Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Liang T, Chopra S. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/livertumorEHE.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE) is a malignant vascular tumor composed of epithelioid cells within a distinctive myxohyaline stroma
Essential features
- Rare malignant vascular neoplasm composed of epithelioid endothelial cells in a background of myxohyaline stroma
- Often presents as multifocal disease in the liver; may be confused for metastatic disease
- Most cases characterized by presence of WWTR1-CAMTA1 gene fusion, subset of cases characterized by YAP1-TFE3 fusion
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9133/3 - epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, malignant
- ICD-11: 2B5Y & XH9GF8 - other specified malignant mesenchymal neoplasms; epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Mostly affects middle aged adults (30 - 50 years); rare in children
- Incidence slightly F > M (Cancer 1999;85:562)
Sites
- Soft tissue, visceral organs (liver and lung), bone
- Often presents as multifocal disease in liver
- Some patients present with both liver and lung or spleen involvement
Etiology
- Sporadic
Clinical features
- Often discovered incidentally in the liver
- Most cases asymptomatic
- May present with abdominal discomfort, weight loss
- Rare cases may present with hemoperitoneum and may cause noncirrhotic portal hypertension
- Multifocal involvement of both left and right hepatic lobes seen in up to 87% of patients (Transplantation 2017;101:555)
- Extrahepatic disease seen in 37% of patients (Transplantation 2017;101:555)
Diagnosis
- Made on biopsy (preferable) or cytology specimen
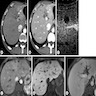
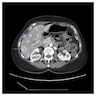
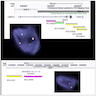
Radiology description
- Radiological findings variable
- Ultrasound: hypoechoic nodules
- CT: hypodense nodules
- MRI: in 30% of cases, the nodules have targetoid appearance with low signal intensity on T1; high signal intensity on T2 called bright dark sign
- References: Case Rep Gastroenterol 2020;14:56, Case Rep Gastrointest Med 2019;2019:7530845
Prognostic factors
- Variable clinical course (ranges from stable / indolent disease to progressive with metastasis)
- Distant metastatic rate is 20 - 30%
- Better prognosis than angiosarcoma of the liver
- Histological features do not reliably predict outcome but increased cellularity and necrosis may be poor prognostic factors (Cancer 1999;85:562)
Case reports
- 25 year old man with multifocal EHE treated successfully with liver transplant (Clin Case Rep 2019;8:108)
- 30 year old man with Crohn's disease presenting with multifocal EHE (Case Rep Gastroenterol 2020;14:56)
- 33 and 62 year old men with metastatic hepatic EHE treated with doxorubicin & olaratumab (Ther Clin Risk Manag 2020;16:141)
- 65 year old woman with YAP1-TFE3 rearranged hepatic EHE (Case Rep Gastrointest Med 2019;2019:7530845)
- 74 year old man with solitary hepatic EHE treated with hepatic resection (Case Rep Gastroenterol 2018;12:402)
