Larynx, hypopharynx & trachea
General
Staging-hypopharynx
Last author update: 8 November 2022
Last staff update: 8 November 2022
Copyright: 2002-2024, PathologyOutlines.com, Inc.
PubMed Search: Staging-hypopharynx
Page views in 2023: 1,208
Page views in 2024 to date: 458
Cite this page: Magliocca K. Staging-hypopharynx. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/larynxstaginghypopharynx.html. Accessed April 18th, 2024.
Definition / general
- All carcinomas of the hypopharynx are covered by this staging system
- The following topics are not covered: metastatic tumors to the hypopharynx, hematopoietic malignancies, sarcomas of the hypopharynx
Essential features
- AJCC 7th edition staging was sunset on December 31, 2017; as of January 1, 2018, use of the 8th edition is mandatory
Terminology
- Hypopharynx:
- Portion of the pharynx extending from the plane of the superior border of the hyoid bone (or floor of the vallecula) to the plane corresponding to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage
- Contents include:
- Pyriform sinus (right and left): represents part of the hypopharynx which expands bilaterally and forward around the sides of the larynx, and lies between the larynx and the thyroid cartilage
- Lateral and posterior hypopharyngeal walls
- Postcricoid region, extending from the level of the arytenoid cartilage and connecting folds to the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage; it connects the 2 piriform sinuses, thereby forming the anterior wall of the hypopharynx
ICD coding
- ICD-10:
- C10.0 - malignant neoplasm of vallecula
- C10.2 - malignant neoplasm of lateral wall of oropharynx
- C10.3 - malignant neoplasm of posterior wall of oropharynx
- C10.8 - malignant neoplasm of overlapping sites of oropharynx
- C10.9 - malignant neoplasm of oropharynx, unspecified
- C11.1 - malignant neoplasm of posterior wall of nasopharynx
- C12 - malignant neoplasm of pyriform sinus
- C13.0 - malignant neoplasm of postcricoid region
- C13.1 - malignant neoplasm of aryepiglottic fold, hypopharyngeal aspect
- C13.2 - malignant neoplasm of posterior wall of hypopharynx
- C13.8 - malignant neoplasm of overlapping sites of hypopharynx
- C13.9 - malignant neoplasm of hypopharynx, unspecified
Primary tumor (pT)
- pN: not assigned (no nodes submitted or found)
- pN: not assigned (cannot be determined based on available pathological information)
- pTis: carcinoma in situ
- pT1: tumor limited to one subsite of hypopharynx or ≤ 2 cm in greatest dimension
- pT2: tumor invades > 1 subsite of hypopharynx or an adjacent site, or tumor > 2 cm but ≤ 4 cm in greatest dimension without fixation of hemilarynx
- pT3: tumor > 4 cm in greatest dimension or with fixation of hemilarynx or extension to esophageal mucosa
- pT4a: tumor of any size invading thyroid / cricoid cartilage, hyoid bone, thyroid gland, esophageal muscle or central compartment soft tissue (central compartment soft tissue includes prelaryngeal strap muscles and subcutaneous fat)
- pT4b: tumor of any size that invades prevertebral fascia, encases carotid artery or involves mediastinal structures
Regional lymph nodes (pN)
- pN: not assigned (no nodes submitted or found)
- pN: not assigned (cannot be determined based on available pathological information)
- pN0: no regional lymph node metastasis
- pN1: metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, ≤ 3 cm and extranodal extension (ENE)-
- pN2: metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, ≤ 3 cm in greatest dimension and ENE+; or > 3 cm but ≤ 6 cm in greatest dimension and ENE-; or metastases in multiple ipsilateral lymph nodes, none > 6 cm in greatest dimension and ENE-; or in bilateral or contralateral lymph node(s), none > 6 cm in greatest dimension and ENE-
- pN2a: metastasis in either:
- Single ipsilateral lymph node that is ≤ 3 cm and ENE+ or
- Single ipsilateral lymph node that is > 3 cm but ≤ 6 cm in greatest dimension and ENE-
- pN2b: metastasis in multiple ipsilateral lymph nodes, none > 6 cm in greatest dimension and ENE-
