Table of Contents
Definition / general | Radiology images | Case reports | Clinical images | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) imagesCite this page: Shankar V. Implant related changes. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/jointsimplantchanges.html. Accessed December 21st, 2024.
Definition / general
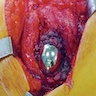
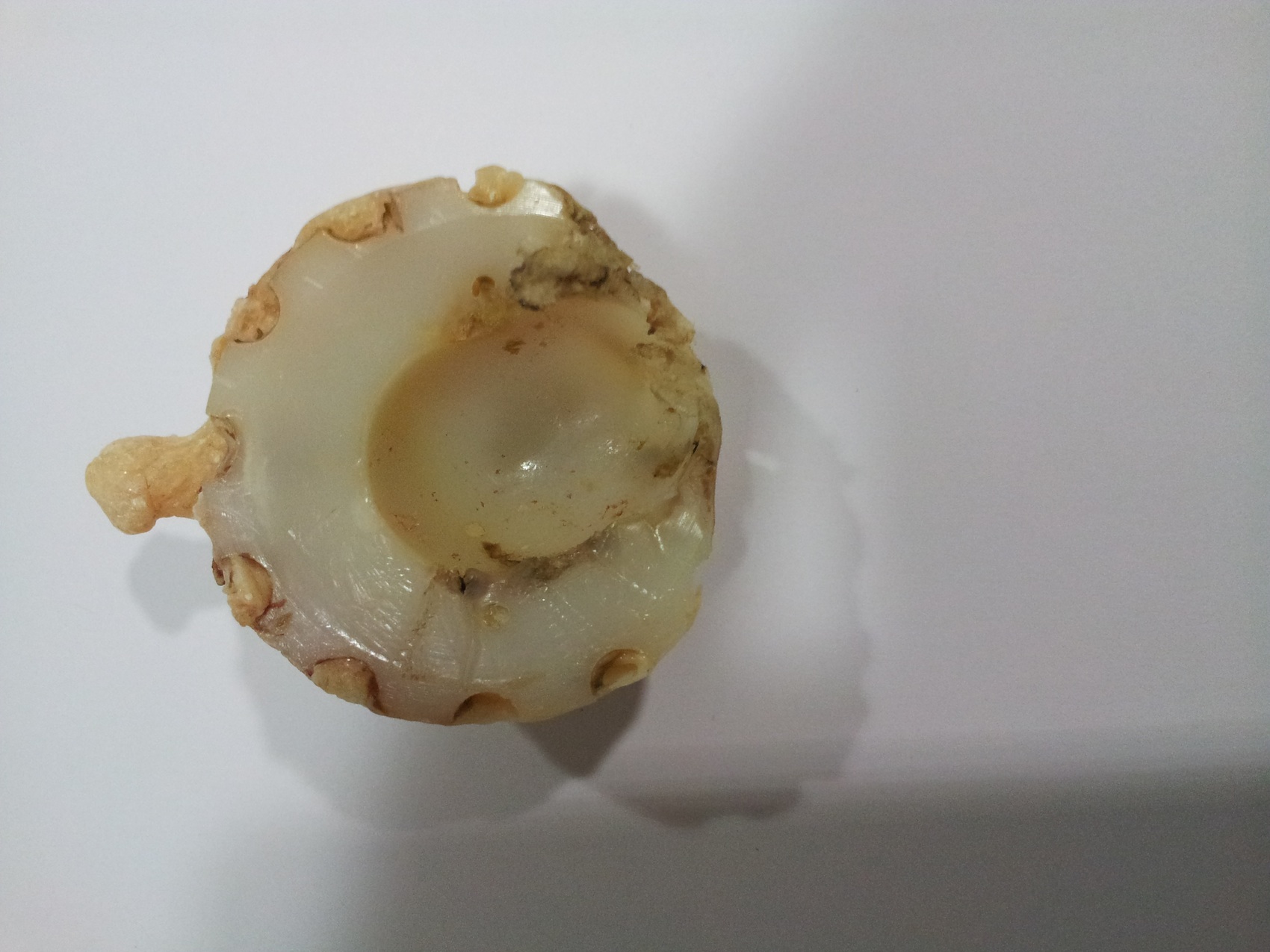
- Tissue around failed implants is often submitted for examination
- Causes of joint failure are infection (usually staphylococci, also inflammatory cells) and mechanical (granulomatous reaction to debris in joint)
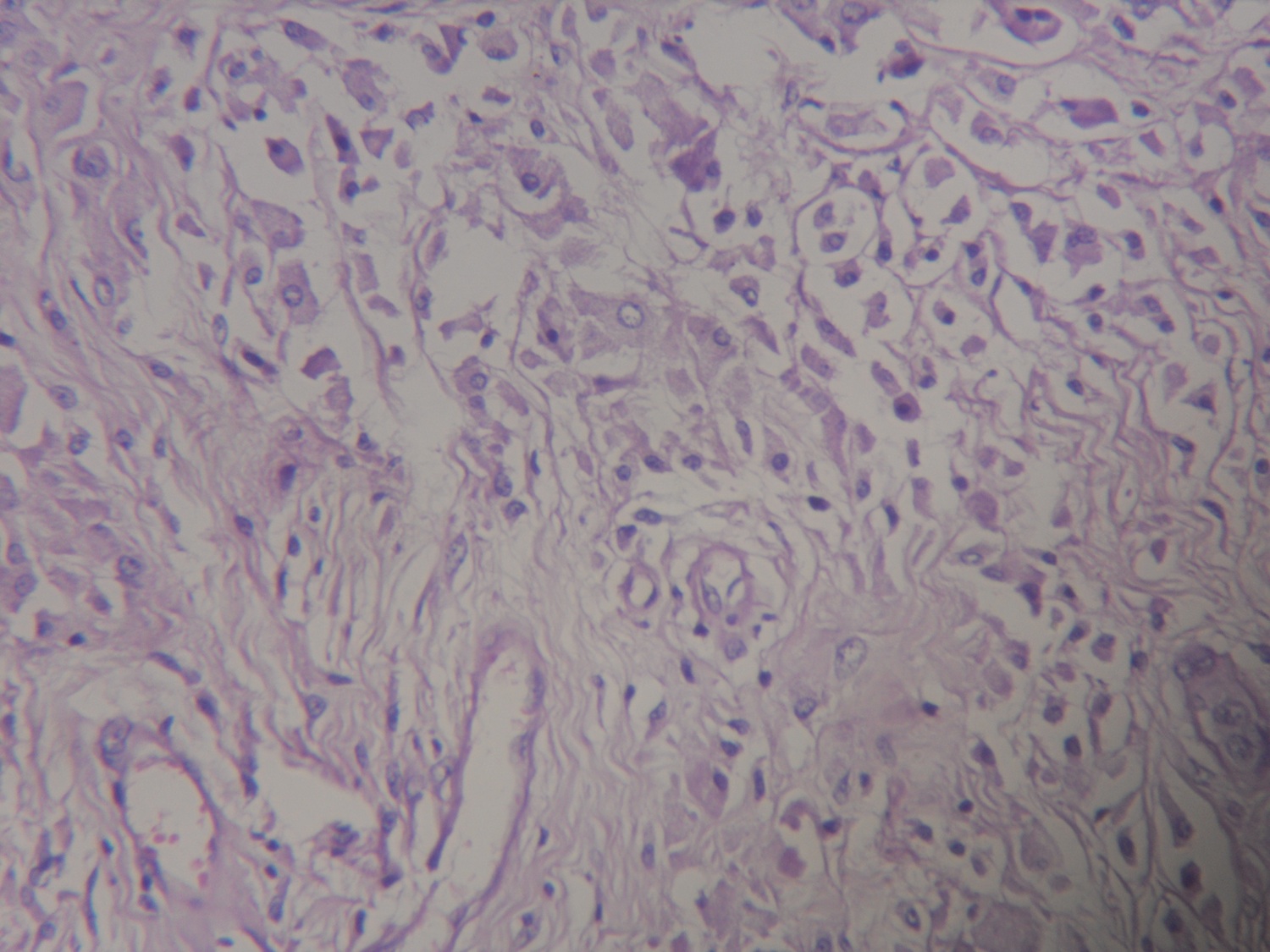
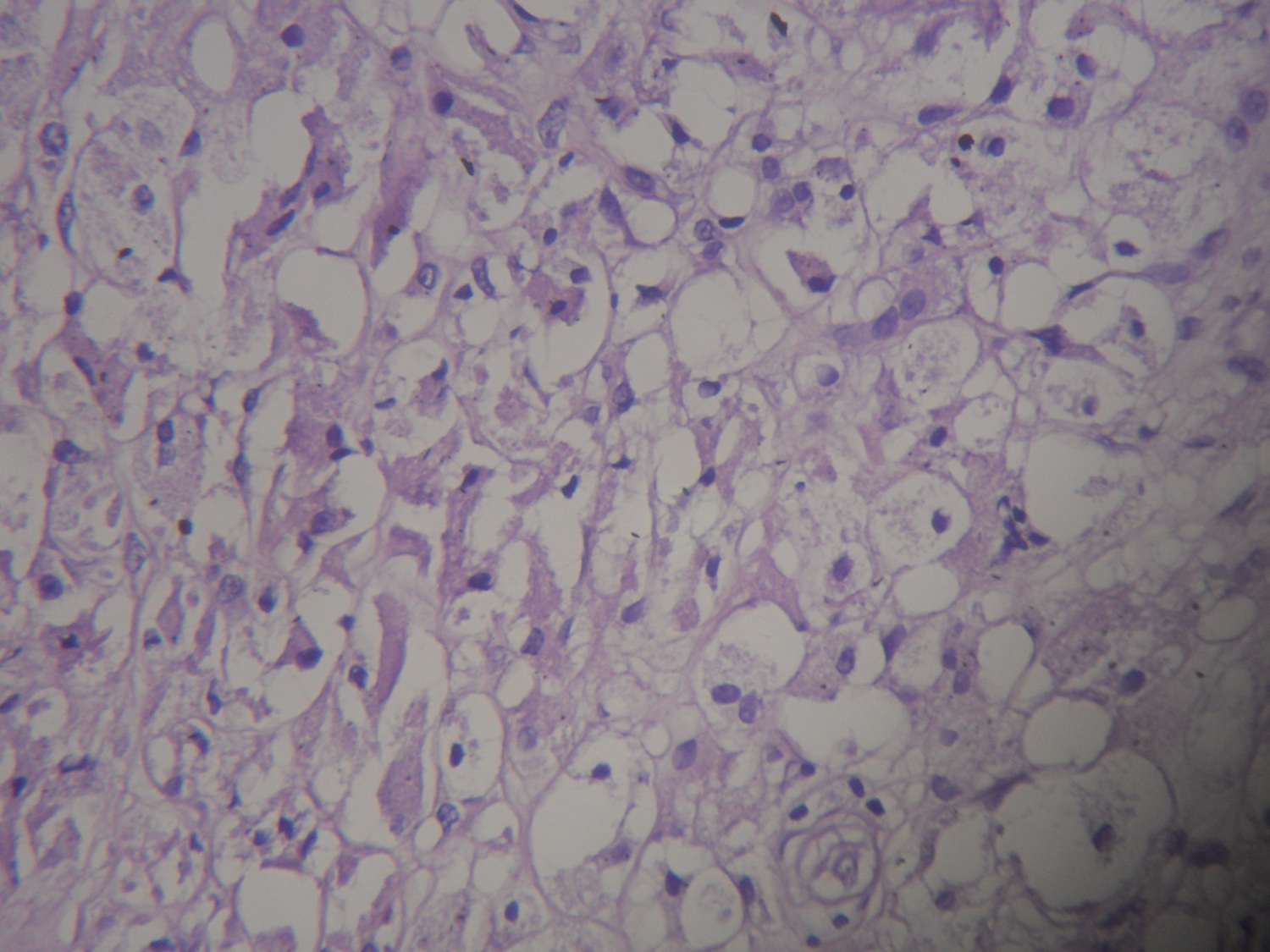
