Gallbladder & extrahepatic bile ducts
General
Staging-perihilar bile duct
Editor-in-Chief: Debra L. Zynger, M.D.
Last author update: 10 December 2020
Last staff update: 31 January 2022
Copyright: 2003-2024, PathologyOutlines.com, Inc.
PubMed Search:
TNM staging of perihilar bile duct tumors
Page views in 2023: 656
Page views in 2024 to date: 217
Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Staging-perihilar bile duct. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/gallbladderstagingextrahepatic.html. Accessed April 18th, 2024.
Definition / general
- All carcinomas of the perihilar bile ducts (arising predominantly in the main lobar extrahepatic bile ducts, distal to segmental bile ducts and proximal to the cystic duct), including poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas, are covered by this staging system
- Cystic duct lesions are staged using the gallbladder template and common bile duct lesions are staged using the distal bile duct template
Essential features
- AJCC, 7th Edition staging was sunset on December 31, 2017; as of January 1, 2018, use of the
AJCC, 8th Edition, 2018 is mandatory
Terminology
- AJCC advocates the term cholangiocarcinoma for adenocarcinomas of this region
ICD coding
- C24.0: malignant neoplasm of extrahepatic bile duct
Primary tumor (pT)
- TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed
- T0: no evidence of primary tumor
- Tis: carcinoma in situ / high grade dysplasia
- T1: tumor confined to the bile duct, with extension up to the muscle layer or fibrous tissue
- T2: tumor invades beyond the wall of the bile duct to surrounding adipose tissue or tumor invades adjacent hepatic parenchyma
- T2a: tumor invades beyond the wall of the bile duct to surrounding adipose tissue
- T2b: tumor invades adjacent hepatic parenchyma
- T3: tumor invades unilateral branches of the portal vein or hepatic artery
- T4: tumor invades the main portal vein or its branches bilaterally or the common hepatic artery; or unilateral second order biliary radicles with contralateral portal vein or hepatic artery involvement
Regional lymph nodes (pN)
- NX: regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
- N0: no regional lymph node metastasis
- N1: one to three positive lymph nodes typically involving the hilar, cystic duct, common bile duct (choledochal), hepatic artery, posterior pancreatoduodenal and portal vein lymph nodes
- N2: four or more positive lymph nodes from the sites described for N1
- Notes: regional lymph nodes are listed above, in the N1 criteria
Stage grouping
- Stage 0:Tis N0 M0
- Stage I:T1 N0 M0
- Stage II:T2a - b N0 M0
- Stage IIIA:T3 N0 M0
- Stage IIIB:T4 N0 M0
- Stage IIIC:any T N1 M0
- Stage IVA:any T N2 M0
- Stage IVB:any T any N M1
Registry data collection variables
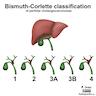
- Tumor location and extent according to Bismuth-Corlette classification:
- I: tumor is limited to the common hepatic duct, below the level of the confluence of the right and left hepatic ducts
- II: tumor involves the confluence of the right and left hepatic ducts
- IIIa: tumor with type II involvement plus extension to the right second order ducts
- IIIb: tumor with type II involvement plus extension to the left second order ducts
- IV: tumor extends into both right and left second order ducts
- Papillary histology (improved prognosis)
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Histologic grade
- GX: grade cannot be assessed
- G1: well differentiated
- G2: moderately differentiated
- G3: poorly differentiated
Histopathologic type
- Adenocarcinoma, biliary type
- Adenocarcinoma, intestinal type
- Adenocarcinoma, gastric foveolar type
- Mucinous adenocarcinoma
- Clear cell adenocarcinoma
- Signet ring cell carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
- Undifferentiated carcinoma
- Neuroendocrine carcinoma
- Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma
- Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma
- Intraductal papillary neoplasm with an associated invasive component
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm with an associated invasive component
Residual tumor
- R0: complete resection with grossly and microscopically negative margins of resection
- R1: grossly negative but microscopically positive margins of resection
- R2: grossly and microscopically positive margins of resection
Board review style question #1
Which of the following histologic patterns portends a good prognosis for perihiliar bile duct cholangiocarcinoma and therefore is considered a registry data collection variable?
- Clear cell
- Mucinous
- Papillary
- Tubular
Board review style answer #1
Back to top