- pN2c: metastasis in bilateral or contralateral lymph node(s), none > 6 cm in greatest dimension and ENE-
- pN3: metastasis in a lymph node > 6 cm in greatest dimension and ENE-; or in a single ipsilateral node > 3 cm in greatest dimension and ENE+; or multiple ipsilateral, contralateral or bilateral nodes, any with ENE+; or a single contralateral node of any size and ENE+
- pN3a: metastasis in a lymph node that is > 6 cm in greatest dimension and ENE-
- pN3b: metastasis in either:
- Single ipsilateral lymph node, > 3 cm and ENE+ or
- Multiple ipsilateral, contralateral or bilateral lymph nodes, any with ENE+ or
- Single contralateral lymph node of any size and ENE+
Notes:
- Per AJCC 8th edition, for pN, a selective neck dissection will include 10+ lymph nodes and a comprehensive neck dissection (radical or modified radical neck dissection) will include 15+ lymph nodes
- Negative pathologic examination of a smaller number of nodes still mandates a pN0 designation
- Midline nodes are considered ipsilateral nodes
- Measurement of tumor metastasis:
- Cross sectional diameter of the largest lymph node metastatic deposit (not the lymph node itself) is measured in the gross specimen at the time of macroscopic examination or if necessary, using the histologic slide; may include matted or fused nodes
- Extranodal extension (ENE):
- AJCC 8th edition introduces the use of ENE in pN categorization
- Must be clearly defined as tumor present within the confines of the lymph node and as extending through the lymph node capsule into the surrounding connective tissue, with or without associated stromal reaction
Prefixes
- y: preoperative radiotherapy or chemotherapy
- r: recurrent tumor
AJCC prognostic stage groups
| Stage 0: | Tis | N0 | M0
|
| Stage I: | T1 | N0 | M0
|
| Stage II: | T2 | N0 | M0
|
| Stage III: | T3 | N0 | M0 | or | T1 - 3
|
| Stage IVA: | T4a | N0 - 1 | M0 | or | T1 - 4a
|
| Stage IVB: | T4b | any N | M0 | or | any T |
|
| Stage IVC: | any T | any N | M1 |
Registry data collection variables
- Extranodal extension clinical (present versus absent)
- Extranodal extension pathological (present versus absent)
- Extent of microscopic extranodal extension (distance of extension from the native lymph node capsule to the farthest point of invasion in extranodal tissue)
- Perineural invasion
- Lymphovascular invasion
- p16 / HPV status
- Performance status
- Tobacco use and pack years
- Alcohol use
- Depression diagnosis
Histologic grade (G)
- GX: cannot be assessed
- G1: well differentiated
- G2: moderately differentiated
- G3: poorly differentiated
Histopathologic type
- Carcinoma of the hypopharynx:
- Squamous cell carcinoma:
- HPV unrelated (negative) squamous cell carcinoma
- Variants of squamous cell carcinoma:
- Keratinizing
- Nonkeratinizing
- Acantholytic squamous cell carcinoma
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
- Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma
- Papillary squamous cell carcinoma
- Spindle cell squamous cell carcinoma
- Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma
- Lymphoepithelial carcinoma
- Carcinoma of minor salivary gland:
- Acinic cell carcinoma
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma, NOS
- Basal cell adenocarcinoma
- Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma
- Carcinoma type cannot be determined
- Carcinosarcoma
- Clear cell adenocarcinoma
- Cystadenocarcinoma
- Epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma
- Secretory carcinoma
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- Mucinous carcinoma
- Myoepithelial carcinoma
- Oncocytic carcinoma
- Polymorphous adenocarcinoma
- Salivary duct carcinoma
- Neuroendocrine carcinoma:
- Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, HPV-
- Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, HPV+
- Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, HPV-
- Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, HPV+
Clinical images
Contributed by Michael Elliott, M.B.B.S., M.Phil. and Carsten Palme, M.B.B.S.