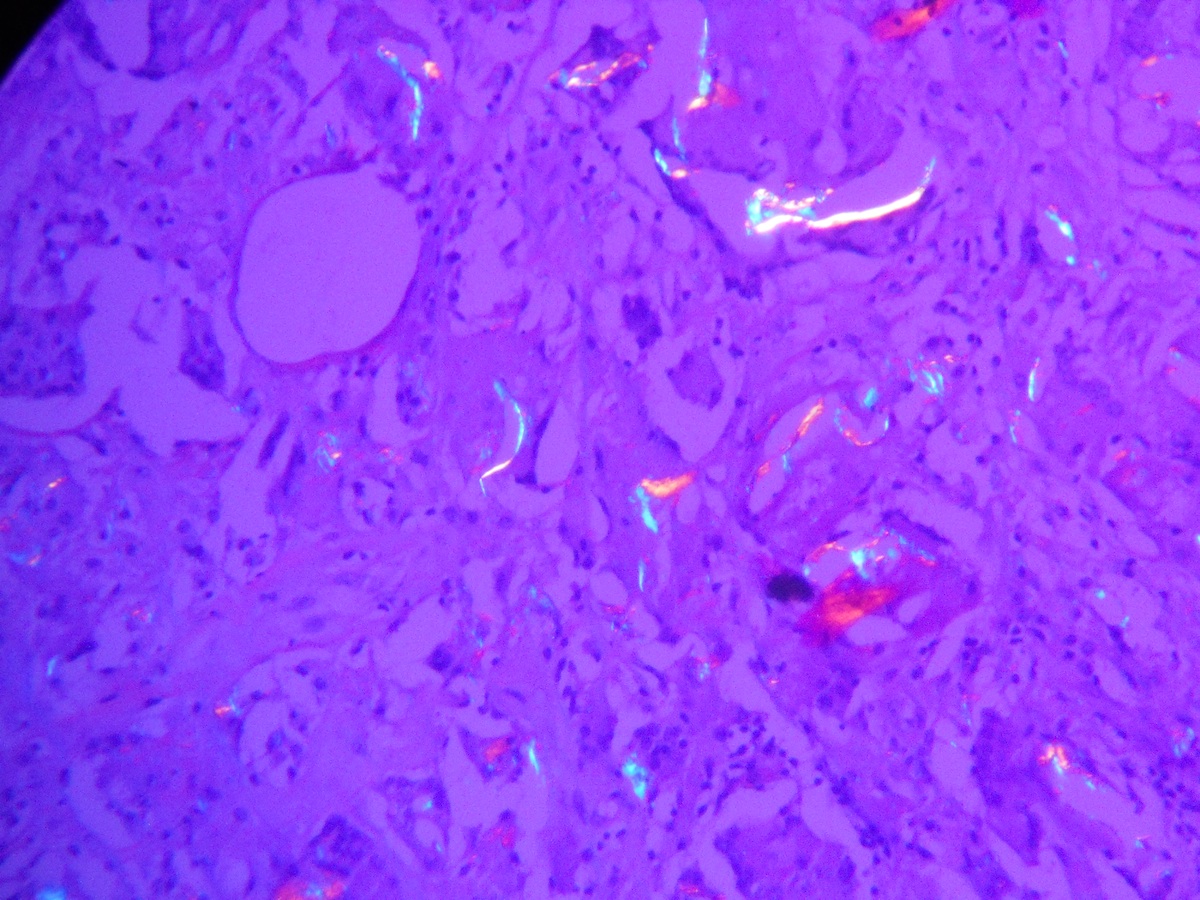
- Debris: due to metallic component of joint (gray black irregular fragments, often within histiocytes, particularly with titanium implants), polyethylene component of joint (thread-like particles up to 20 microns within histiocytes, visible only under polarized light), methyl methacrylate "grout" (dissolution