Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Clinical images | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Electron microscopy description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Serinelli S, de la Roza G. Ganglion cyst. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/jointsganglion.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Most common soft tissue mass found in the hand and wrist (StatPearls: Ganglion Cyst [Accessed 2 March 2021])
- Cystic structure containing mucoid material
Terminology
- Ganglion cyst (synonym)
- Mucous cyst (when occurring at the distal interphalangeal joint) (StatPearls: Ganglion Cyst [Accessed 2 March 2021])
ICD coding
- ICD-10: M67.40 - ganglion, unspecified site
Epidemiology
- 60 - 70% of the soft tissue masses in the hand and wrist (StatPearls: Ganglion Cyst [Accessed 2 March 2021])
- F:M = 3:1
- Can occur at any age
- Most common: 20 - 50 years
- Risk factors:
- Repetitive microinjuries due to overuse of the joint
- Previous traumas
Sites
- Dorsal aspect of the wrist, from the scapholunate ligament or scapholunate articulation → 70%
- Volar aspect of the wrist, from the radiocarpal joint or scaphotrapezial joint → 20%
- Distal interphalangeal joint, hip, knee, ankle, foot, others → 10%
- Some studies found the volar location to be more common than the dorsal (J Ultrasound Med 2019;38:2155)
Pathophysiology
- Cystic fluid analysis: gelatinous material containing mainly hyaluronic acid and lesser amounts of glucosamine, globulins and albumen (Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 2008;1:205)
- Since no epithelial lining exists in these structures, they should not be classified as true cysts
Etiology
- Unclear
- Numerous theories (Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 2008;1:205):
- Displacement of synovial tissue during embryogenesis
- Herniation of synovial capsule / fluid from joints into the surrounding tissues → reaction between fluid and local tissue results in the creation of the cyst
- Proliferation of pluripotential mesenchymal cells
- Myxoid degeneration of connective tissue after trauma: repetitive injury to the capsular and ligamentous structures → production of hyaluronic acid from fibroblasts → accumulation of mucin jelly-like material to form the cyst (most likely)
- Inflammatory etiology