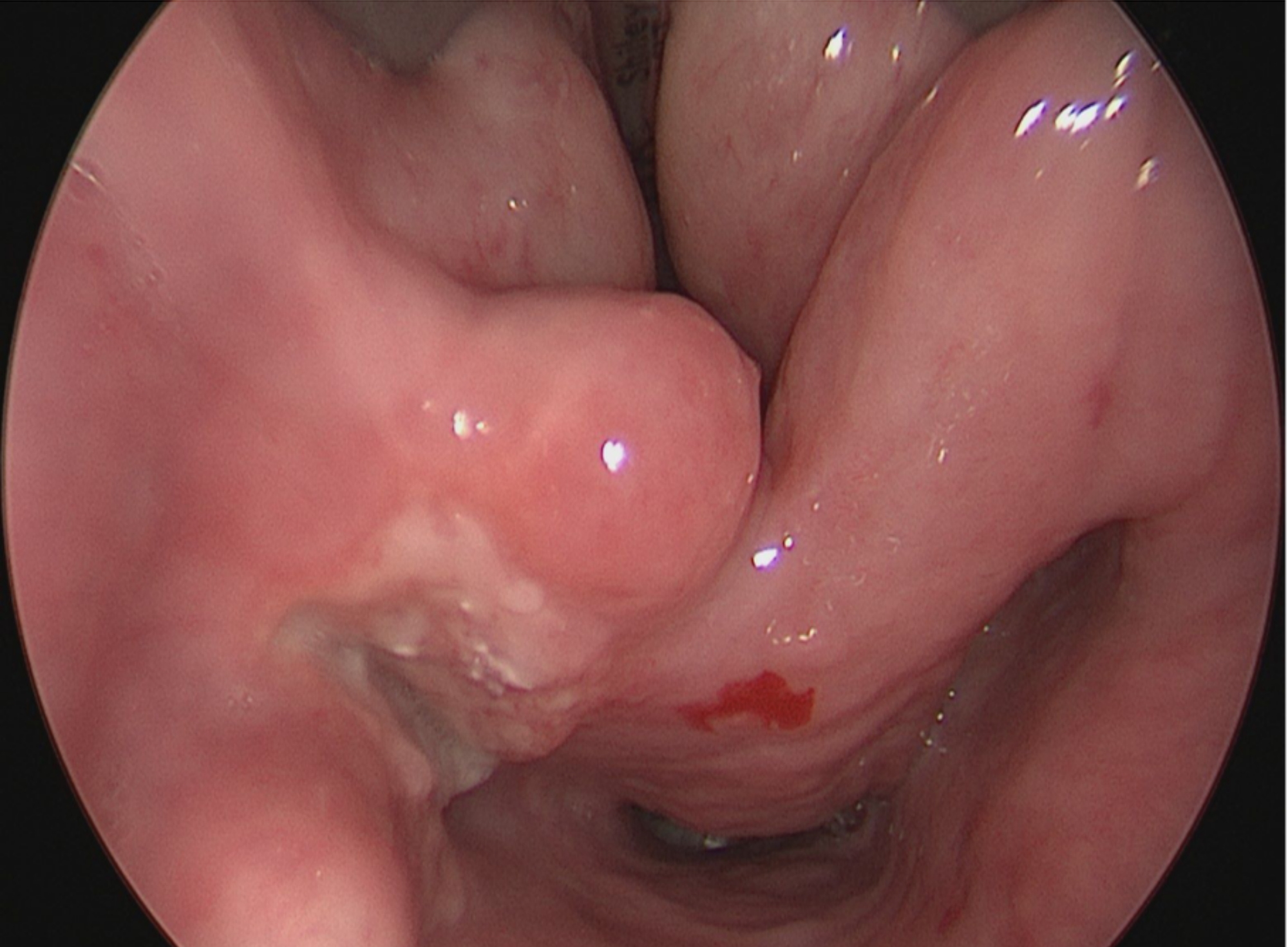
Ulcerated hypopharyngeal lesion
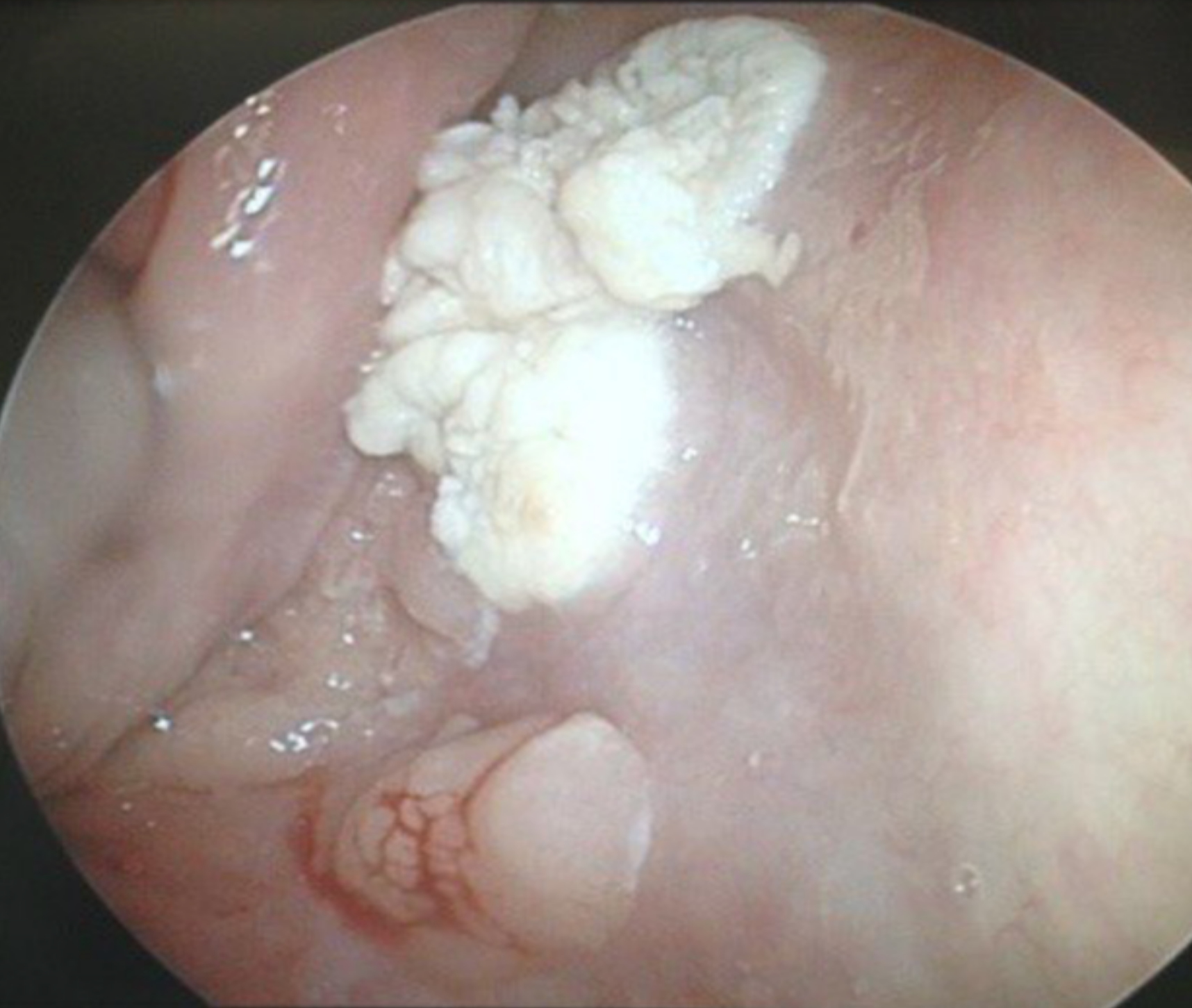