during routine process reveals irregular holes from 1 - 100 microns), silicone rubber (bosselated, faintly yellow, refractile but not birefringent); all are associated with histiocytes and giant cells
- Implants can result in aggressive metallosis eroding bone and causing joint failure (Acta Orthop 2010;81:402)
- Frozen section: assessment of infected joint based on 5+ neutrophils/HPF (excluding surface fibrin and inflammatory exudates) in 5+ separate fields is 43% sensitive and 97% specific for infection compared to culture (Mod Pathol 1998;11:427)
Case reports
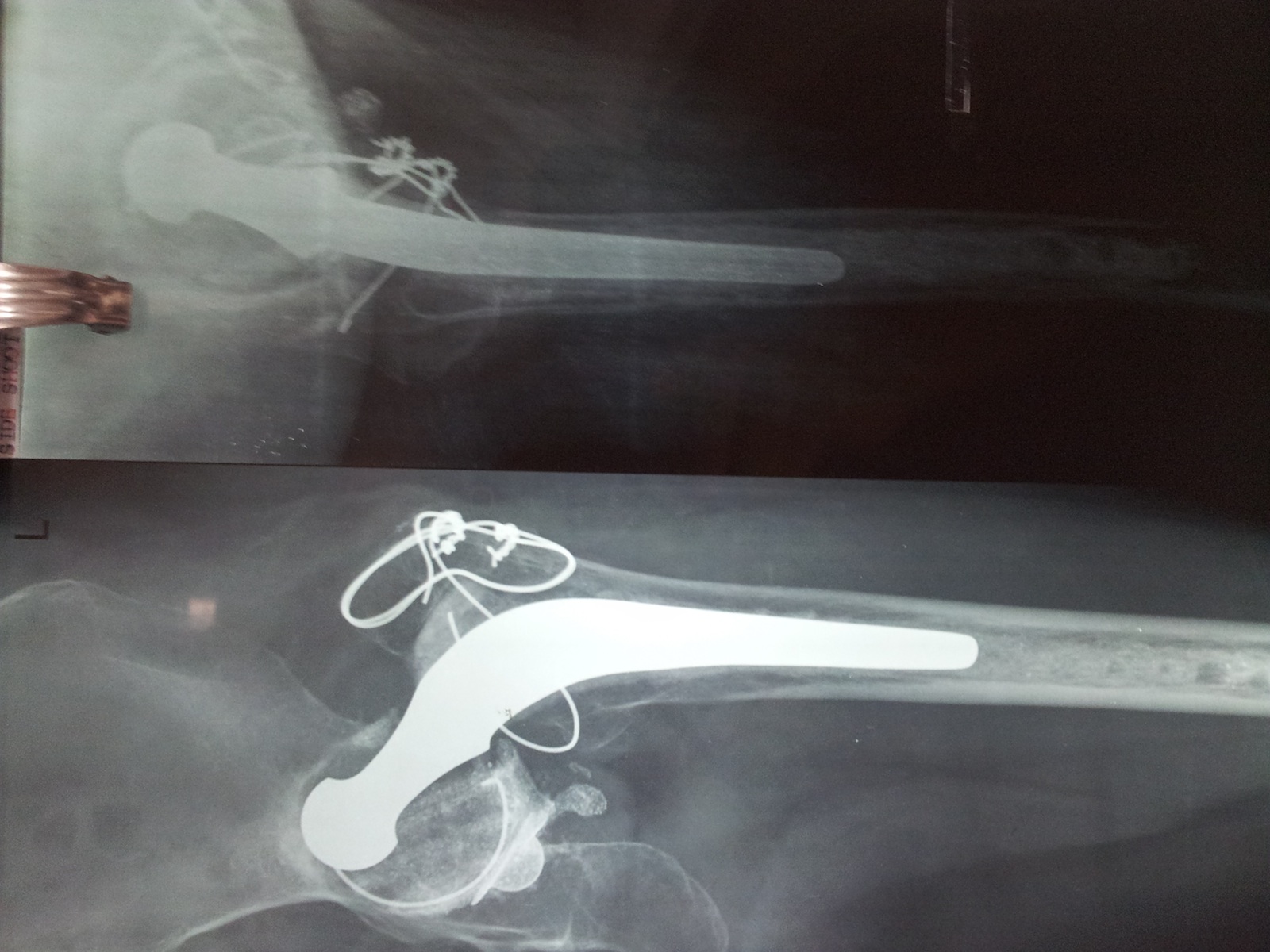
- 61 year old woman with loosening of her total hip replacement (THR) prosthesis after a fall (Case #300)