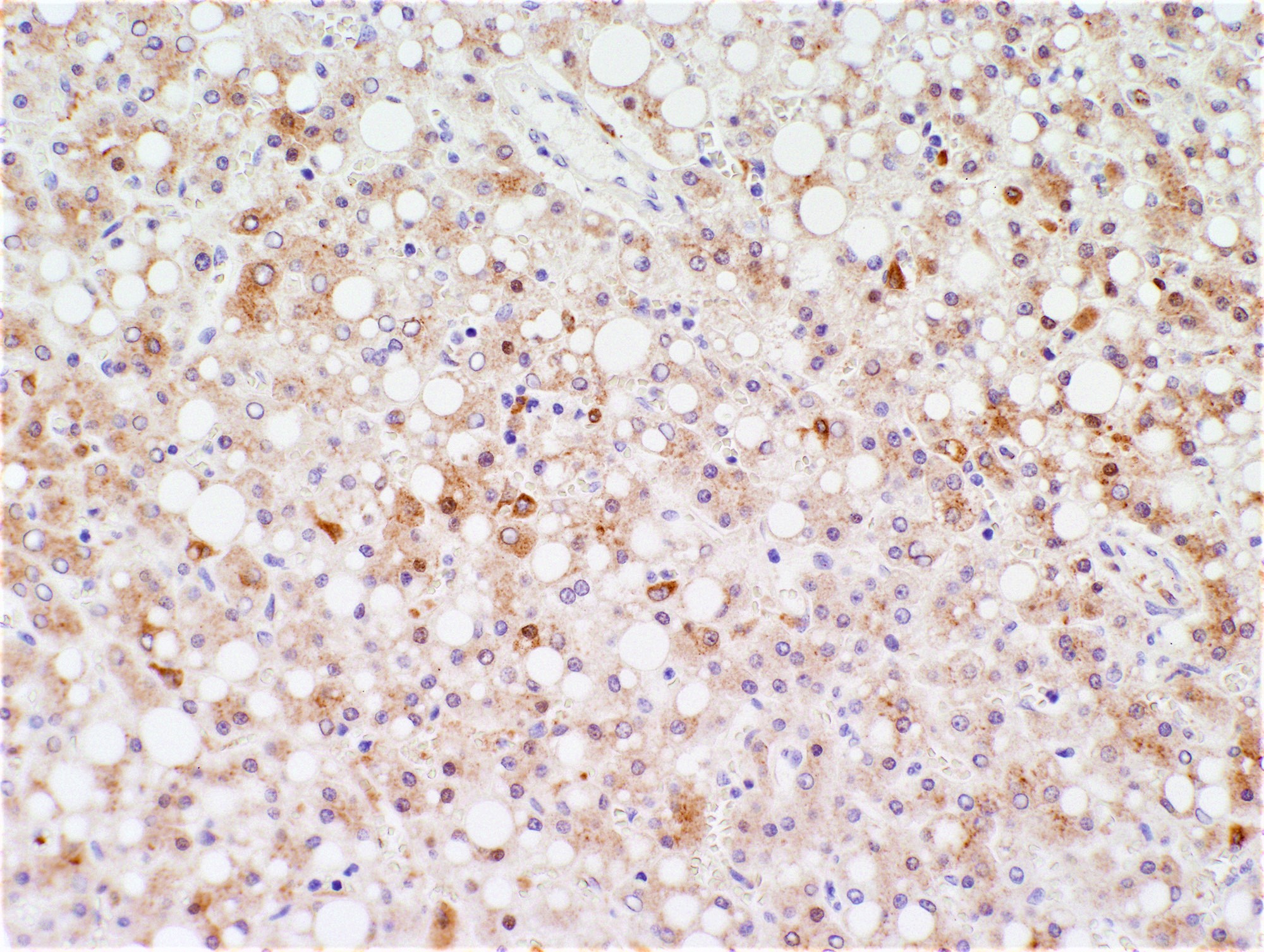
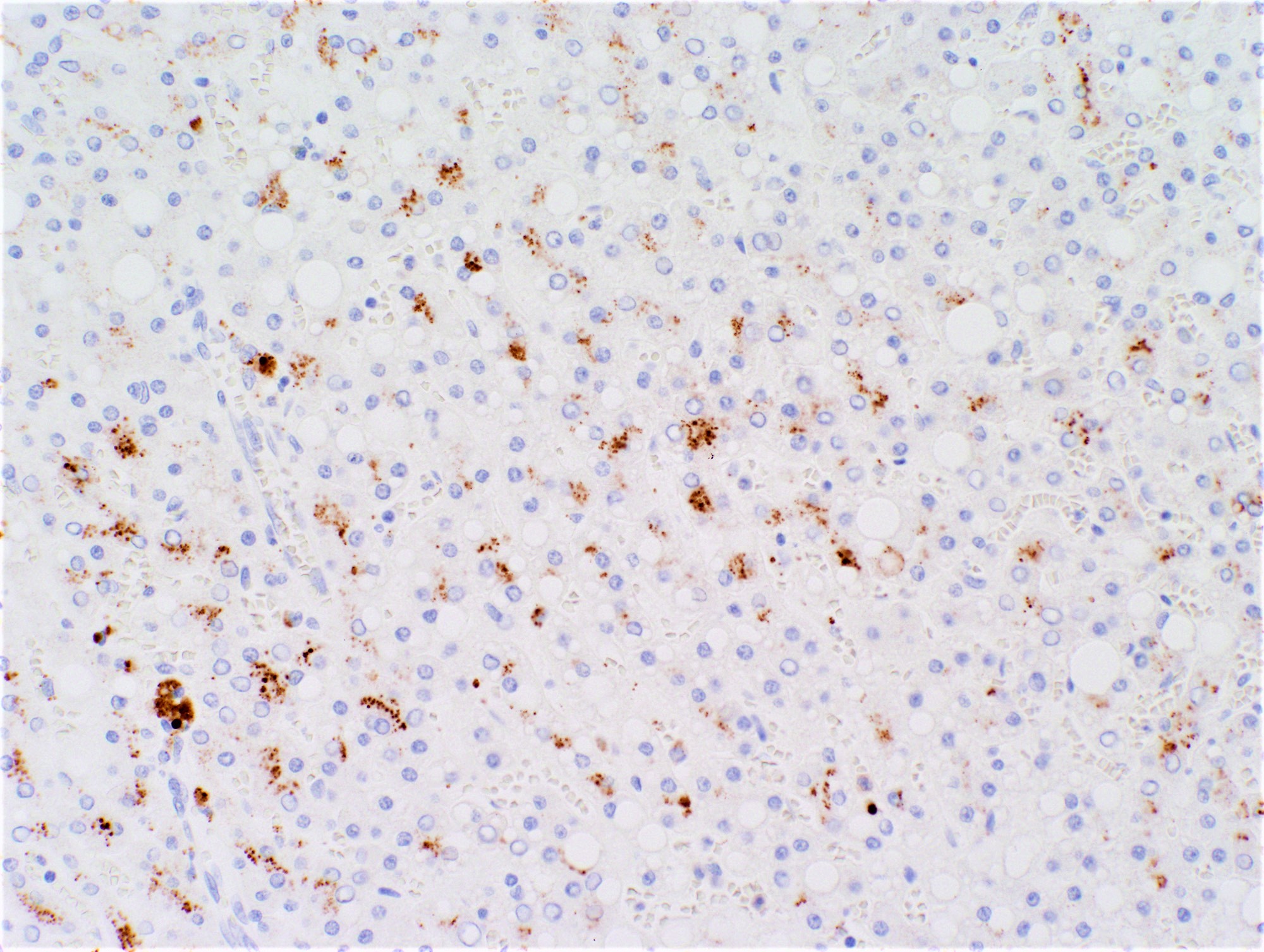
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Monica Abdelmalak, M.D., Avani Pendse, M.D., Ph.D. and Raul S. Gonzalez, M.D.