Keratotic hypopharyngeal lesion
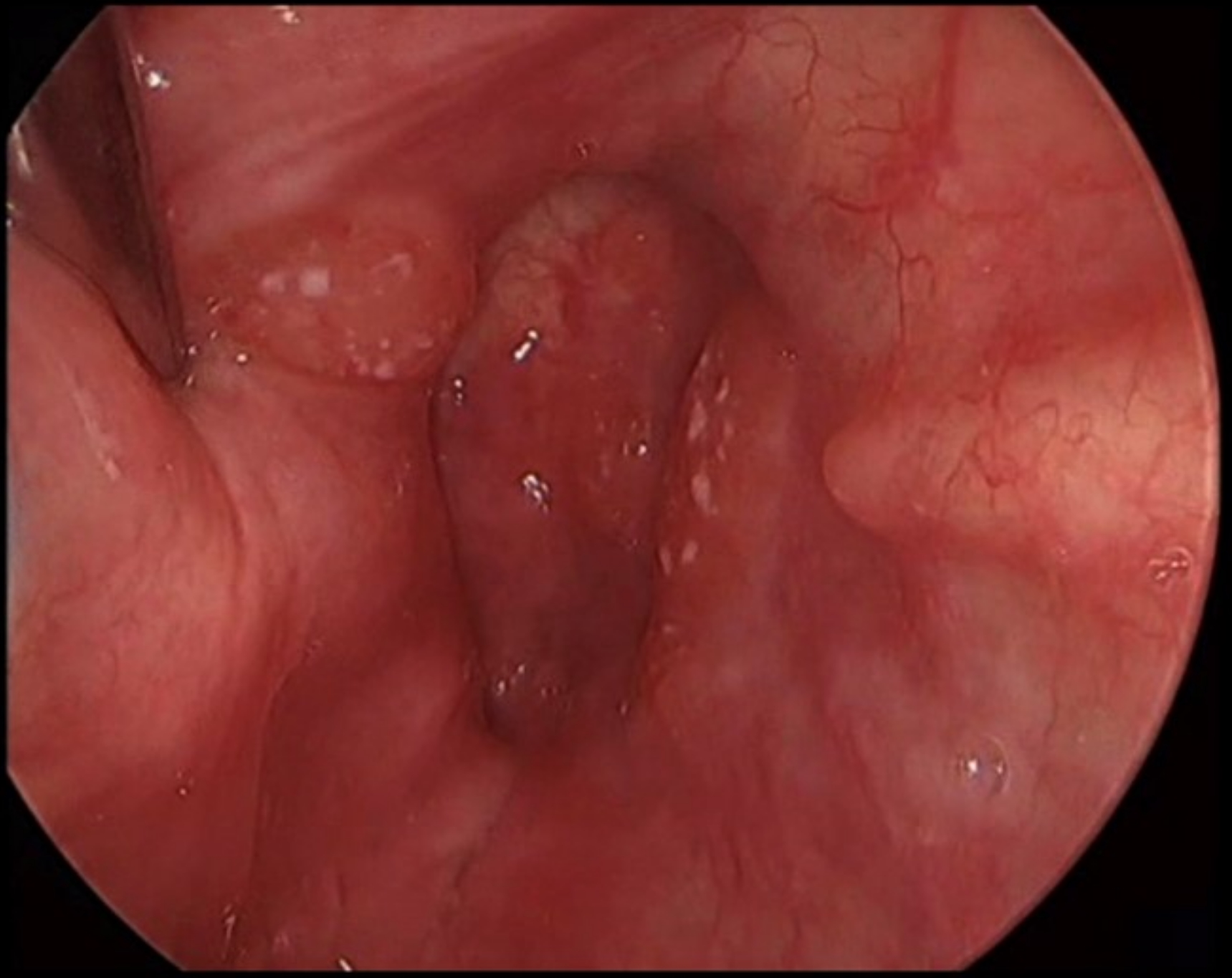
Polypoid ulcerated hypopharyngeal lesion
Gross images
Contributed by Kelly Magliocca, D.D.S., M.P.H.
