Table of Contents
Definition / general | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Mihova D. AML with maturation (FAB AML M2). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/leukemiaM2.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- 10% of AML cases; 5% of childhood leukemias
- Any age, 20% are < 25 years and 40% are 60 years+
- Anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia; variable number of blasts in peripheral blood
- Variable prognosis
- Criteria for diagnosis: 20%+ nonerythroid cells in peripheral blood or bone marrow are myeloblasts; monocytic precursors are < 20% in bone marrow and granulocytes are 10%+ of cells
- Enzyme cytochemistry: most blasts are positive for myeloperoxidase or Sudan Black B, and chloroacetate esterase
Case reports
- 7 year old boy with myeloid sarcoma with acute myeloblastic leukemia (J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2011;21:369)
- 30 year old man with t(5;11) (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2007;172:154)
- 35 year old pregnant woman (Rinsho Ketsueki 2011;52:18)
- Three patients with variant t(8;21) (Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2010;199:31)
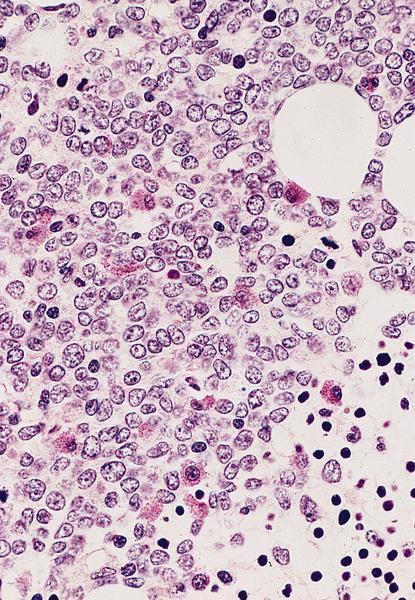
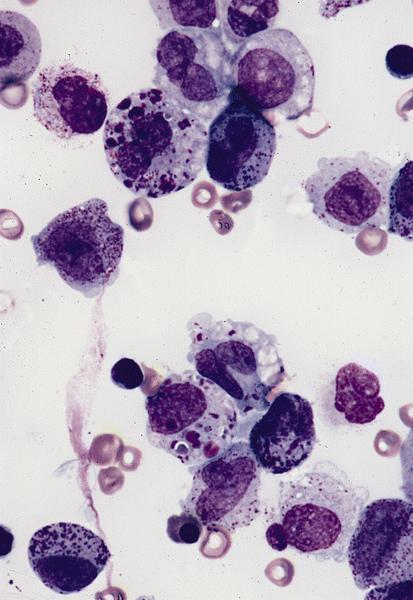
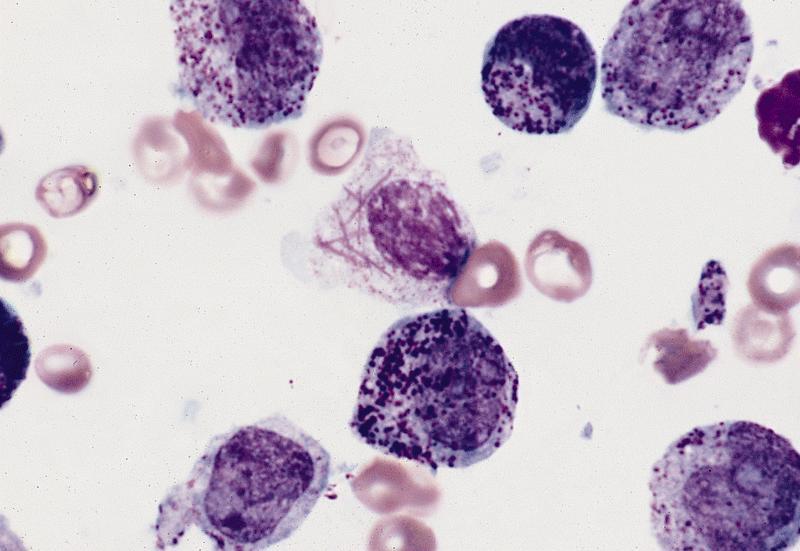
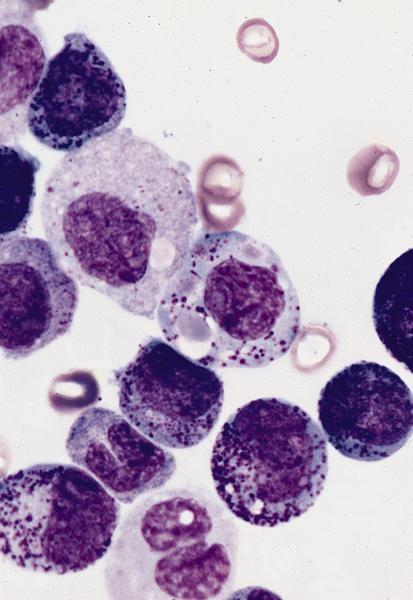
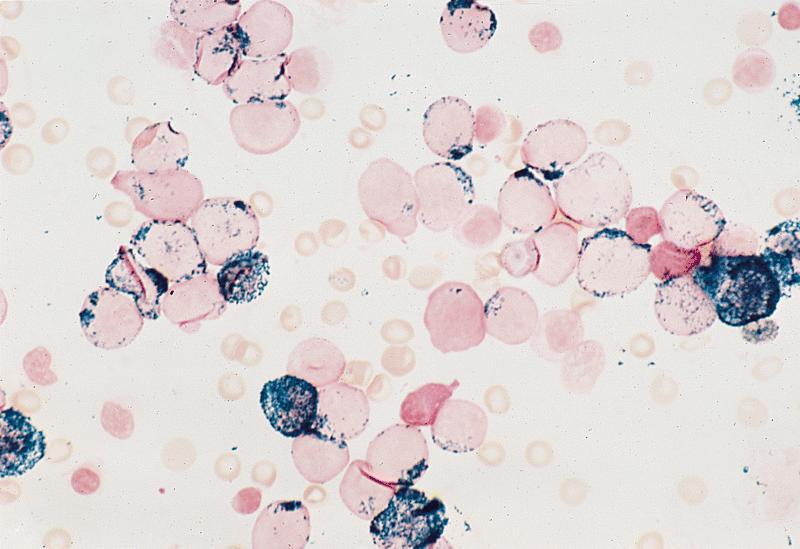
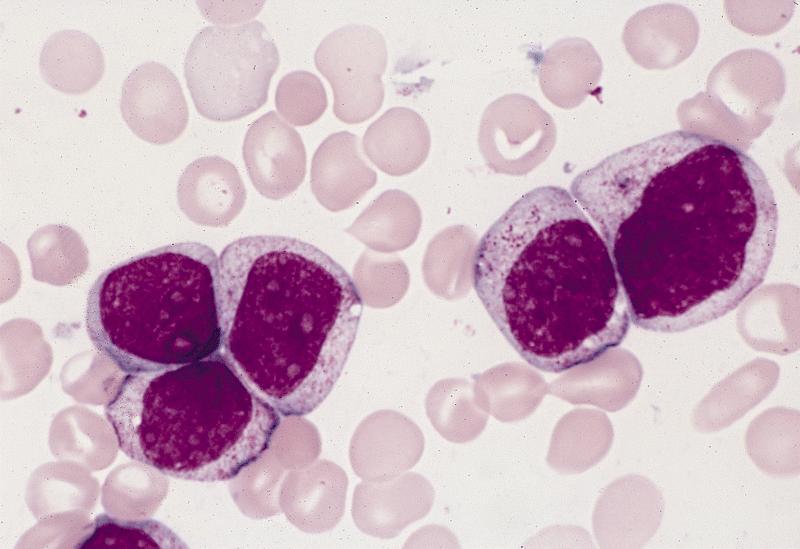
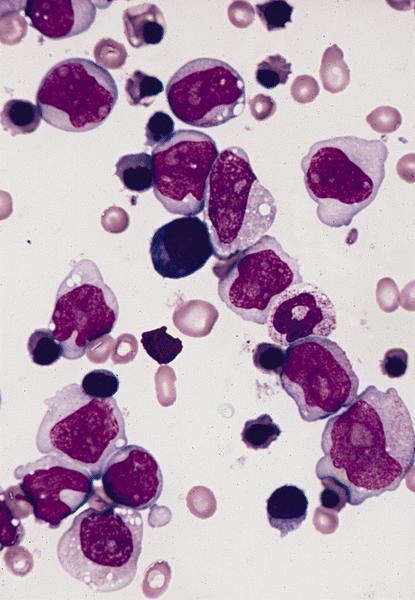
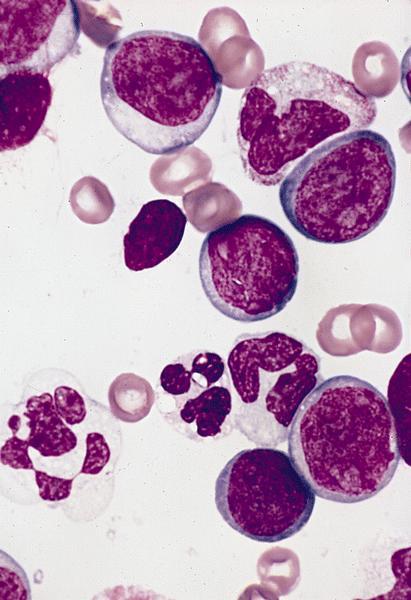
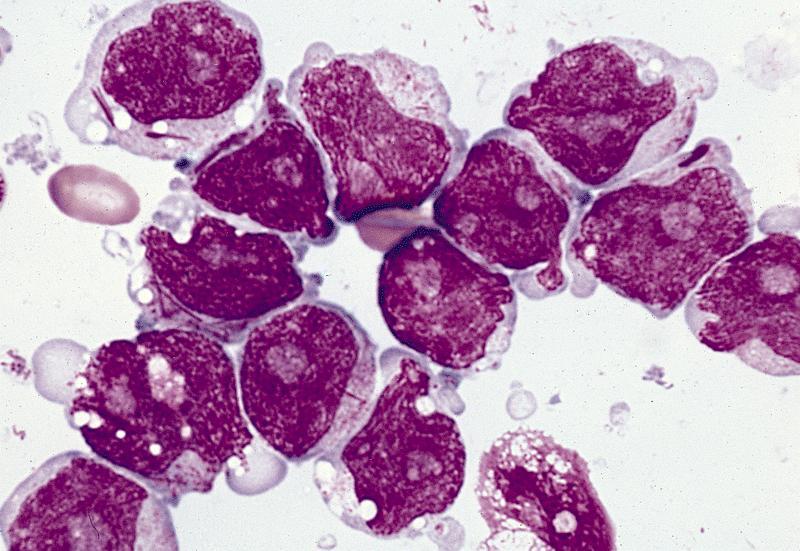
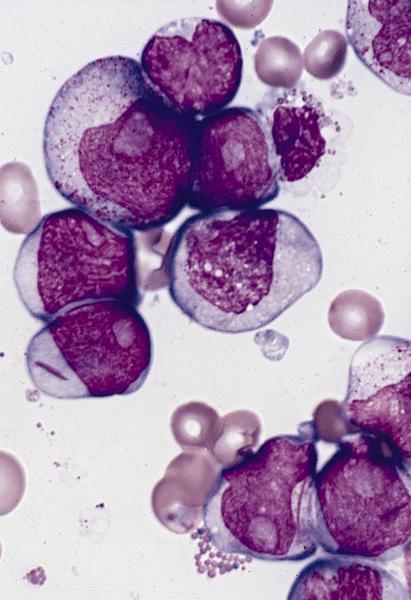
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Usually hypercellular marrow
- Full range of myeloid maturation through maturing neutrophils, often with abnormal segmentation and 10%+ bone marrow cells with variable degree of dysplasia