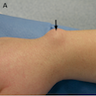
Clinical features
- Firm, rubbery, superficial mass (Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 2008;1:205)
- May form suddenly or gradually (J Hand Surg Am 2015;40:546)
- May be a history of trauma
- Symptoms (Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 2008;1:205):
- Majority are asymptomatic (StatPearls: Ganglion Cyst [Accessed 2 March 2021])
- May be painful or tender but usually the pain is not debilitating (Lindberg: Diagnostic Pathology - Soft Tissue Tumors, 2nd Edition, 2015)
- Pain may be due to nerve compression / involvement or less frequently, due to inflammatory changes related to complications by rupture, hemorrhage or infection (Insights Imaging 2016;7:179)
- May cause decreased range of motion, decreased strength and paresthesias
Clinical images
Diagnosis
- Clinical presentation is usually adequate for diagnosis
- Cyst typically transilluminates on the exam
- Ultrasound is used for a definitive diagnosis
- MRI is useful to rule out a possible solid tumor or in case of occult dorsal ganglion cyst (which is not clinically observed or palpated but is found on imaging studies or intraoperatively) (J Wrist Surg 2019;8:276)
Radiology description
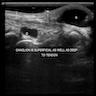
- Ultrasound: well defined, unilocular or multilocular, noncompressible and anechoic or hypoechoic fluid collection (J Ultrasound Med 2019;38:2155)
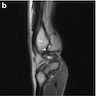
- MRI: well circumscribed, thin walled cyst, typically hypo to isointense on T1 weighted images and homogenously hyperintense on T2 (StatPearls: Ganglion Cyst [Accessed 2 March 2021], Insights Imaging 2016;7:179)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Benign condition
- Prognosis for most patients is excellent
- Ganglion cysts spontaneously recede in more than half of patients (ISRN Orthop 2013;2013:940615)
- Recurrence rate is approximately 10 - 15% after surgery (Adv Clin Exp Med 2019;28:95)
- Recurrence after surgery is unpredictable and independent of patient demographic factors or surgical techniques
- Aspiration has higher rates of recurrence (ISRN Orthop 2013;2013:940615)
Case reports
- 51 year old woman with a recurrent right foot ganglion cyst (J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2020;110:Article9)