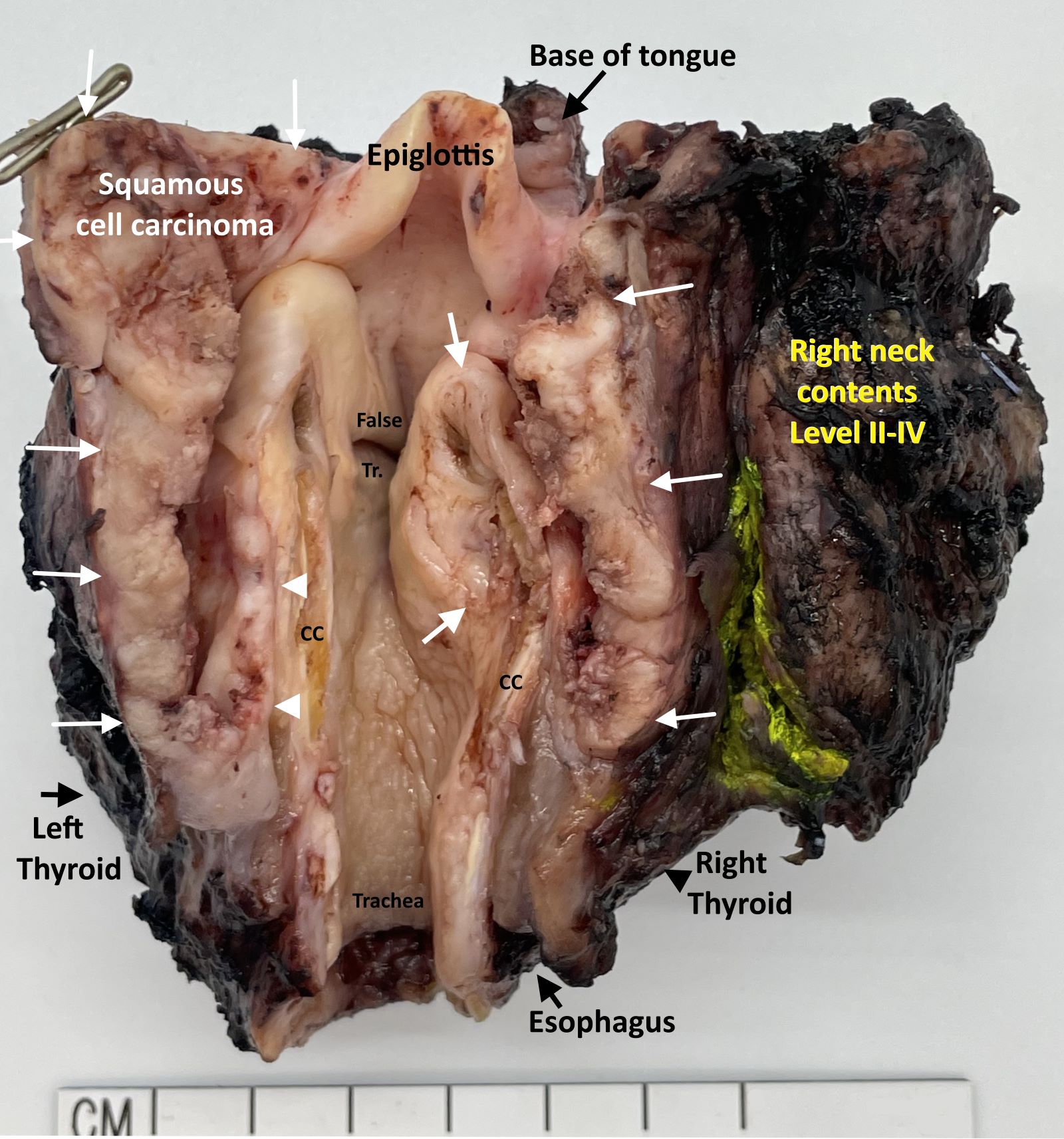
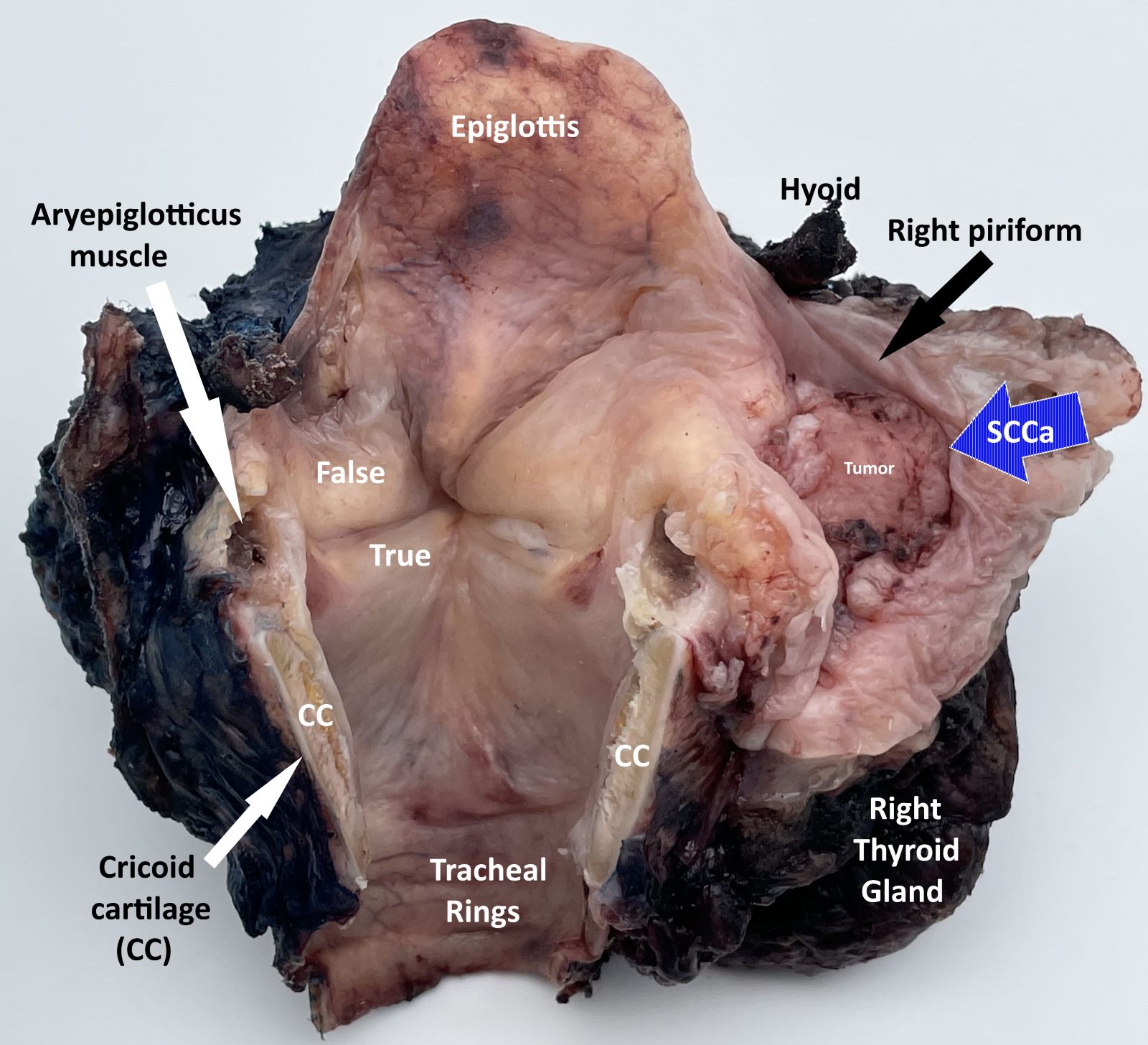
Laryngopharyngectomy, opened posteriorly (pT4a)
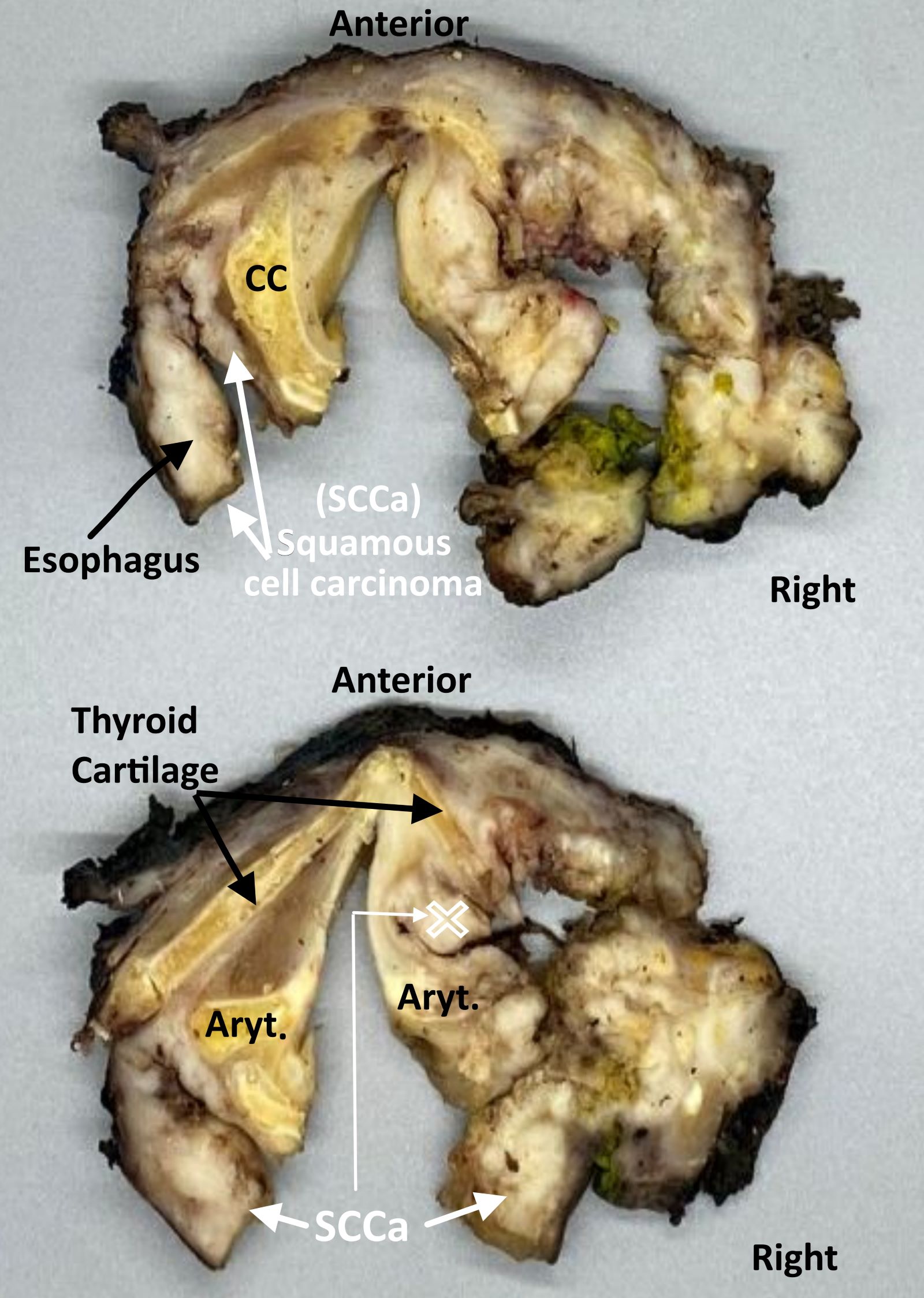
Laryngopharyngectomy,
sectioned (pT4a)
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is the pTNM stage (per the AJCC 8th edition) of a 3.1 cm right hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma invading the right thyroid cartilage and true cord, with no lymph node metastases identified?
- pT1c N0, stage IC
- pT1c N0, stage IVB
- pT3b N0, stage IIIB
- pT3c N0, stage IVB
- pT4a N0, stage IVA
Board review style answer #1
E. pT4a N0, stage IVA. Invasion into the thyroid cartilage, irrespective of tumor size is pT4a.
Comment Here
Reference:
Staging-hypopharynx
Back to top