Cytology description
- Cytologically bland hepatocytes on smears; uniform, regular nuclei with low N/C ratios and rare mitoses (Cibas: Cytology - Diagnostic Principles and Clinical Correlates, 4th Edition, 2014)
- Diagnosis is difficult by cytology alone given that a well differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma is in the differential diagnosis and presence or lack of invasion cannot be evaluated on smears alone
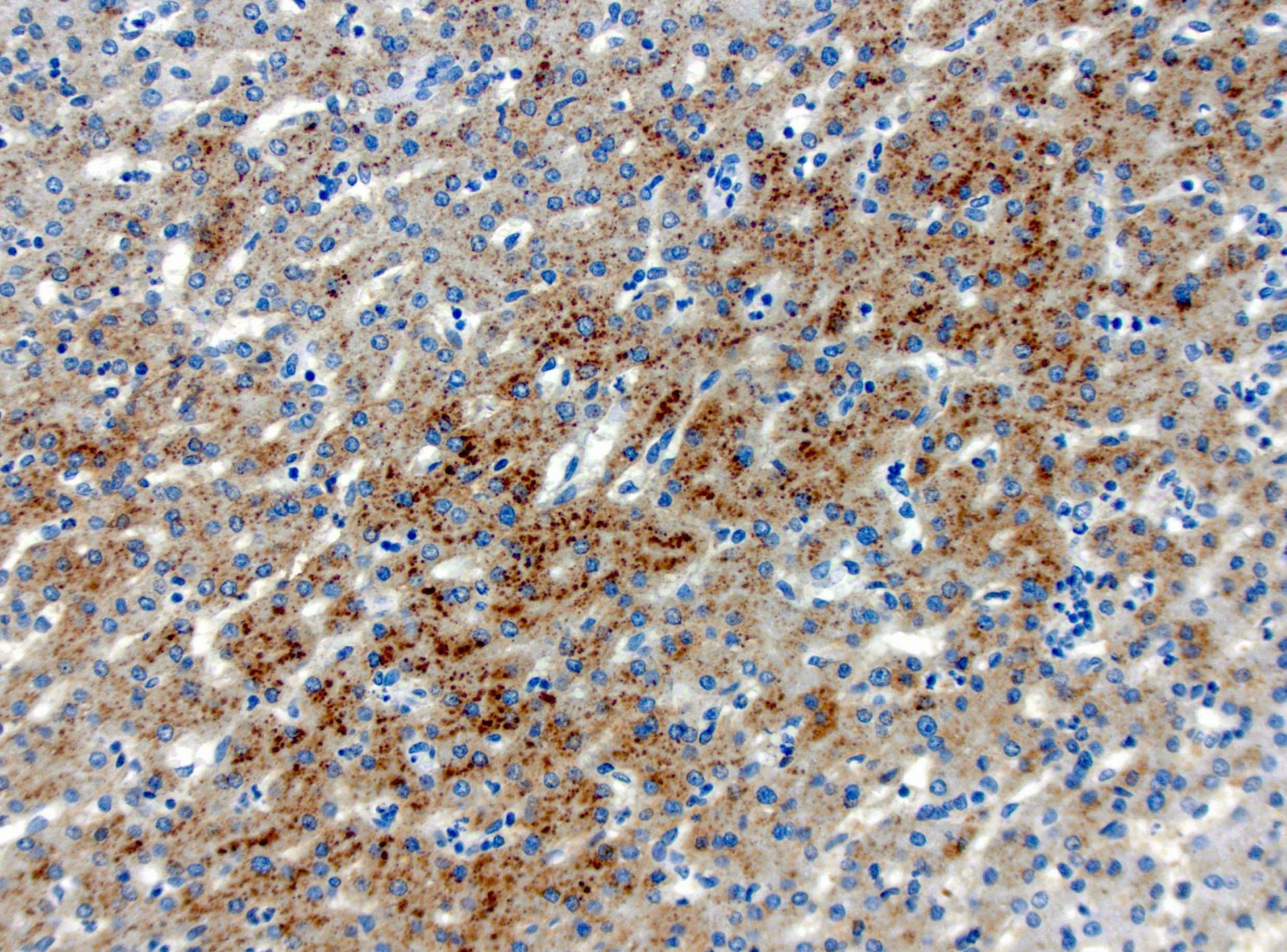
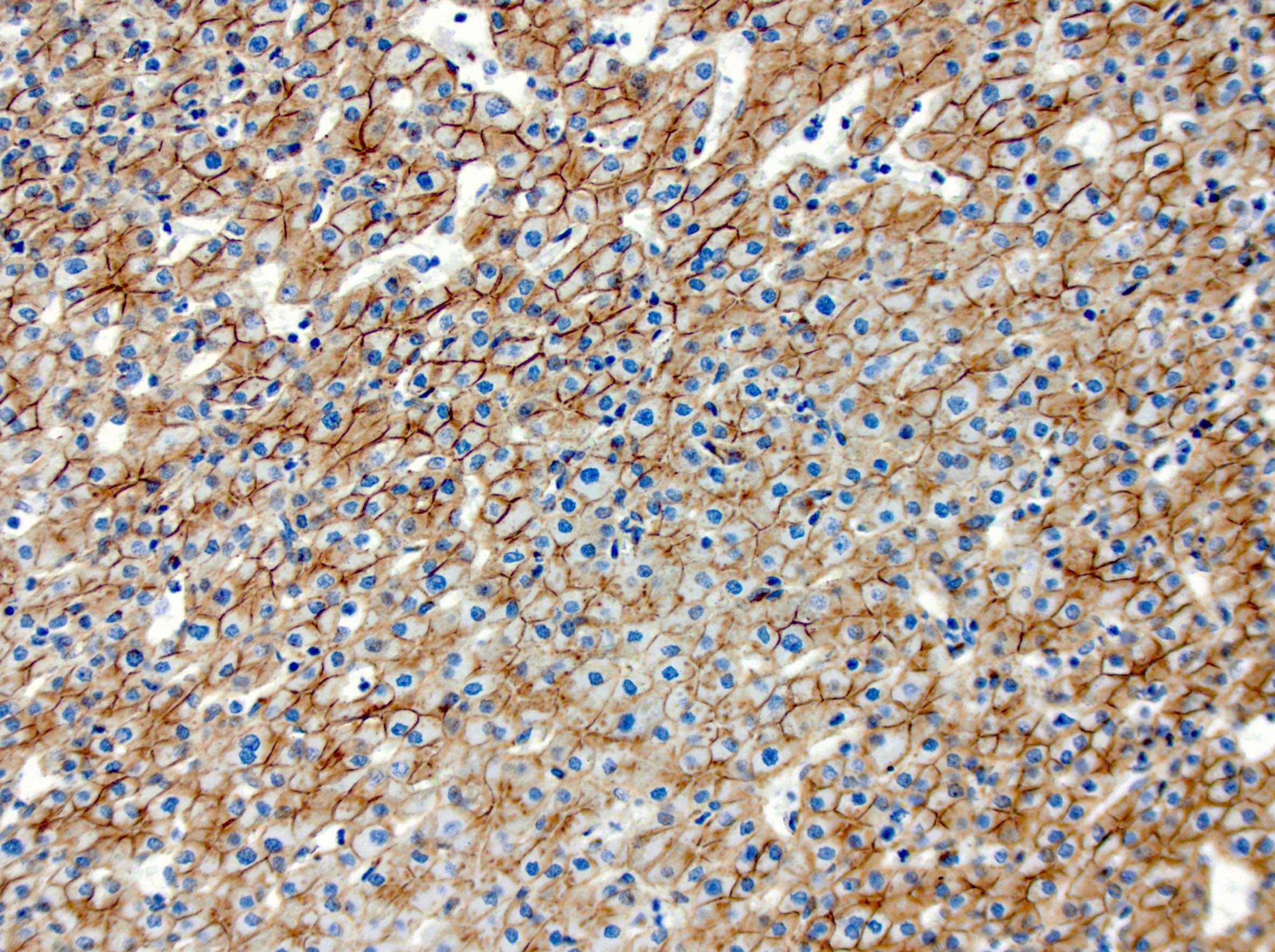
Positive stains
- HepPar1
- Reticulin: intact staining pattern with focal loss in steatotic areas (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:537)
- Characteristic staining for individual subtypes:
- Beta catenin mutated hepatocellular adenoma (HA-B): beta catenin nuclear (often focal), glutamine synthetase (strong and diffuse)
- Inflammatory hepatocellular adenoma (HA-I): SAA, CRP
Negative stains
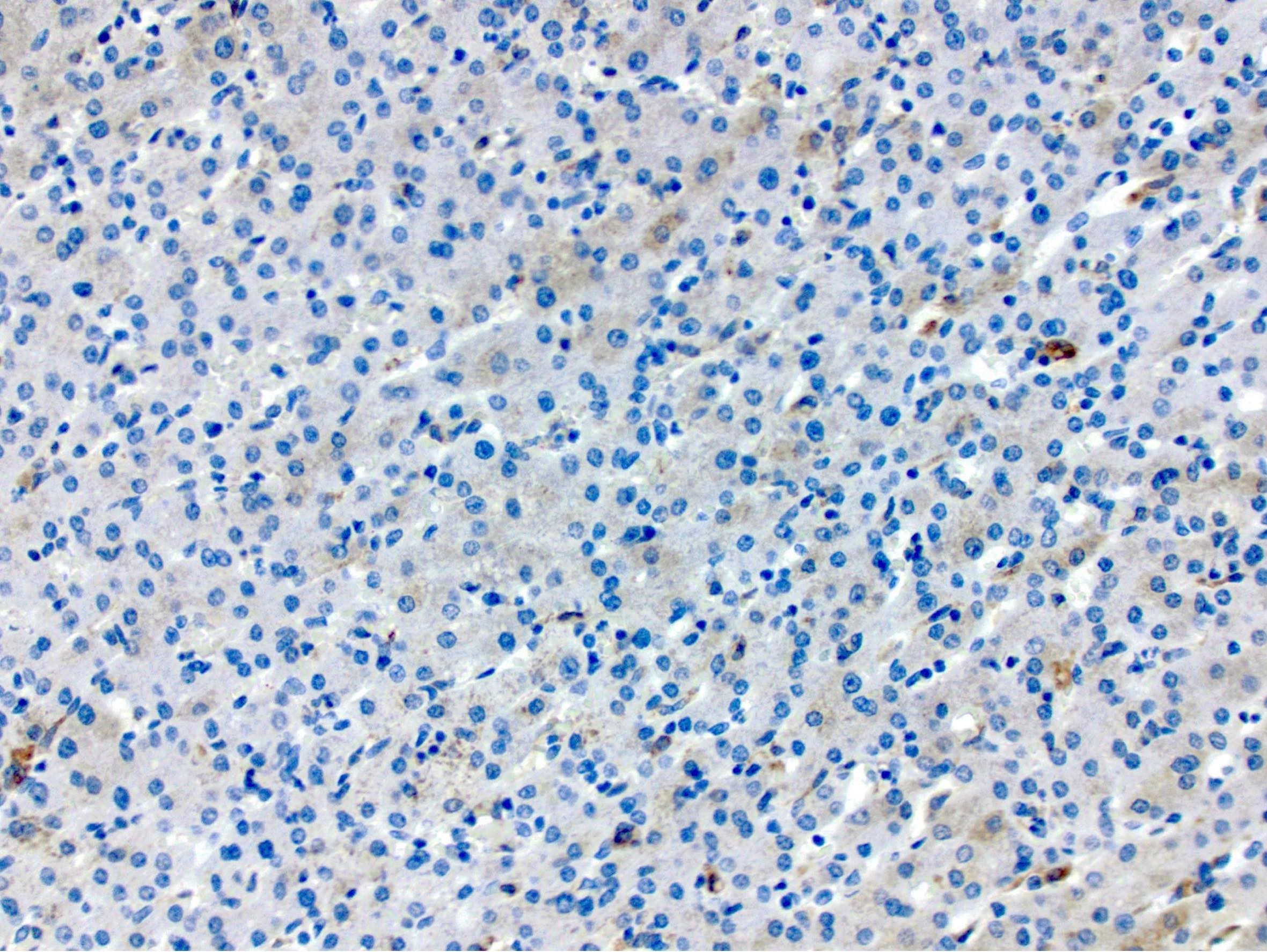
- Glypican 3: majority negative (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:433)