- 54 year old man with posttraumatic extensive ganglion cyst to the knee (Clin Pract 2011;1:e61)
- 88 year old woman with a large multilocular ganglion cyst of the right temporomandibular joint (J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2016;74:1783)
Treatment
- Indications for treatment include pain, stiffness, weakness and cosmetic appearance (J Hand Surg Am 2015;40:546)
- Three general treatment approaches:
- Observation
- Aspiration: often combined with some form of injection, electrocautery or multiple puncture
- Excision: open or arthroscopic
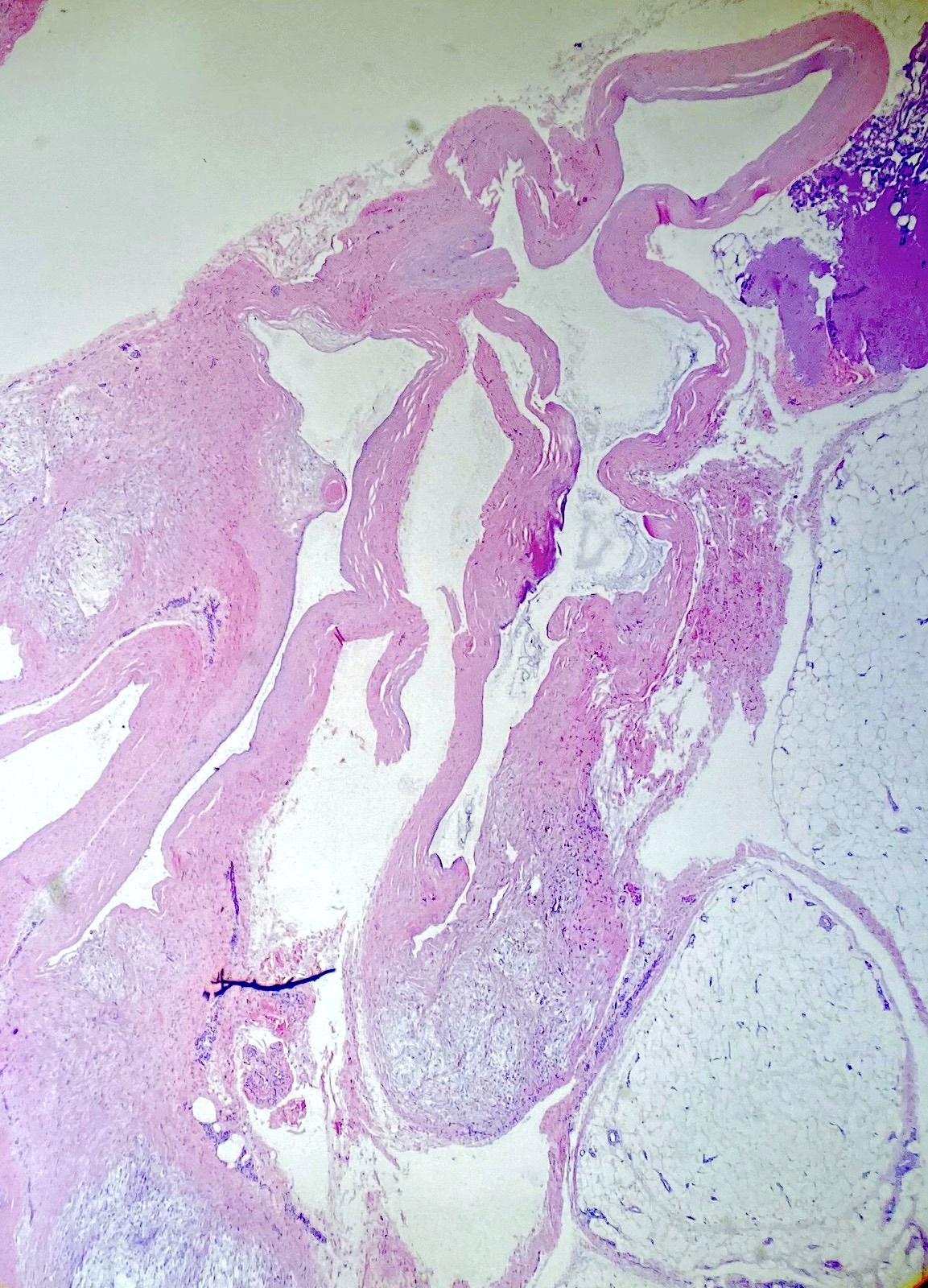
Gross description
- Cystic structure
- Typically, 1 - 2 cm in size
- Either uni or multilocular
- Usually attached to the underlying tendon sheath or joint capsule through a stalk (Lindberg: Diagnostic Pathology - Soft Tissue Tumors, 2nd Edition, 2015)
- Does not communicate with the joint cavity (Goldblum: Rosai and Ackerman's Surgical Pathology, 11th Edition, 2018)
- Contains viscous / gelatinous fluid
- Often excised in fragments
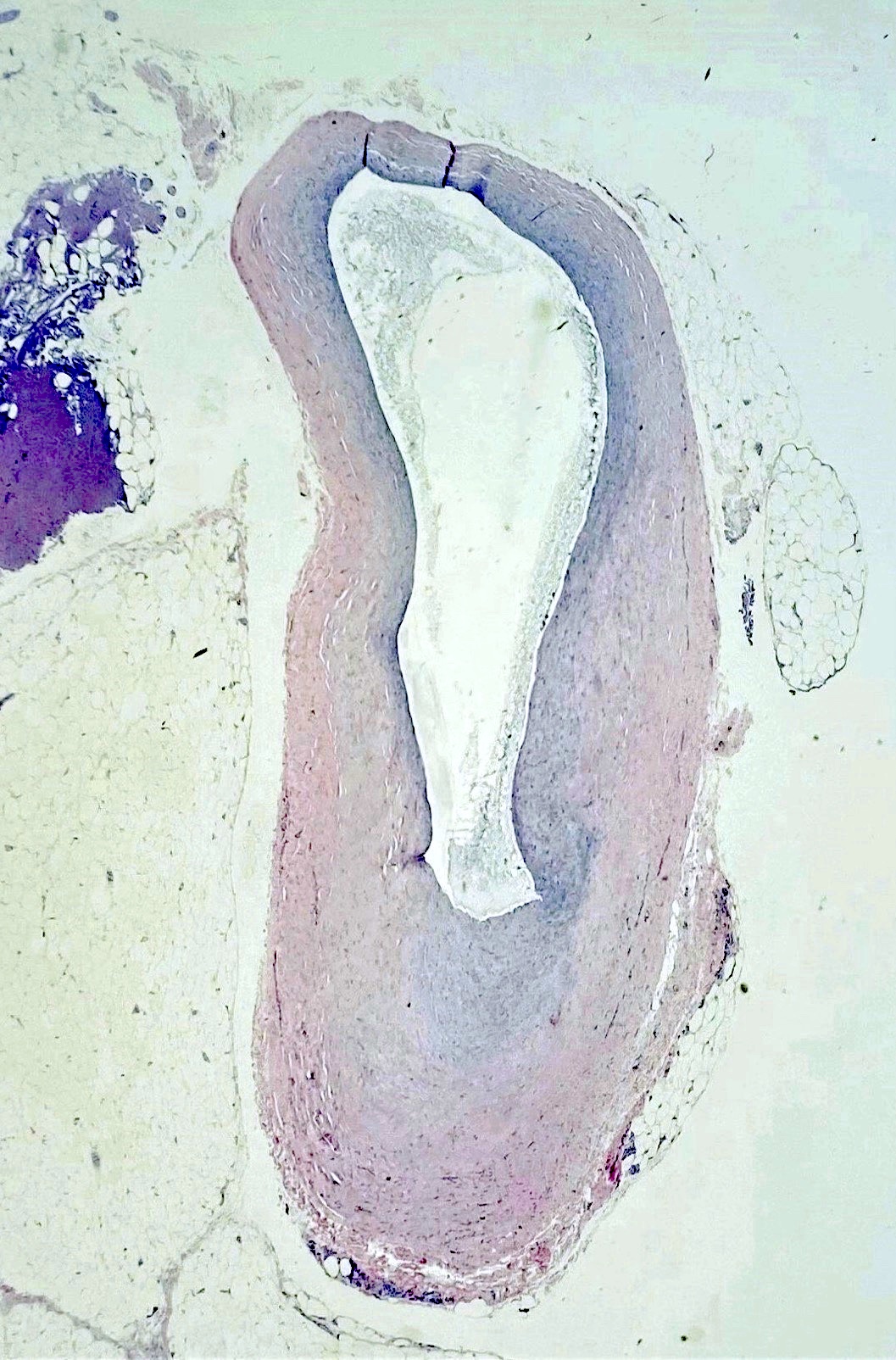
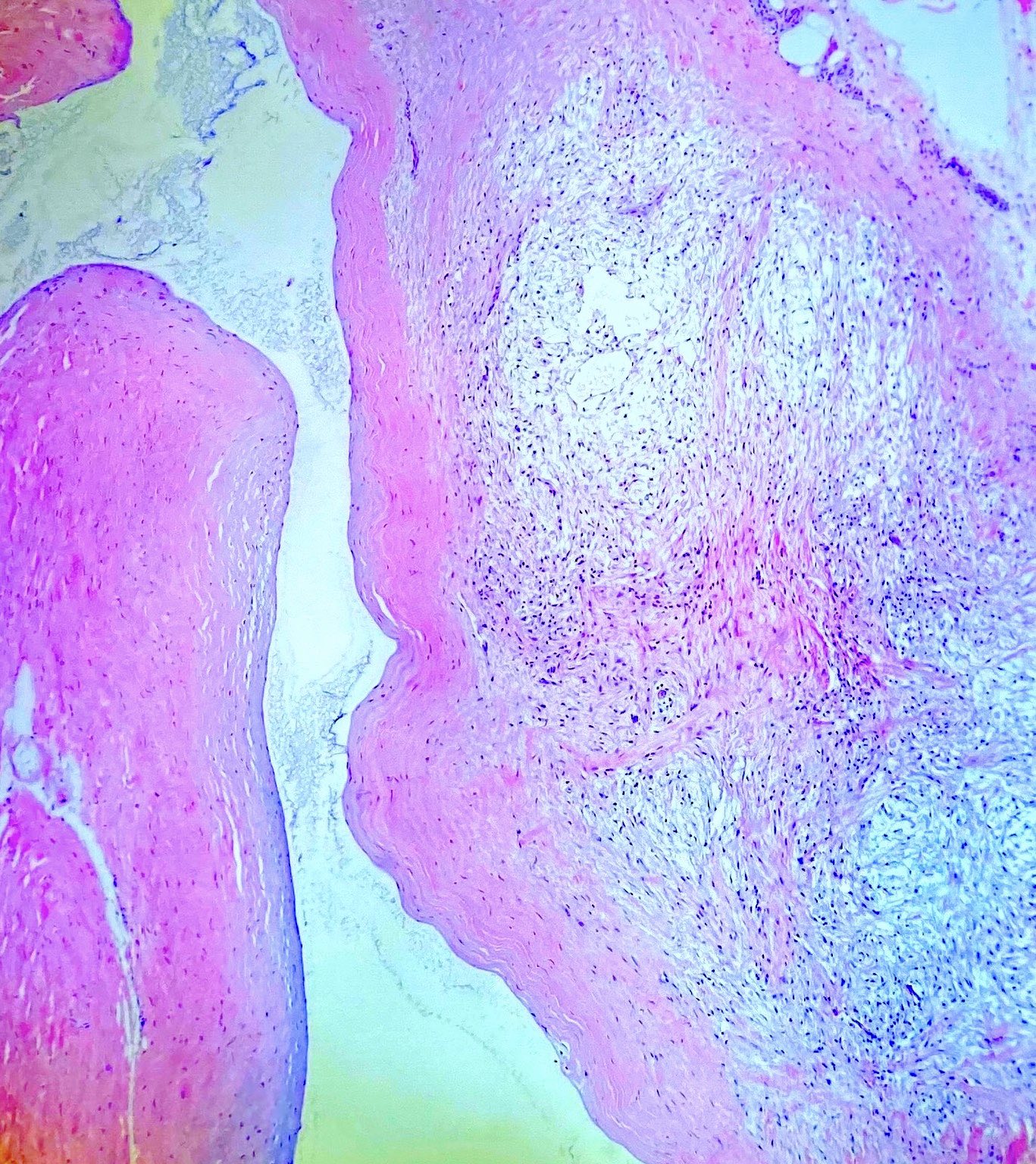
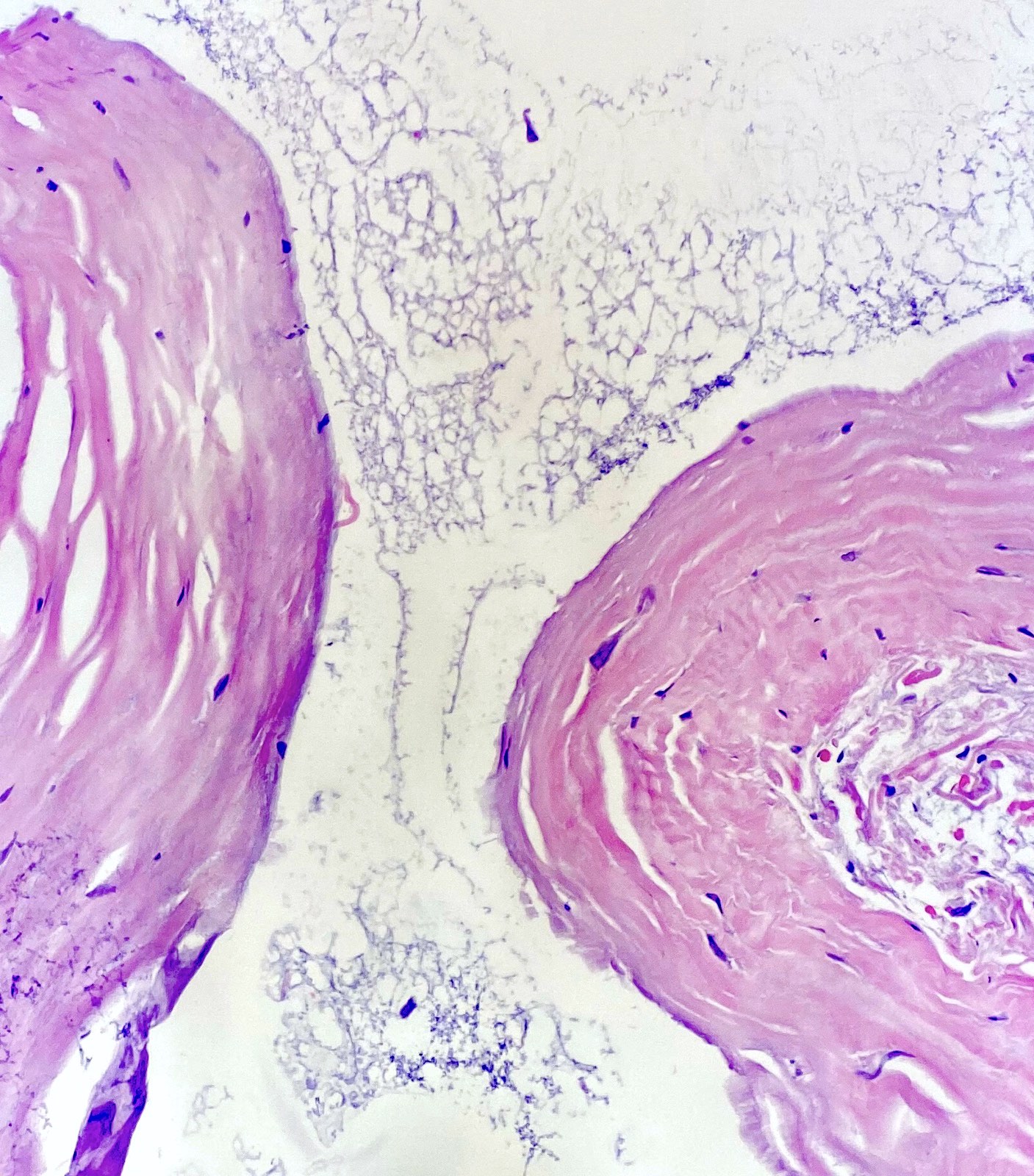