Treatment
- Solitary disease: resection (curative)
- Multifocal disease: observation, liver transplantation, chemotherapy
- References: Dig Liver Dis 2020;52:1039, Cancer 2006;107:2108
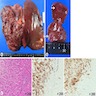
Gross description
- Can range in size from subcentimeter nodules to large, coalescing masses > 10 cm
- Cut surface is white and firm and can have infiltrative pattern with prominent myxohyaline or fibrous stroma
- Background liver appears normal
- References: Case Rep Gastroenterol 2020;14:56, Case Rep Gastroenterol 2018;12:402
Frozen section description
- Epithelioid, stellate and spindle cells with fine chromatin with occasional intracytoplasmic vacuoles in myxohyaline stroma
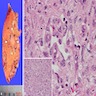
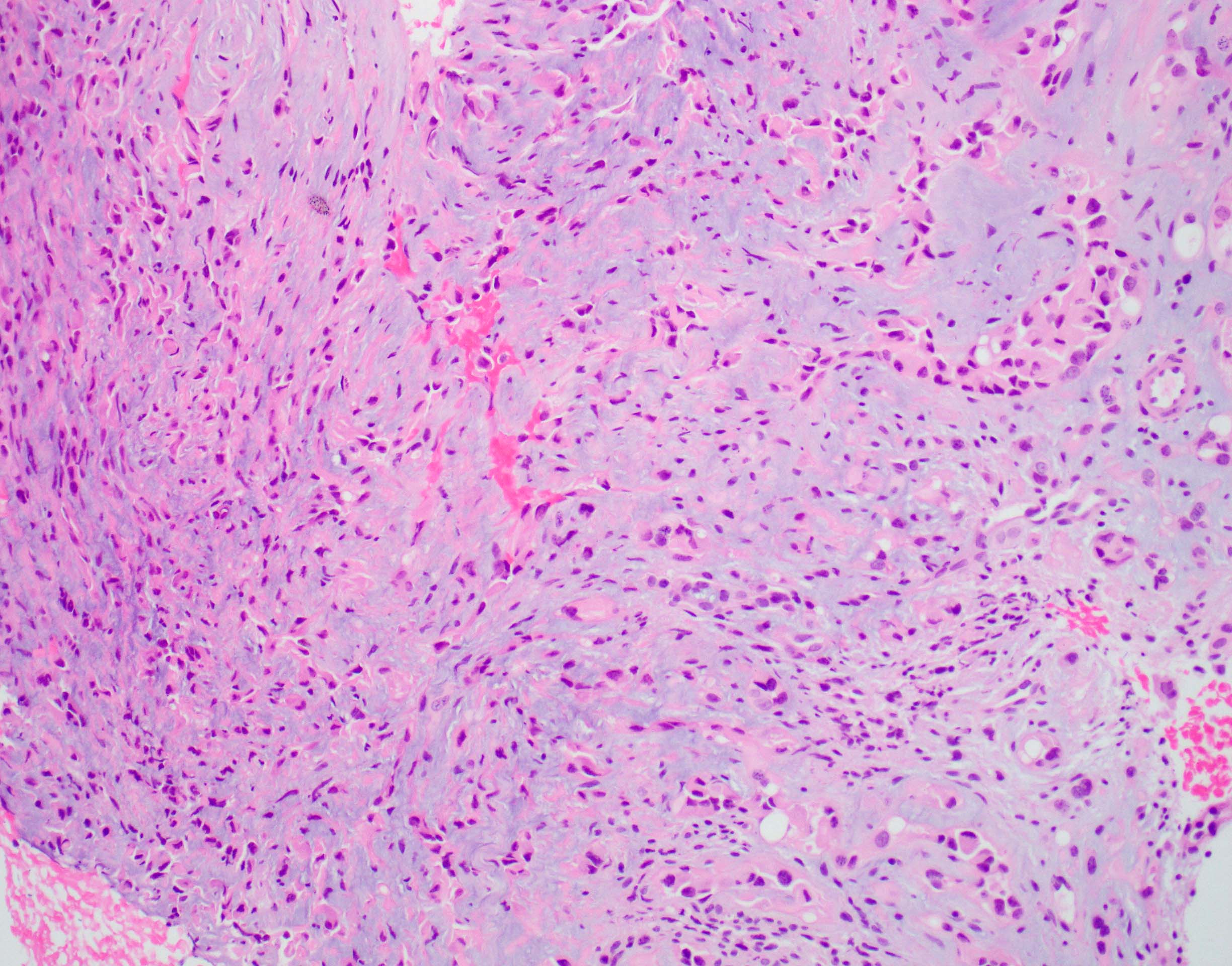
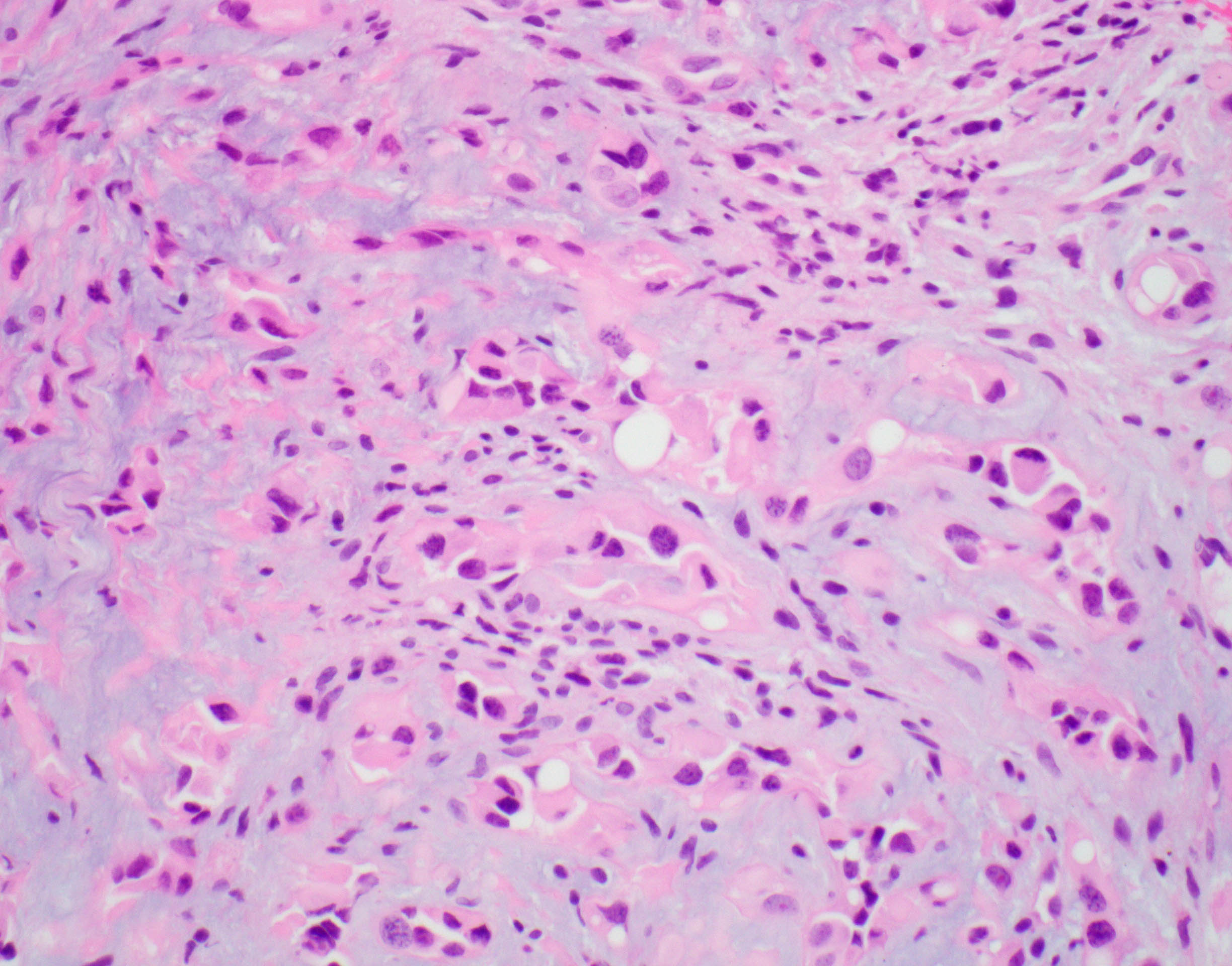
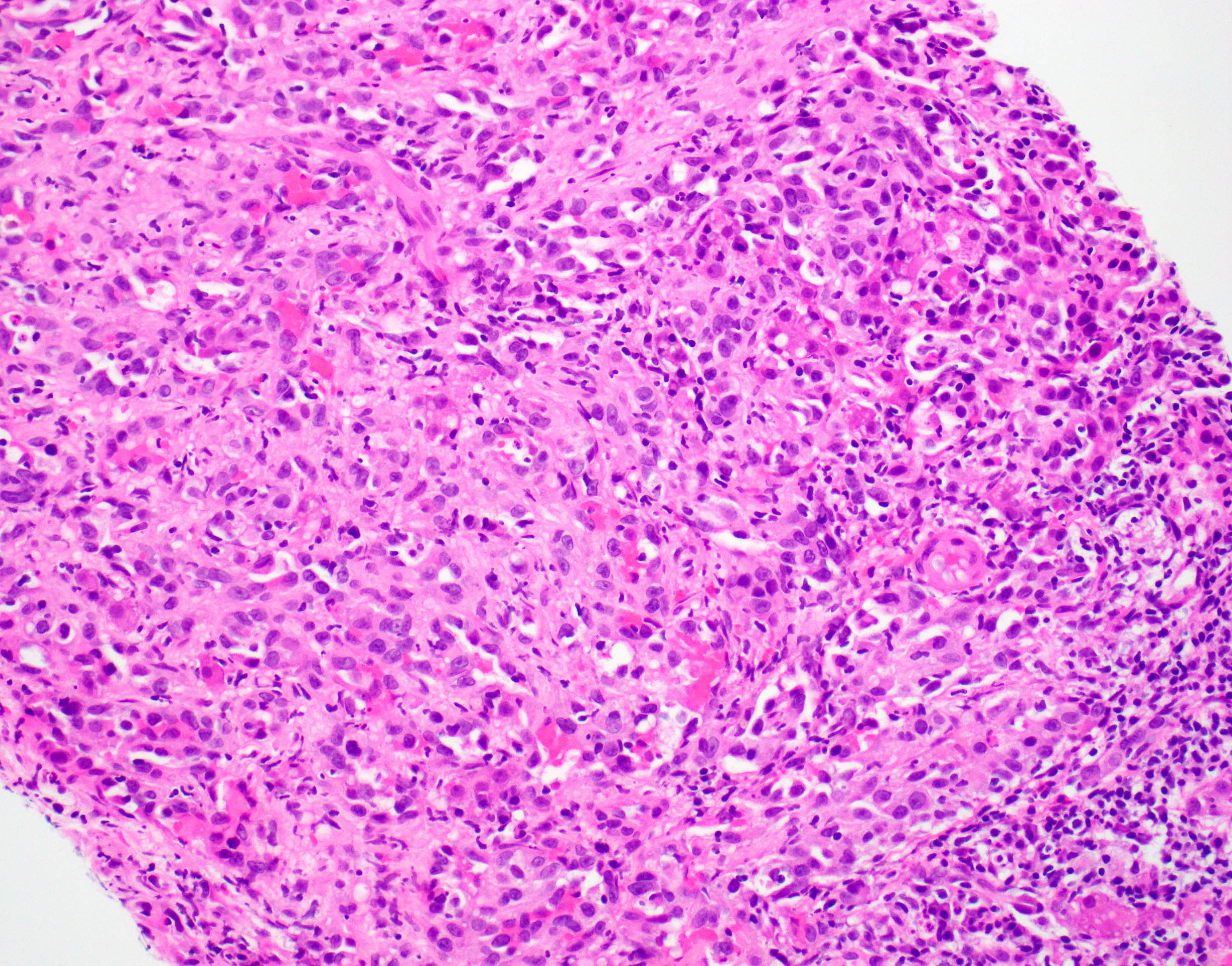
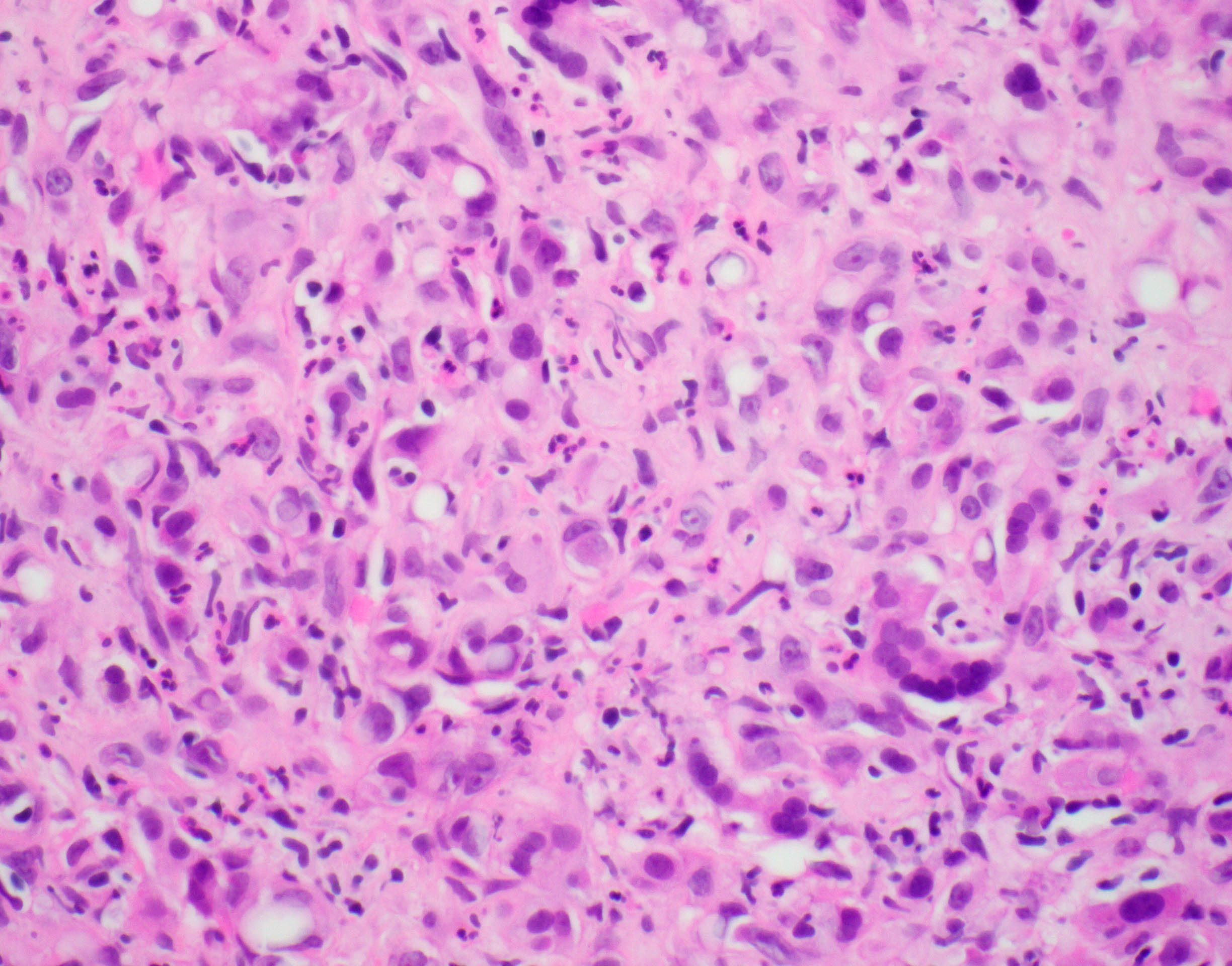
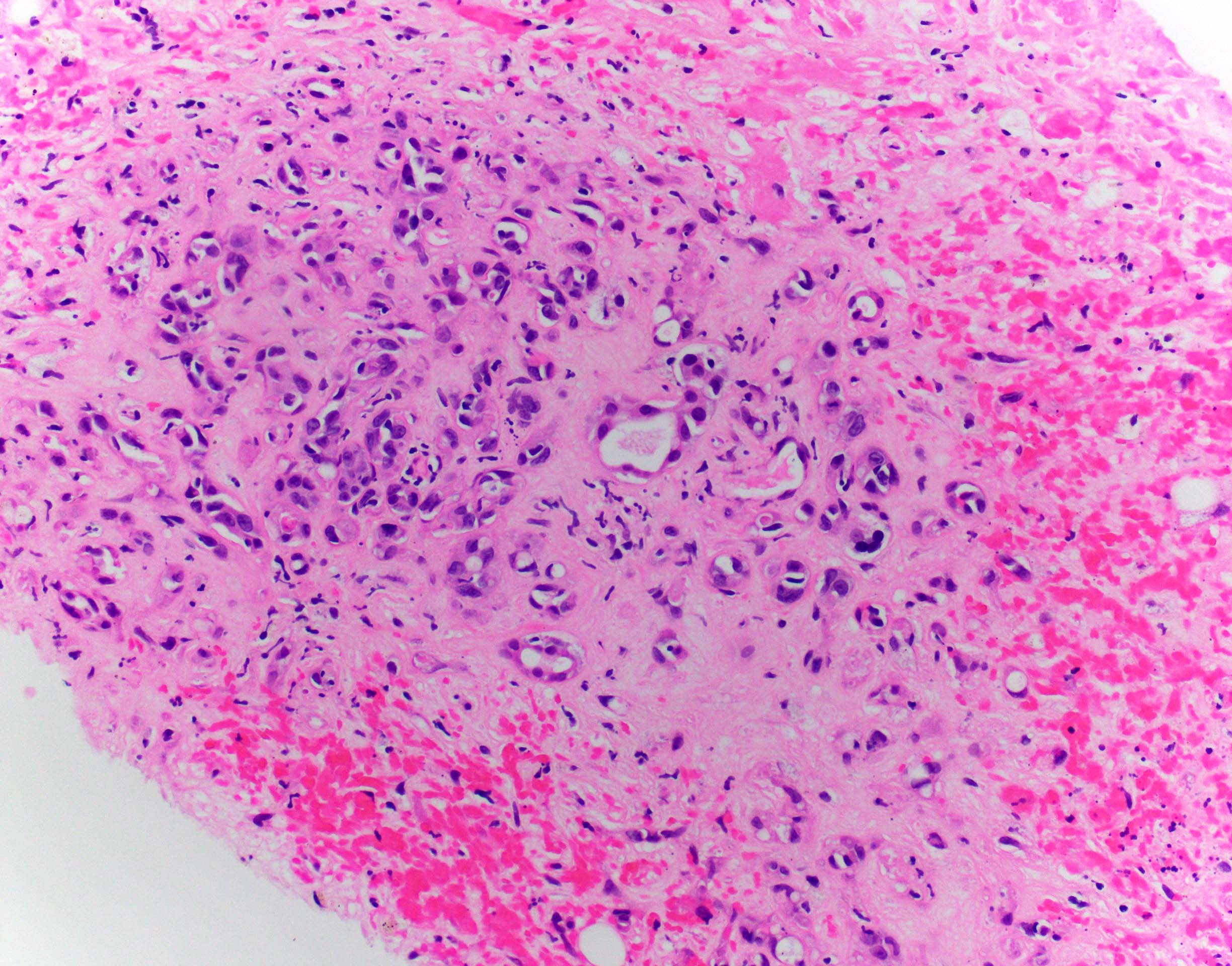
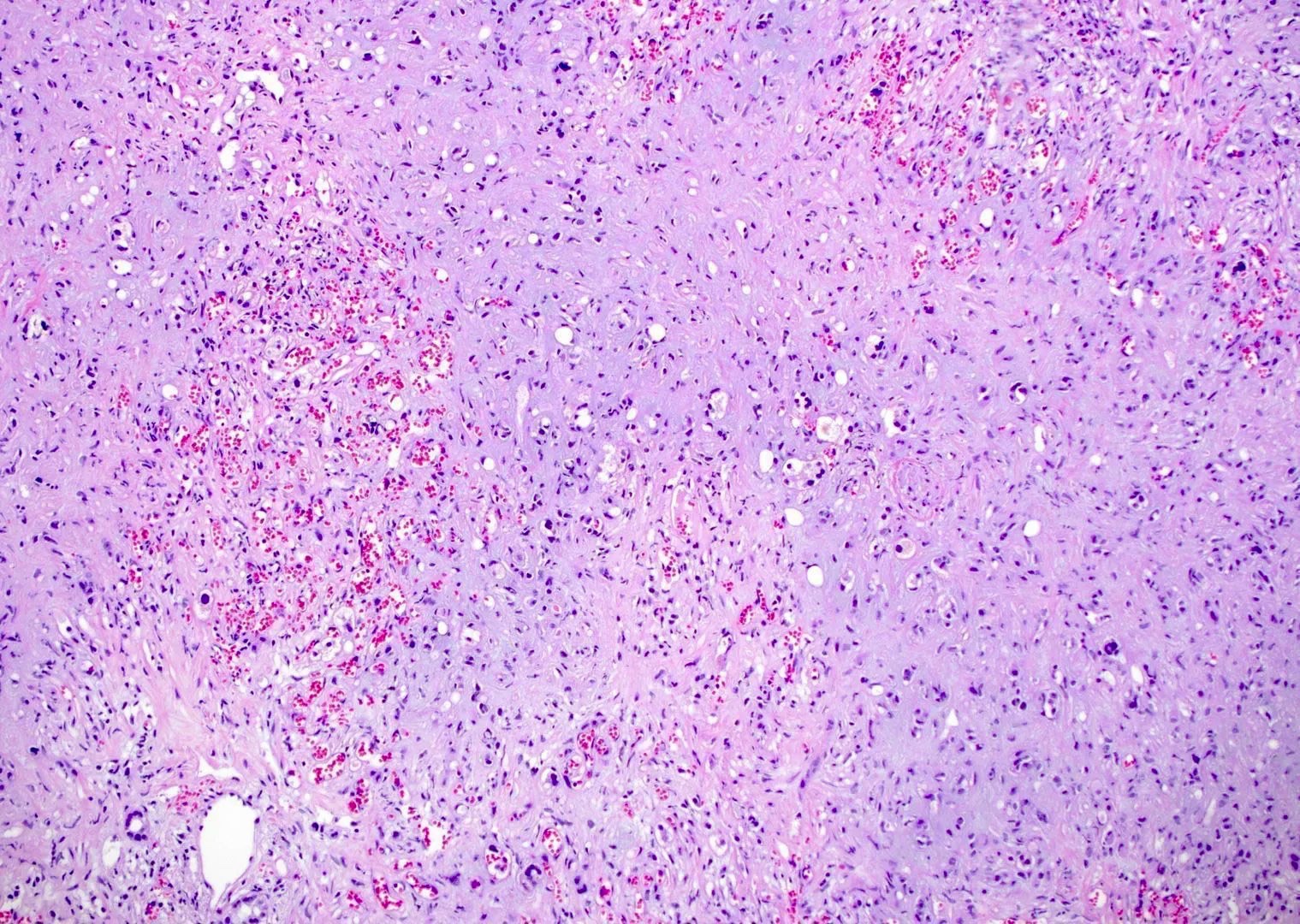
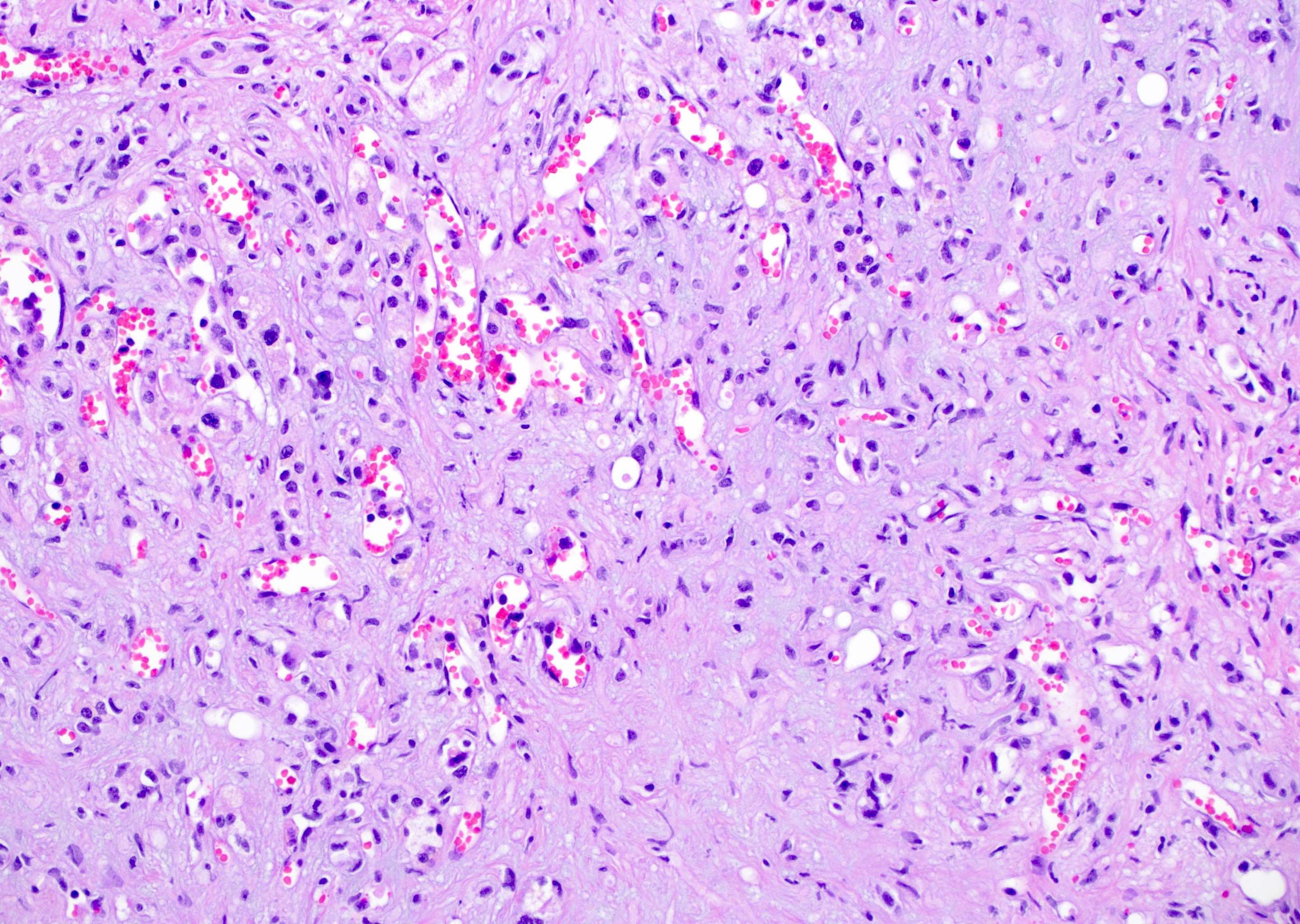
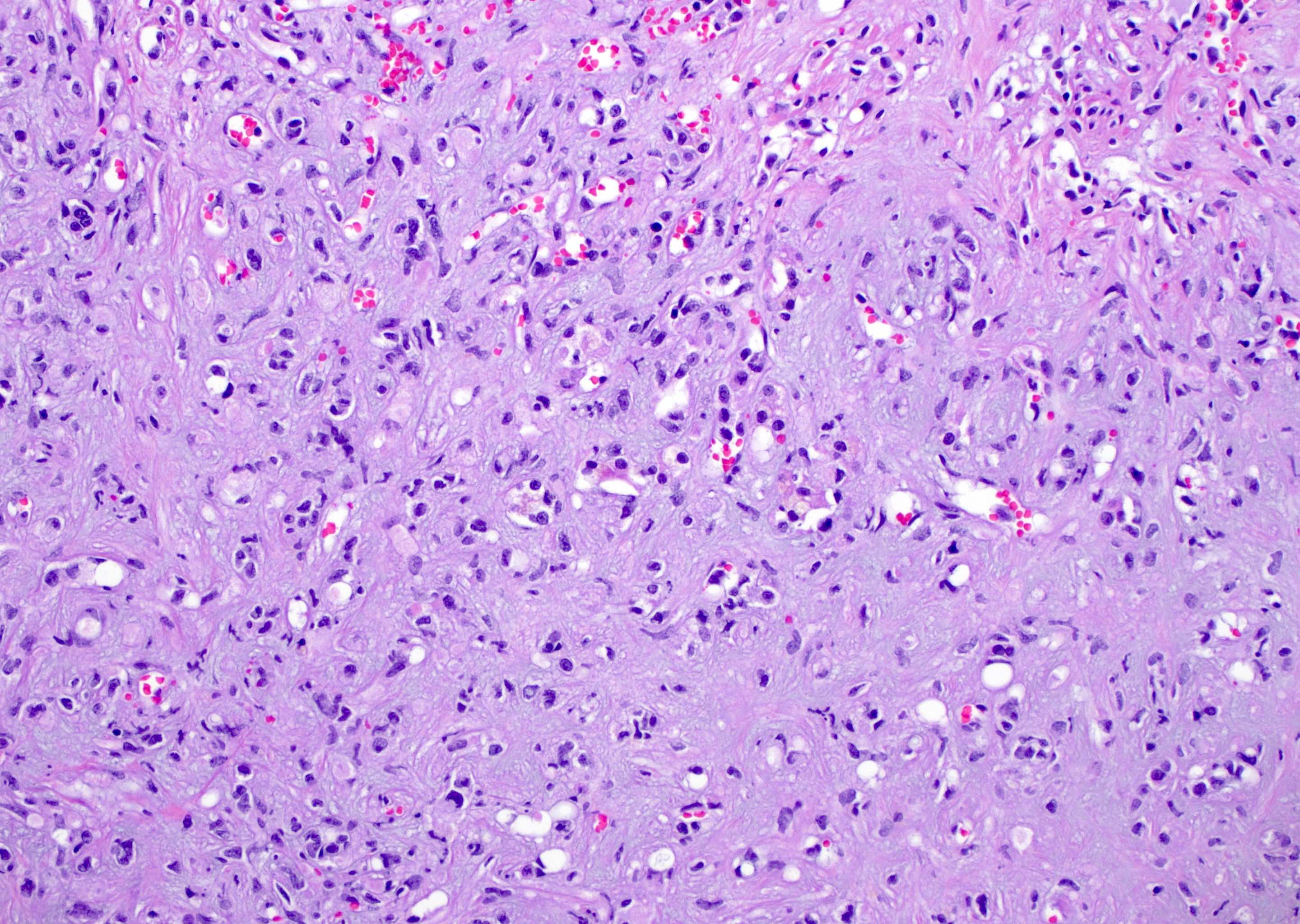
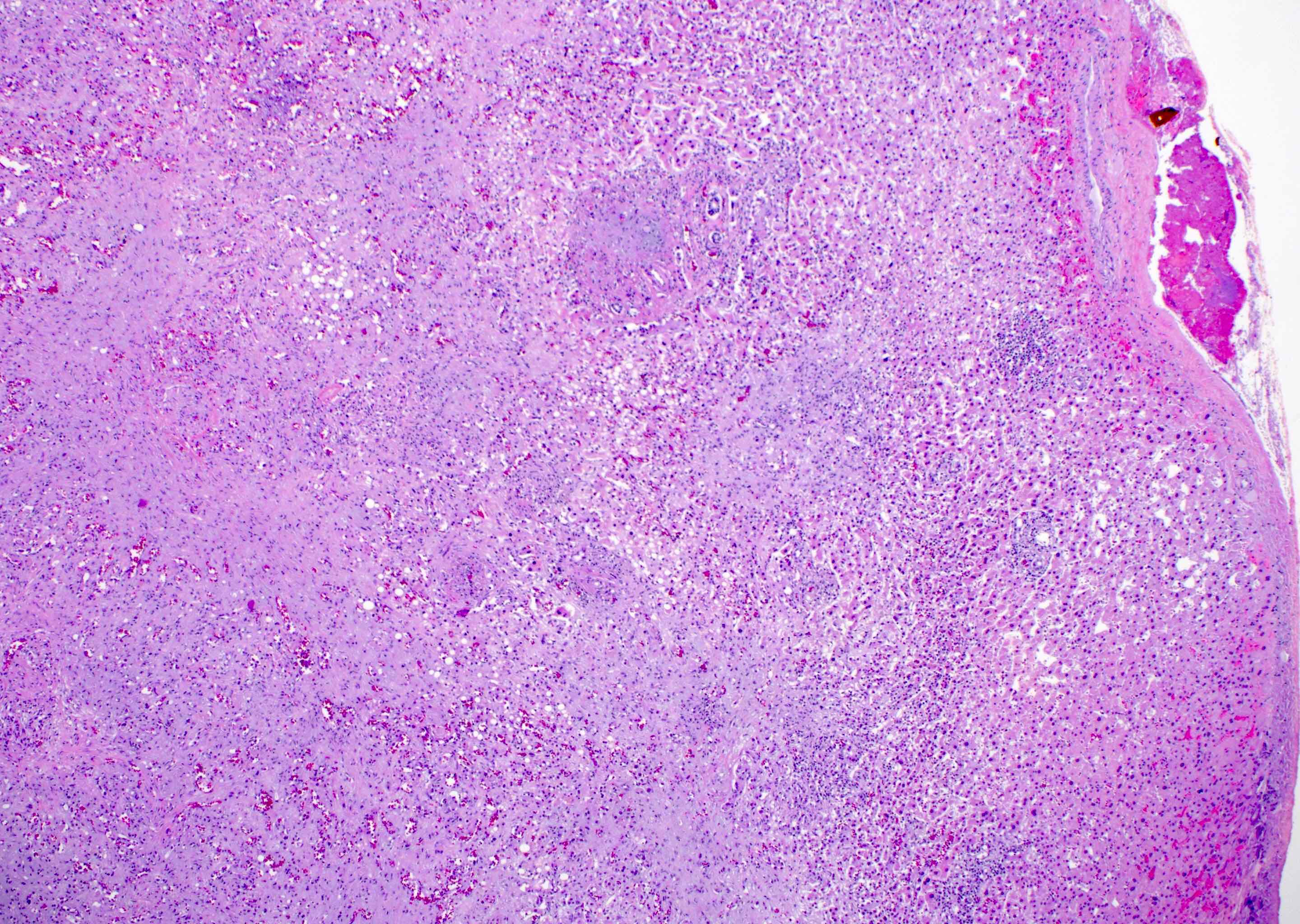
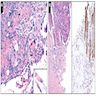
Microscopic (histologic) description
- EHE with WWTR1-CAMTA1 gene fusion
- Cords, nests, solid sheets and single cells with infiltrative growth pattern in myxohyaline / fibrous stroma with increased cellularity at tumor edge
- Invasion of sinusoids, portal and hepatic veins
- No vascular channel formation
- Cells can be epithelioid, stellate, spindle with fine chromatin