- Auer rods in 70% of blasts; myeloblasts with or without azurophilic granules
- Erythroid and megakaryocyte precursors may have dysplastic changes
- Often increased eosinophilic precursors without cytological and cytochemical abnormalities of inv(16)(p13.1q22)
- Basophils may be increased, rarely mast cell hyperplasia (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2007;50:655)
Microscopic (histologic) images
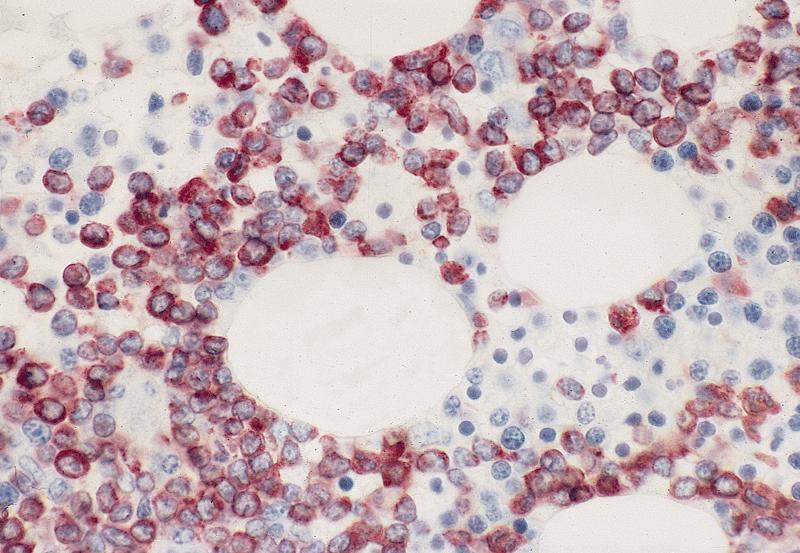
Positive stains
Flow cytometry description
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- t(8;21) cases classified as AML with t(8;21); RUNX1-RUNX1T1; may be only genetic abnormality or part of more complex abnormalities (Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2008;74:25)
- FLT3 mutations associated with HLA-DR negative patients (Leuk Res 2007;31:921)
Differential diagnosis