Table of Contents
Definition / general | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Peripheral smear images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Mihova, D. M5b. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/leukemiaacutemonocyticleukemiam5b.html. Accessed December 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Acute monocytic leukemia (M5b)
- 3 - 6% of AML
- Affects all ages
- Mature monocytes or promonocytes predominate in peripheral blood (< 80% of monocyte lineage cells are monoblasts, usually < 20%)
- Treatment may cause tumor lysis syndrome, DIC and falsely elevated platelet counts (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1999;123:1111)
Case reports
- 47 year old man with spontaneous remission after infection (Int J Lab Hematol 2007;29:386)
- 50 year old man with cutaneous disease (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:425)
- 63 year old man with preceding aleukemic leukemia cutis (Case Rep Oncol 2011;4:547)
- 74 year old man with mycosis fungoides now with increased circulating immature mononuclear cells (Univ Pittsburgh case #460)
- 77 year old man with coexisting myeloma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:1506)
- With mononucleosis syndrome due to varicella zoster virus (Eur J Haematol 2002;68:236)
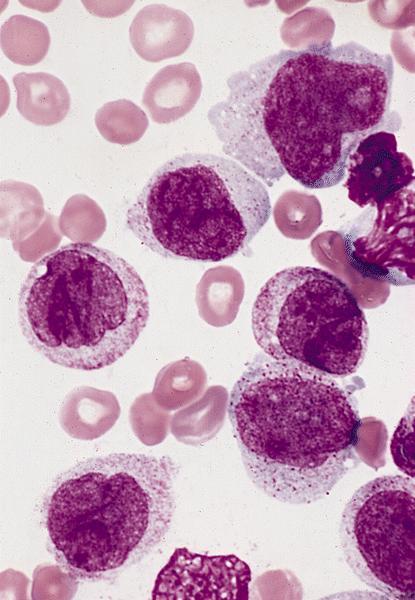
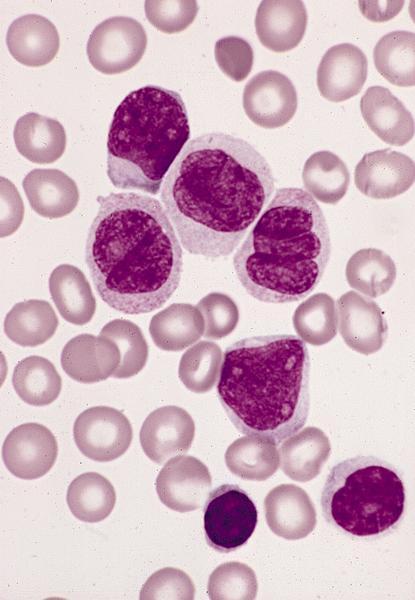
Microscopic (histologic) description
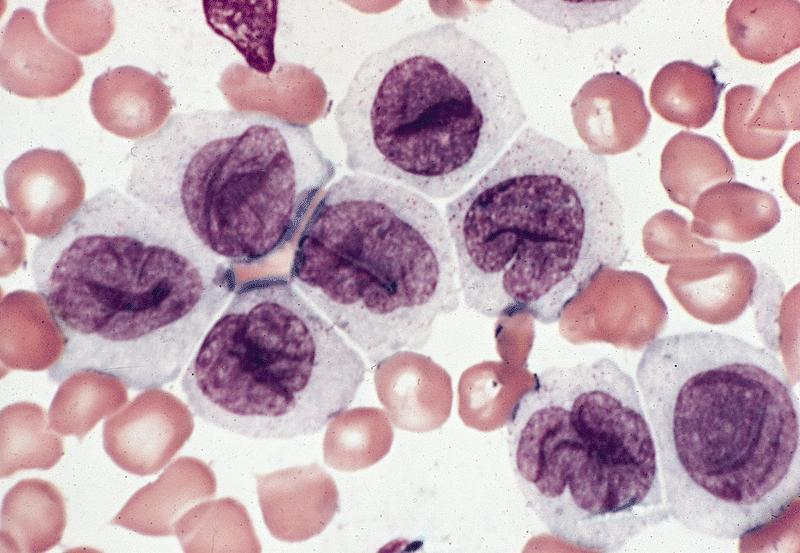
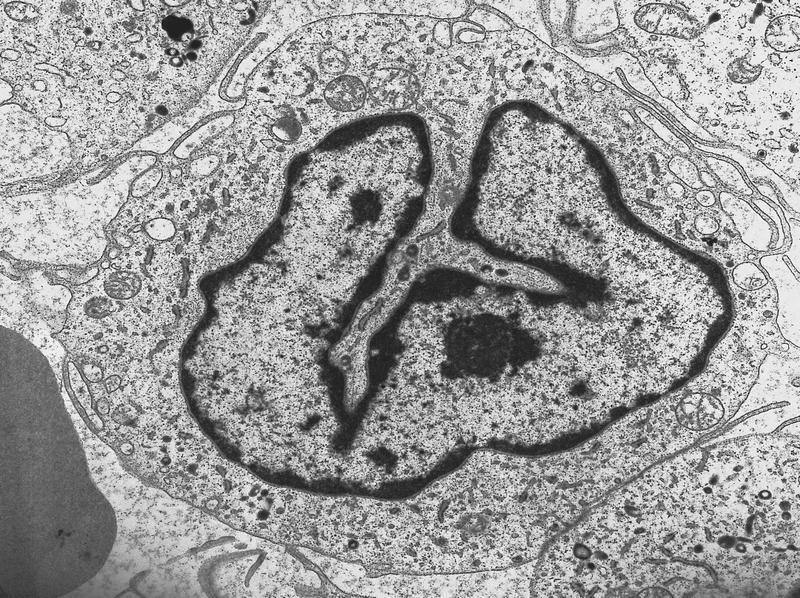
- Leukemic cells are often promonocytes with less basophilic cytoplasm and more azurophilic granules than monoblasts
- Have folded or cerebriform nuclei with fine chromatin
- Erythrophagocytosis is common
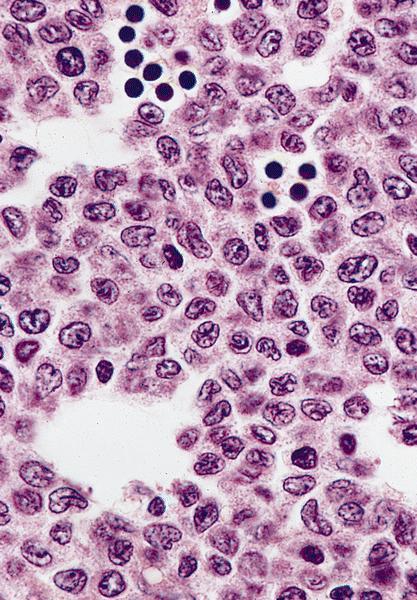
Microscopic (histologic) images
Negative stains
Flow cytometry description
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- 30% have cytogenetics abnormalities, including 11q23 in 12% (these cases should be classified as a recurrent genetic abnormality)
- FLT3 mutations in 30%
- t(8;16)(p11;p13) fuses MOZ gene at 8p11 with CBP gene at 16p13 and is associated with erythrophagocytosis and coagulopathy
Differential diagnosis
- AML M4
- Malignant histiocytic disorders
- Microgranular acute promyelocytic leukemia
- Myelodysplastic syndrome: to distinguish, count promonoblasts in M5 with monoblasts