- Eosinophilic cytoplasm with occasional intracytoplasmic vacuoles ("blister cells")
- < 10% can have atypical histological features like nuclear pleomorphism, increased mitotic activity, solid sheet pattern and necrosis
- EHE with YAP1-TFE3 gene fusion (rare in liver)
- Well formed vascular channels and areas of solid growth
- Epithelioid cells with bright eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Lacks the characteristic stromal component seen in classic EHE
- References: Cancer 1982;50:970, Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:363
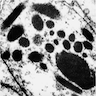
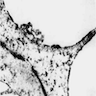
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Round to polygonal plasmacytoid cells with minimal pleomorphism and few mitoses
- Frequent nuclear grooves and psuedoinclusions
- Dense cytoplasm with occasional intracytoplasmic lumina
- Hyaline stroma
- Reference: Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:739
Positive stains
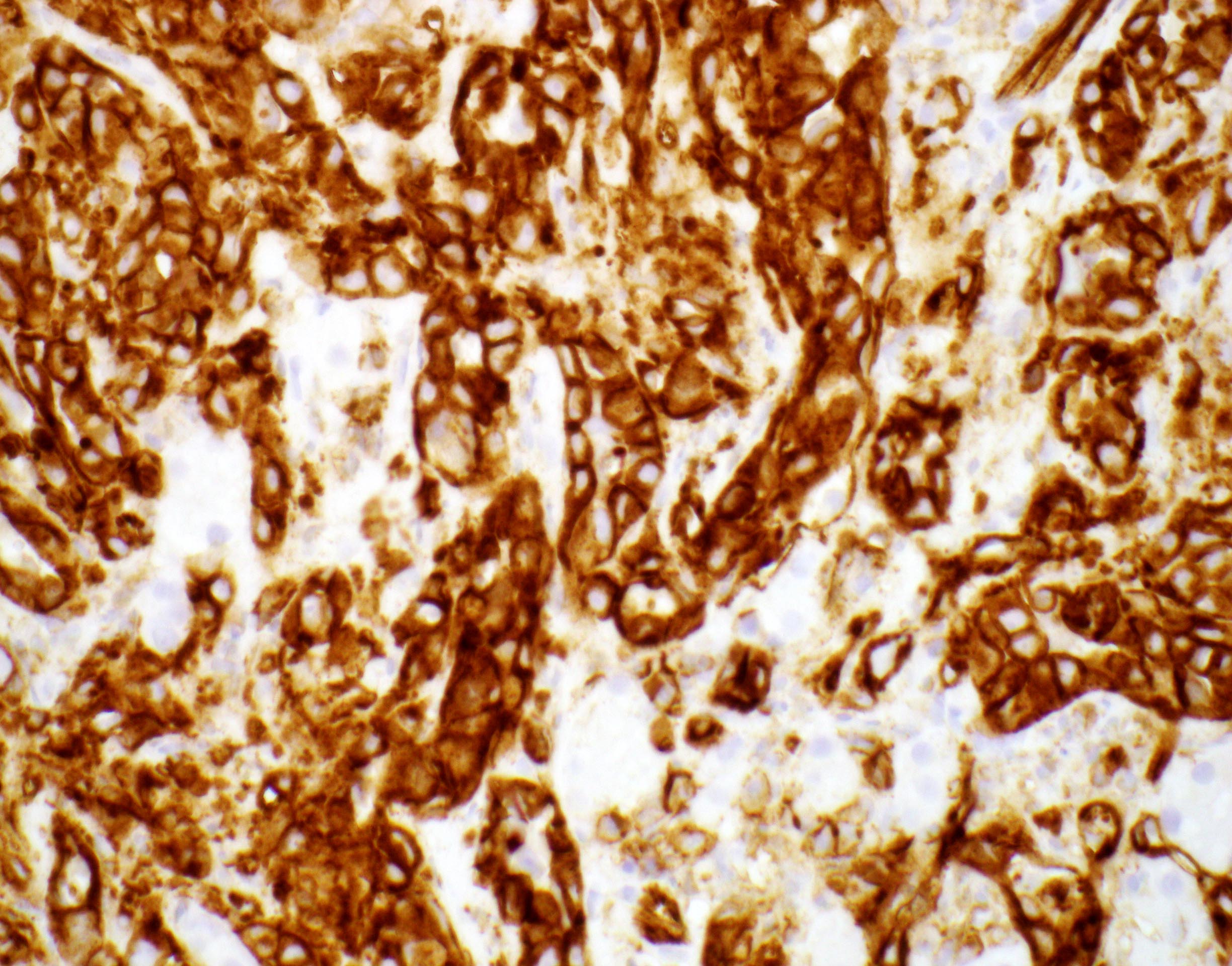
- Vascular markers: CD31, CD34 and ERG
- Keratins: especially CK8 and CK18
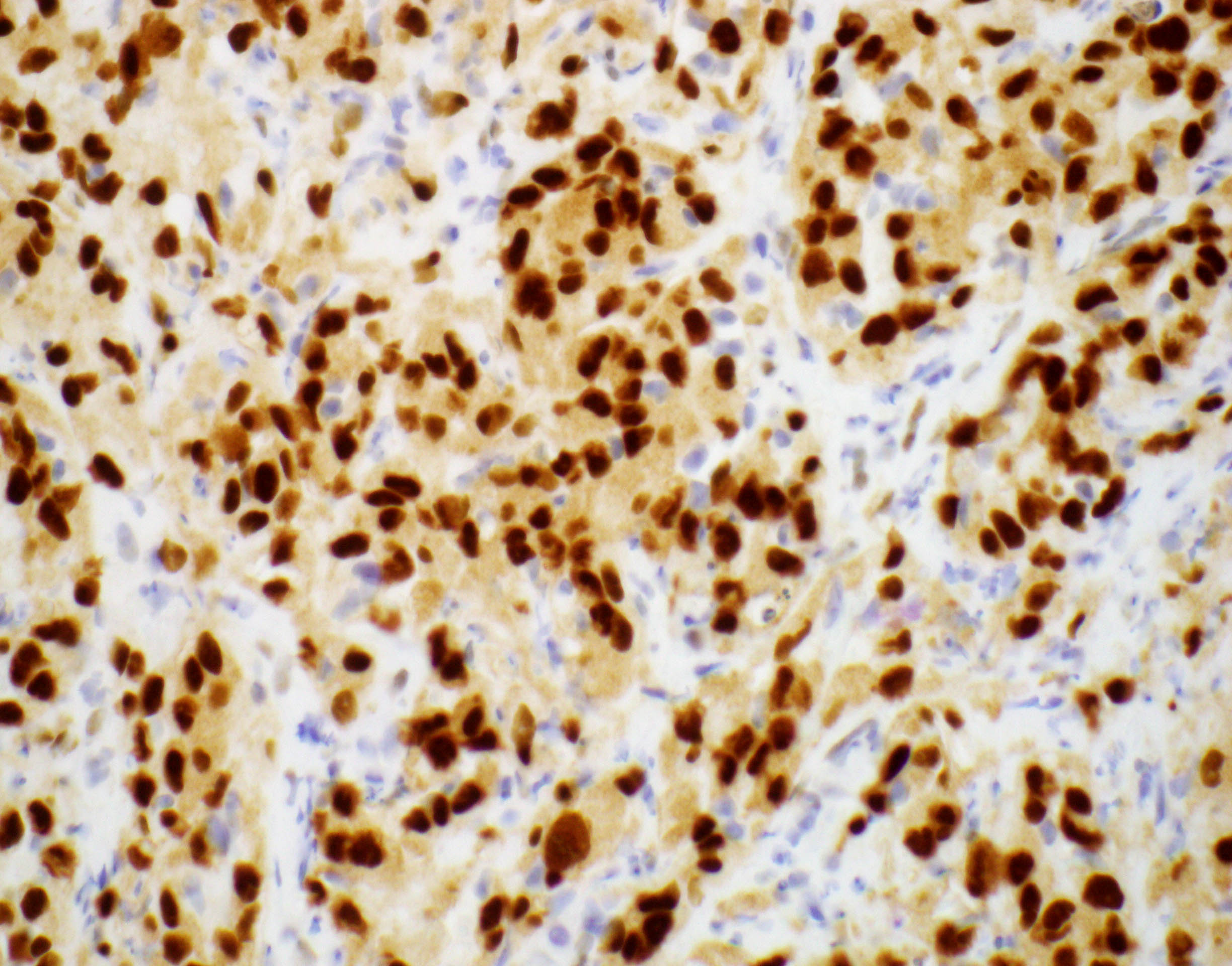
- WWTR1-CAMTA1 gene fusion tumors: positive for CAMTA1 (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:94)
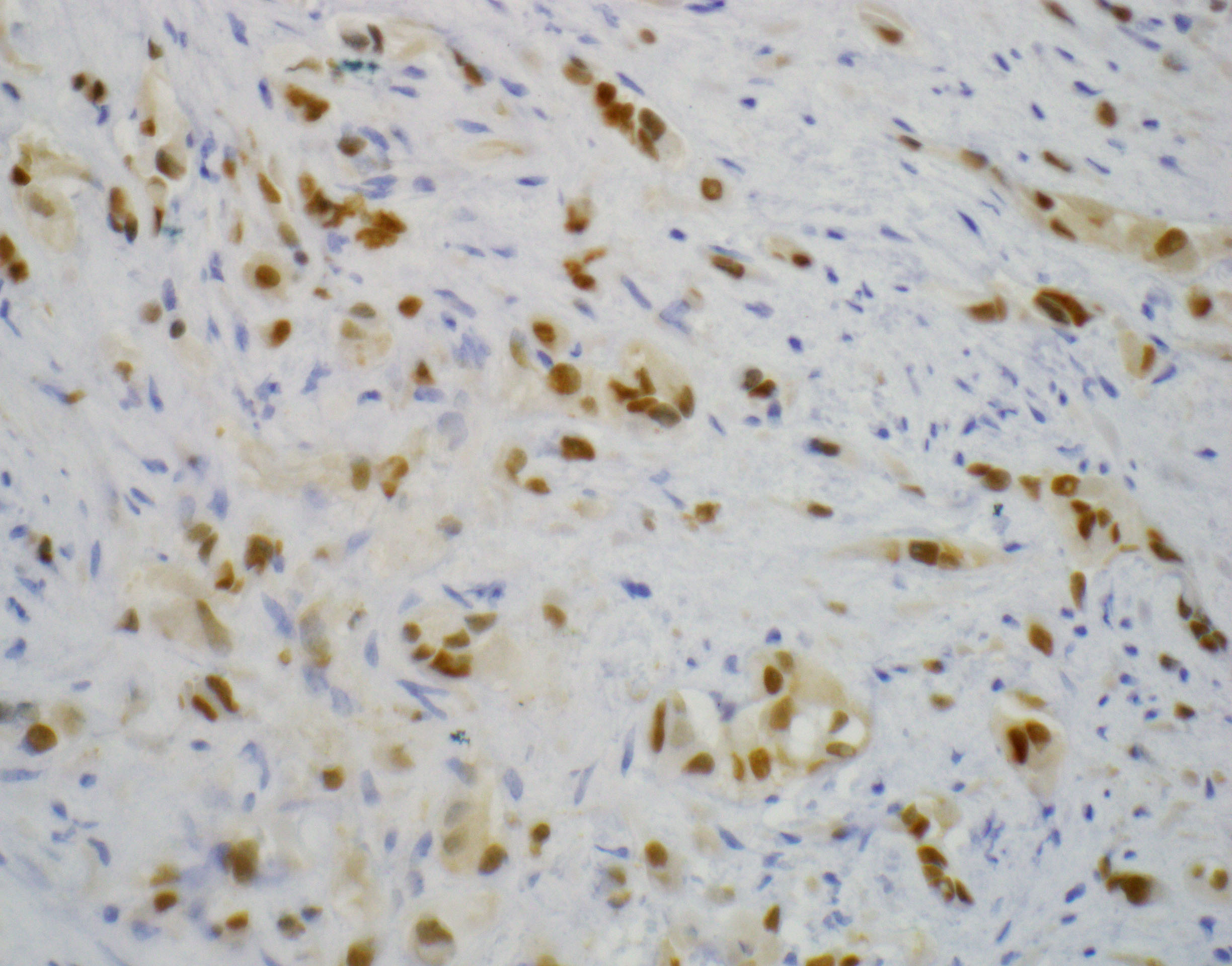
- YAP1-TFE3 fusion tumors: nuclear expression of TFE3
- AE1 / AE3, CK7: usually negative, though a few cases can be positive (Ann Diagn Pathol 2020;49:151589
Negative stains
- EMA
- Desmin
- HepPar1
- Reference: Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:363