- CD34: negative or incomplete positive (rare complete positive) (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:433)
- HSP70: negative (can be useful to differentiate from hepatocellular carcinoma which shows positive nuclear staining) (Health Educ Q 1989;16:397)
- Characteristic staining for individual subtypes:
- HNF1A mutated hepatocellular adenoma (HA-H): LFABP (positive in background liver)
Sample pathology report
- Liver, partial hepatectomy:
- Hepatic adenoma, HNF1A mutated subtype
- Tumor is __ cm in greatest dimension
- Closest approach to the parenchymal resection margin is __ mm
- Background liver with no specific pathologic diagnosis
- Microscopic description: The tumor is a well differentiated hepatocellular neoplasm morphologically compatible with hepatic adenoma. The tumor is characterized by well circumscribed borders and many of the lesional hepatocytes are steatotic. Bile ducts are absent and scattered unpaired arterioles are present. No significant cytologic atypia, widening of hepatocyte plates or infiltrative features are noted. The tumor also contains foci of hemorrhage, necrosis and rare calcifications. Based on the steatotic morphology and immunohistochemistry profile, the tumor is best classified as HNF1A mutated subtype.
- Hepatic adenoma, HNF1A mutated subtype
- Liver, right lobe, resection:
- Hepatic adenoma, inflammatory subtype, __ cm, __ cm from parenchymal margin
- Hepatic adenoma, HNF1A mutated subtype, __ cm, __ cm from parenchymal margin
- Background liver with no specific pathologic change
Differential diagnosis
- Focal nodular hyperplasia (Clin Mol Hepatol 2016;22:199):
- Prominent central scar detected by imaging or gross evaluation
- Radiating fibrous septa with inflammatory infiltrate and prominent thick walled, abnormal vessels and associated ductular reaction
- Map-like glutamine synthetase positive staining pattern
- Well differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma:
- Mass effect adjacent to mass lesion:
- Sinusoidal dilation may mimic HA-I, especially on biopsy (Hum Pathol 2017;61:105)
- Unpaired arteries and CD34 positivity help confirm HA-I
Board review style question #1
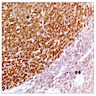
A representative section of a well differentiated hepatocellular lesion shows strong and diffuse positive staining for glutamine synthetase. Which entity should be considered in the differential diagnosis?
- Beta catenin mutated hepatocellular adenoma
- Focal nodular hyperplasia
- Inflammatory type hepatocellular adenoma
- Poorly differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma
Board review style answer #1
A. Beta catenin mutated hepatocellular adenoma (Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 2017;13:740)
Comment Here
Reference: Hepatocellular adenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Hepatocellular adenoma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is most strongly associated with hepatocellular adenoma?
- Alcohol
- Cigarette smoking
- Nulliparity
- Oral contraceptives
Board review style answer #2