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Uni or multilocular cystic structure
- Dense collagenous walls with foci of myxoid changes (Lindberg: Diagnostic Pathology - Soft Tissue Tumors, 2nd Edition, 2015)
- No true epithelial lining
- Lumen may contain myxoid fluid
- There is no nuclear atypia or mitotic activity
- Inflammation / hemorrhage may be observed if the cyst has previously been ruptured
Microscopic (histologic) images
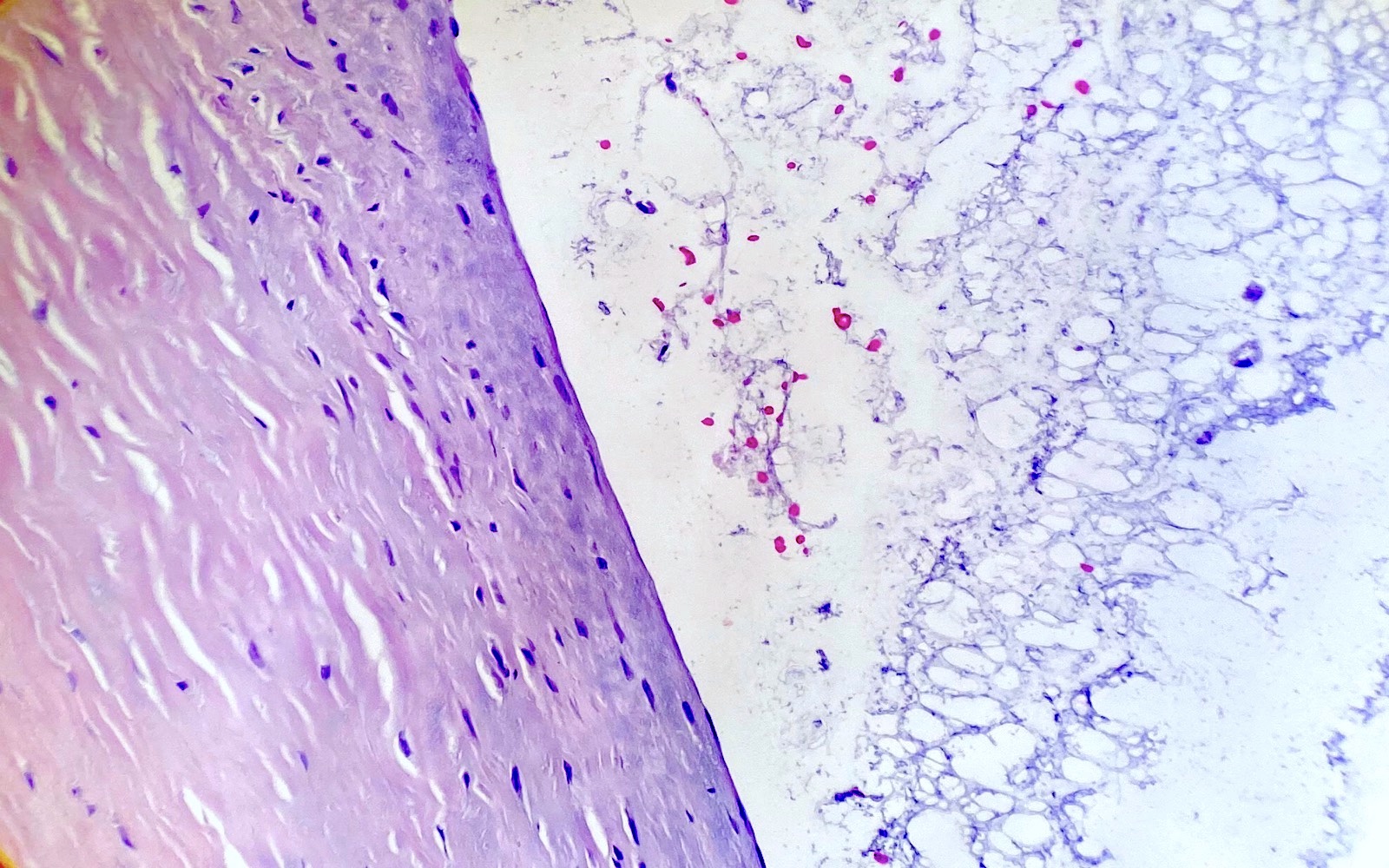
Cytology description
- Aspiration of a ganglion can be used as a preoperative diagnostic tool or a therapeutic procedure
- Paucicellular myxoid material that contains scattered / clustered histiocytes (Am J Clin Pathol 2005;123:858)
- Myxoid material of the cyst usually forms thick folds on the slide
Cytology images
Electron microscopy description
- Wall is composed of randomly oriented sheets of collagen arranged in loose layers
- Rare cells are present in the collagen sheets and appear to be fibroblasts or mesenchymal cells (Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 2008;1:205)
Videos
Ganglion cyst features
Sample pathology report
- Soft tissue, left dorsal wrist, excision:
- Ganglion cyst
Differential diagnosis
- Myxoma:
- Lobulated, gelatinous cut surfaces
- Most commonly occurring within large muscles (thigh, shoulder, upper arm)
- Low grade myxofibrosarcoma:
- Multinodular cut surfaces
- At least focal nuclear atypia
- Conspicuous, elongated, curvilinear, thin walled blood vessels are characteristic
- Most common in subjects older than 50
- Neurofibroma:
- Absence of cystic spaces
- S100+
Additional references
Board review style question #1
40 year old woman presents with a superficial lesion over the dorsal wrist. The lesion is excised and displays a cystic appearance. The histology is shown above. What is one of the main features of this condition?
- Cyst shows no true epithelial lining
- Invariably consists of a unilocular cyst
- Marked cellular atypia is seen
- Mitoses are frequent
- Rare condition
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Which of the following statements is true regarding ganglion cysts?
- More common among females
- More common in the pediatric population
- Myxoid changes in the cyst wall are never observed
- Nuclear atypia is required for the diagnosis
- Rarely found in the hand / wrist area
Board review style answer #2