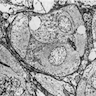
Electron microscopy description
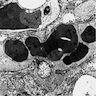
- Weibel-Palade bodies, prominent intracytoplasmic vacuoles, endothelial cells with elaborate intercellular contacts and desmosomes (Cancer 1982;50:970)
Electron microscopy images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Multifocal hepatic disease is monoclonal
- t(1;3)(p36.3;q25) WWTR1-CAMTA1 gene fusion is characteristic, found in up to 90% of cases
- Fusion of WWTR1 to CAMTA1 results in dysregulation of the Hippo pathway, driving oncogenic transformation
- YAP1-TFE3 fusion found in small subset of tumors
- Similar to WWTR1, YAP1 is a downstream transcriptional regulator of the Hippo pathway
- References: Sci Transl Med 2011;3:98ra82, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2011;50:644, Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013;52:775
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Videos
Laparoscopic segment 6 liver resection for hepatic EHE
Overview of vascular tumors of the skin (by Dr. Jerad Gardner)
Sample pathology report
- Liver, core biopsy:
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (see comment)
- Comment: FISH testing for CAMTA1 / WWTR1 fusion is positive. IHC for CAMTA1 shows nuclear positivity.
Differential diagnosis
- Angiosarcoma:
- Angiosarcomas have greater atypia and more mitoses and tend to be hemorrhagic with destructive growth pattern
- No nuclear staining for CAMTA1
- Adenocarcinoma (including cholangiocarcinoma):
- Sclerotic hepatocellular carcinoma:
- Abundant fibrous stroma separating nests or trabeculae of tumor cells
- Positive for arginase1, CK7 and glypican 3
- Negative for vascular markers
- Epithelioid hemangioma:
- Most commonly cutaneous and soft tissue lesions in head and neck, followed by distal extremities and trunk; visceral organs rare with lung being the only reported organ
- Histology shows proliferation of well formed small blood vessels lined by plump and epithelioid endothelial cells with mild cytological atypia; no myxohyaline stroma seen as in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
- Marked lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates, prominent lymphoid follicles and abundant eosinophils are present, a feature not seen in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
- Tumor cells express endothelial markers CD31, ERG and CD34 and can be EMA and keratin positive
- FOSB can be positive
- Immunostain for CAMTA1 negative
- Anastomosing hemangioma:
- Anastomosing sinusoidal capillary sized vessels with scattered hobnail endothelial cells
- Mild cytologic atypia and no multilayering of cells seen
- Mitoses are absent or rare (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1761)
- No myxohyaline stroma seen
- Frequent GNAQ and GNA14 activating hotspot mutation seen, similar to those described in hepatic small vessel neoplasm (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1201)
- Immunostain for CAMTA1 negative
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A liver biopsy of a 45 year old woman with multiple liver lesions is shown. Regarding this entity, which of the following is true?
- AE1 / AE3, CK7 and CDX2 are usually positive
- Arginase1, glypican 3 and albumin ISH are usually positive
- CD31, ERG and CAMTA1 are usually positive
- GNAQ mutations are common
Board review style answer #1
C. CD31, ERG and CAMTA1 are usually positive. This photo shows a tumor with poorly vasoformative epithelioid and spindle shaped cells growing in small nests and cords. Other scattered single cells are seen in a background of myxohyaline stroma. These histologic findings as well as multifocal presentation are consistent with an epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. EHE is a low grade malignant vascular neoplasm that commonly occurs in younger patients (30 - 50 year old), has a slight female predominance and may arise in multiple areas in the body (soft tissue and visceral organs, liver, lung). Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma is usually defined by a WWTR1-CAMTA1 fusion (~ 90% of cases), with a subset defined by a YAP1-TFE3 fusion. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma is negative for arginase1, glypican 3, albumin ISH, CK7 and CDX2. They are usually negative for AE1 / AE3. GNAQ mutations are seen in a vast majority of cases of anastomosing hemangioma but not EHE.
Comment Here
Reference: Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
Comment Here
Reference: Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
Board review style question #2
The presence of a WWTR1-CAMTA1 fusion transcript, resulting in t(1;3) translocation can be used as a molecular test to confirm diagnosis of which vascular tumor?
- Epithelioid angiosarcoma
- Epithelioid hemangioma
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
- Pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma
Board review style answer #2
C. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma are low grade malignant vascular neoplasms and may arise in multiple areas in the body (soft tissue and visceral organs, liver, lung). They usually have a WWTR1-CAMTA1 fusion (~ 90% of cases). The WWTR1-CAMTA1 translocation is present in EHE across all anatomical sites and fusion of WWTR1 to CAMTA1 results in dysregulation of the Hippo pathway, driving oncogenic transformation. A separate translocation YAP1-TFE3 has been identified in a subset of tumors and YAP1, similarly to WWTR1, is a downstream transcriptional regulator of Hippo pathway. Epithelioid hemangiomas are characterized by recurrent fusion genes involving FOS or FOSB in as many as half the cases. Psuedomyogenic hemangioendothelioma is caused by a balanced translocation t(7;19)(q22;q13) resulting of fusion of SERPINE1 to FOSB and ACTB-FOSB. No recurrent gene fusions have been described in angiosarcoma, though MYC amplification can be seen, primarily in the setting of irradiation or lymphedema associated angiosarcoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
Comment Here
Reference: Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma