Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Clinical features | Case reports | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Schwannoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colontumorschwannoma.html. Accessed January 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Uncommon mesenchymal tumor of colon
Essential features
- Benign spindle cell lesion of muscularis propria with prominent lymphoid cuff
- Positive for S100, unlike gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST)
- No syndromic association
Terminology
- GANT is an outdated term for GIST, not schwannoma
Epidemiology
- Rare; less common than colonic GIST
Sites
- Colon is second most common site in gastrointestinal tract for schwannoma, after stomach
Clinical features
- Median age 65 years; may have slight female predilection (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:846)
- Benign; not associated with neurofibromatosis
Case reports
- 52 year old and 59 year old women with small colonic masses (J Korean Surg Soc 2011;80:367)
- 62 year old woman with 4 cm ascending colon mass (Oncol Lett 2016;11:2580)
- 68 year old woman with colonic adenocarcinoma and incidental 1.5 cm nodule (Can J Gastroenterol 2010;24:233)
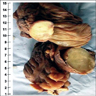
Gross description
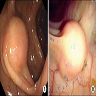
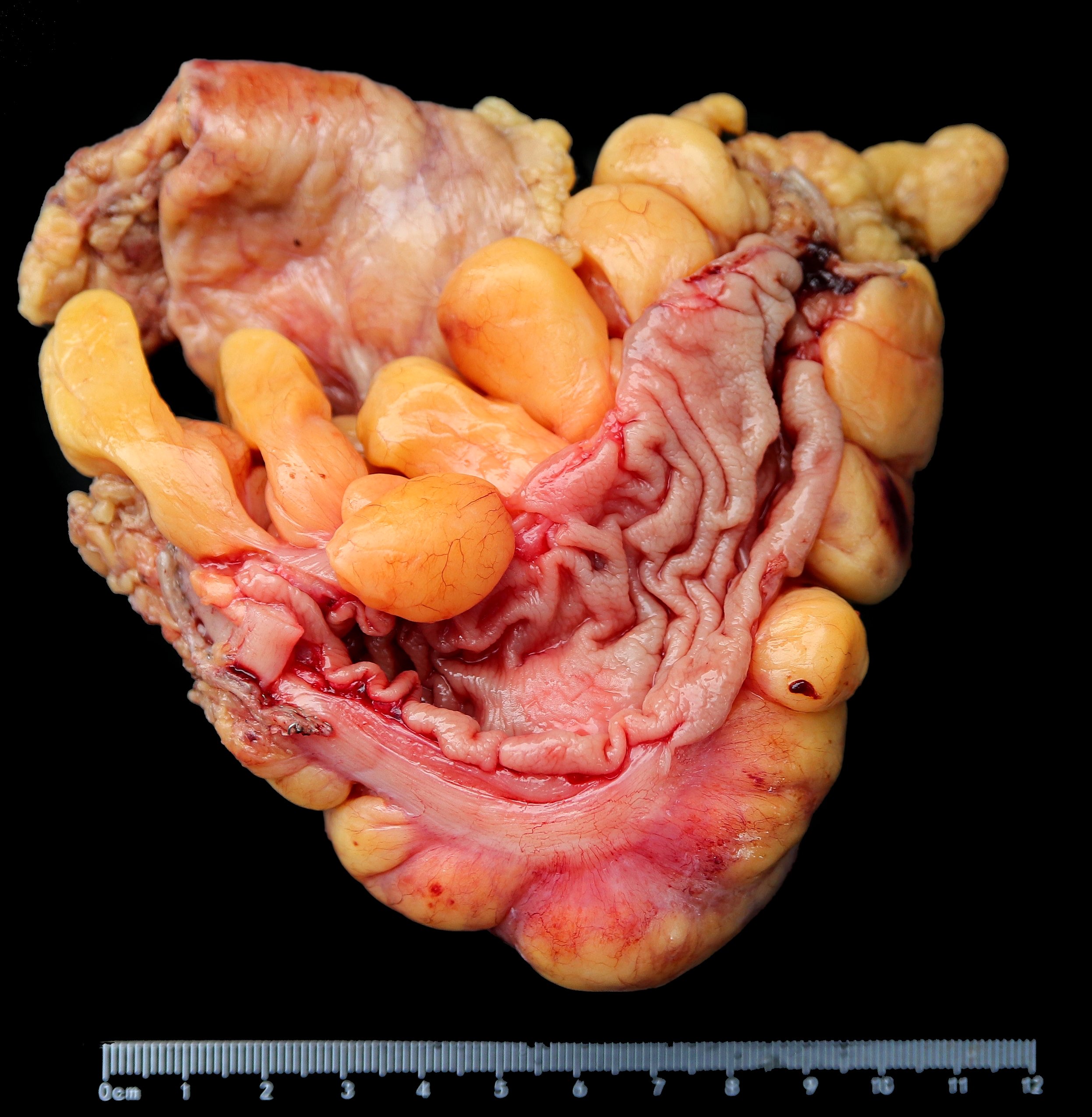
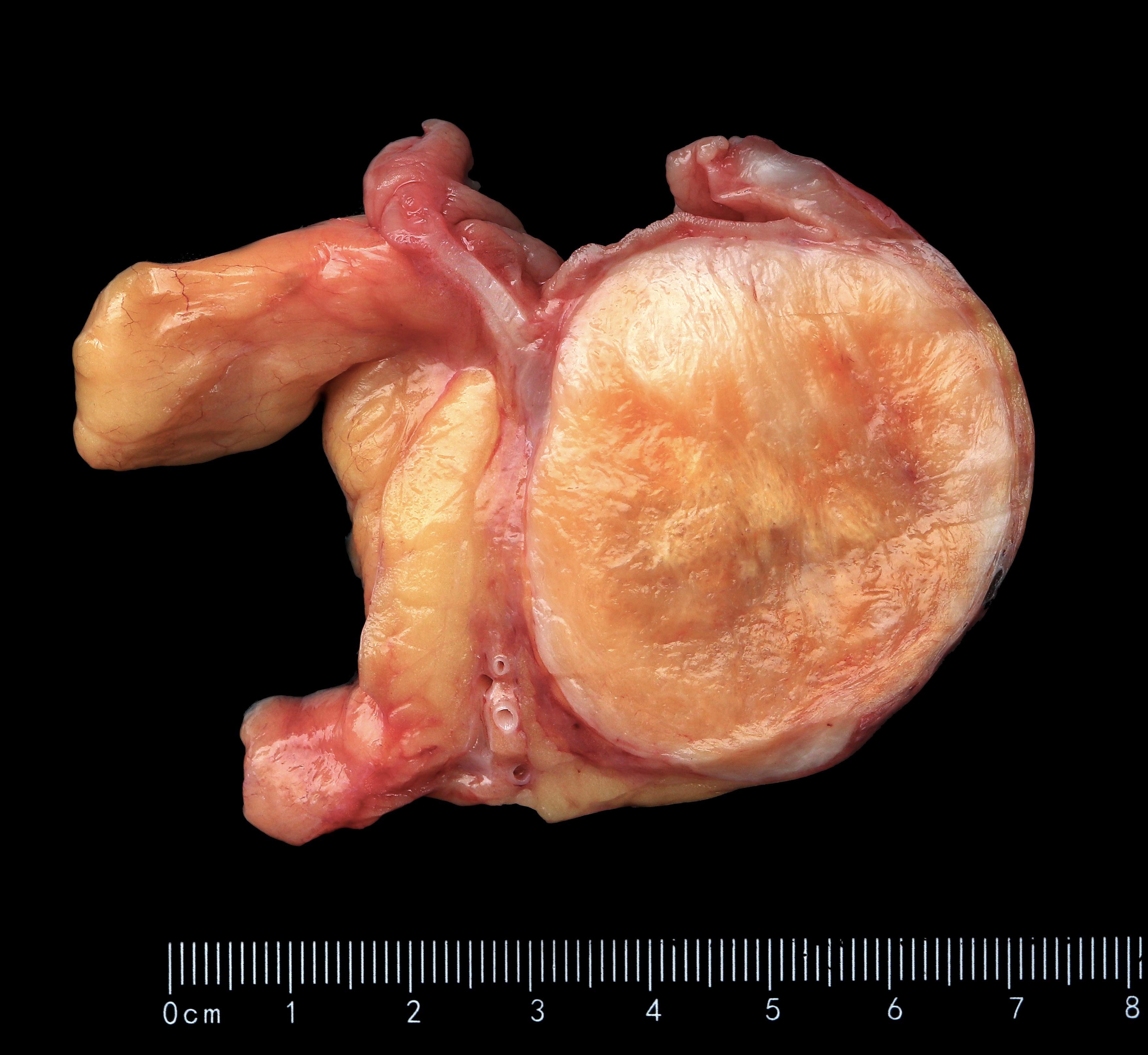
- Well circumscribed but usually not encapsulated
- Polypoid intraluminal mass with mucosal ulceration, usually in right colon
Gross images
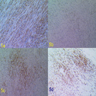
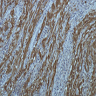
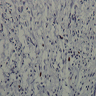
Microscopic (histologic) description
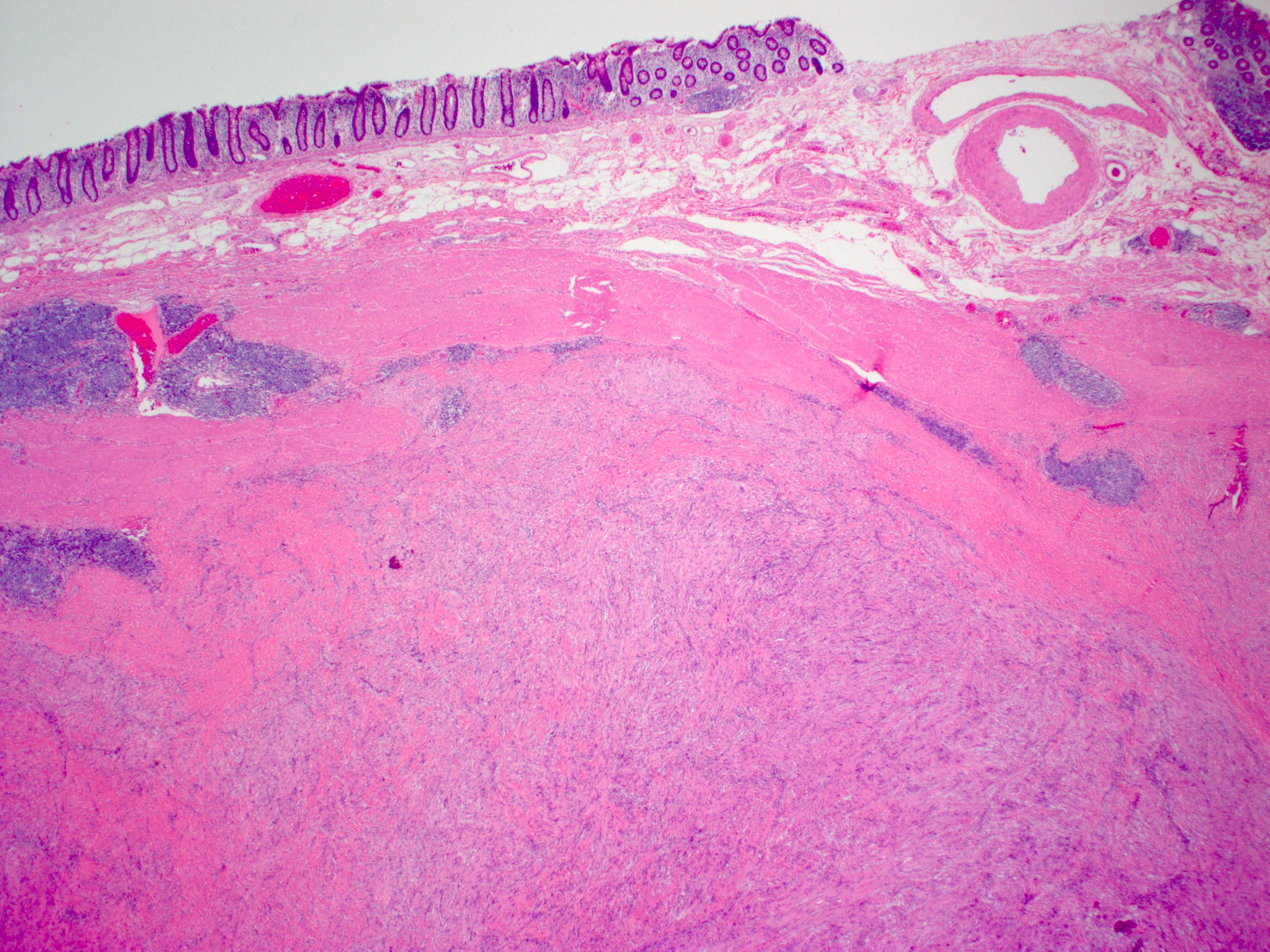
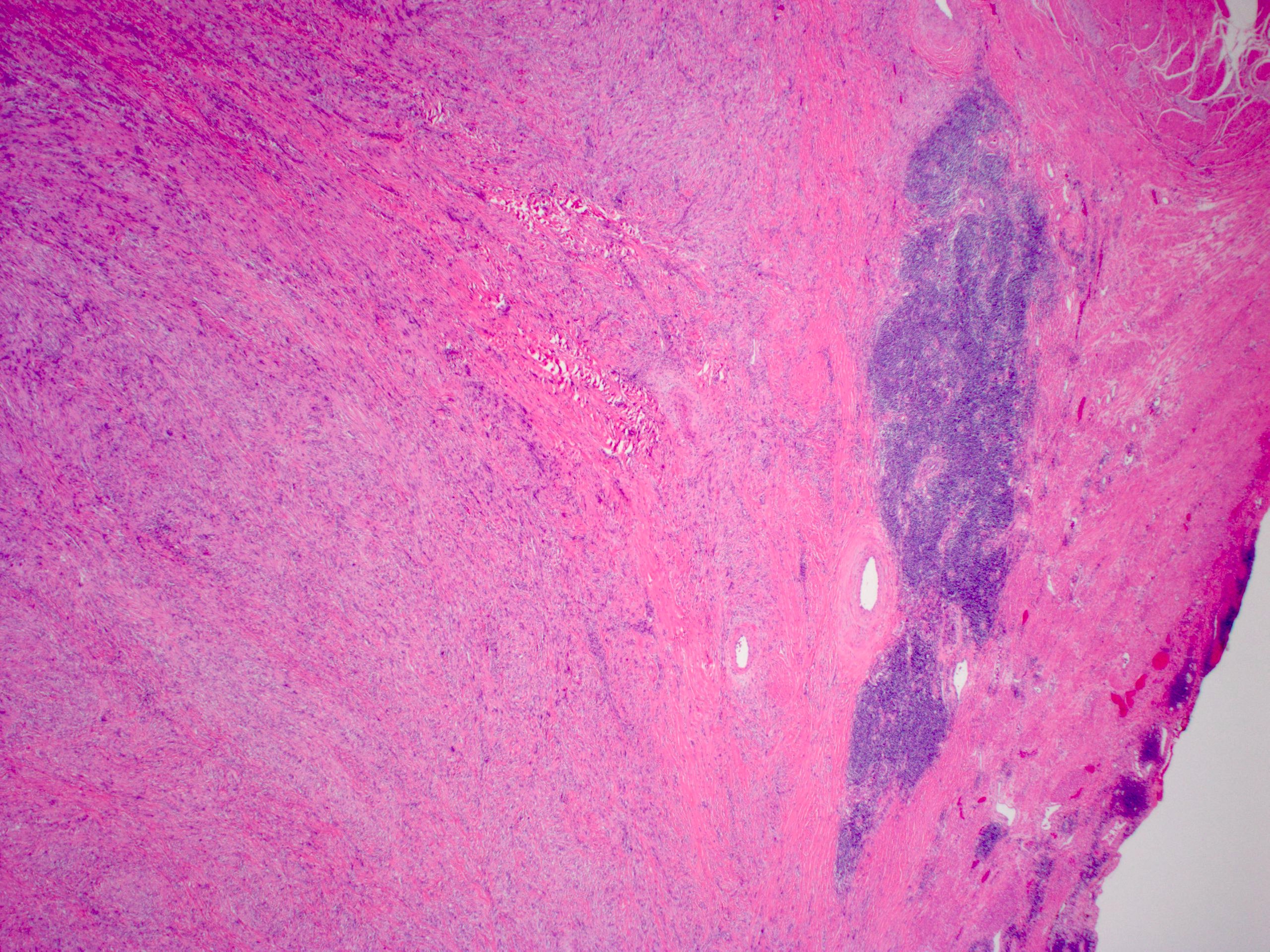
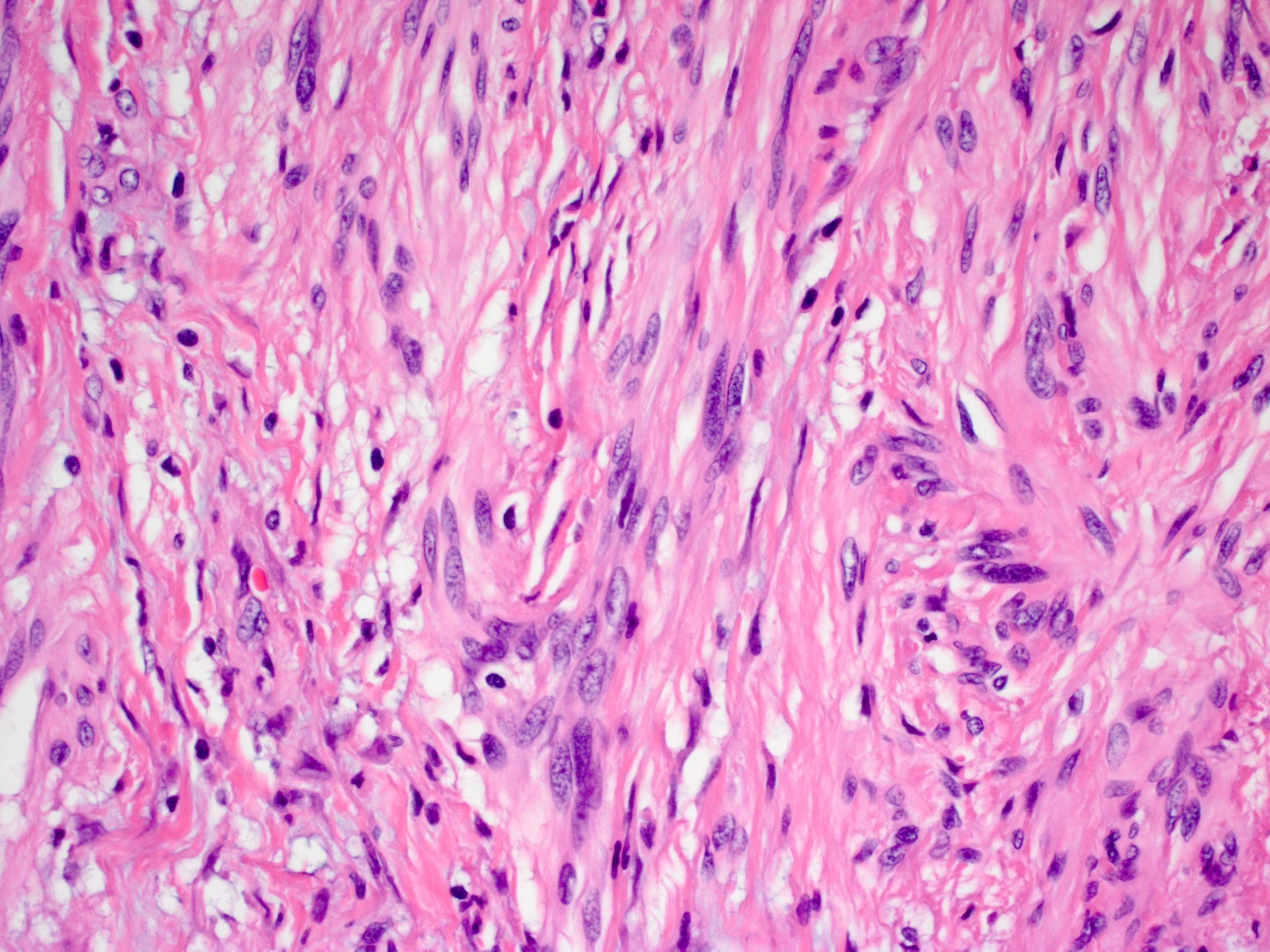
- Nonencapsulated, polypoid lesion arising in muscularis propria (Mod Pathol 2015;28:S47)
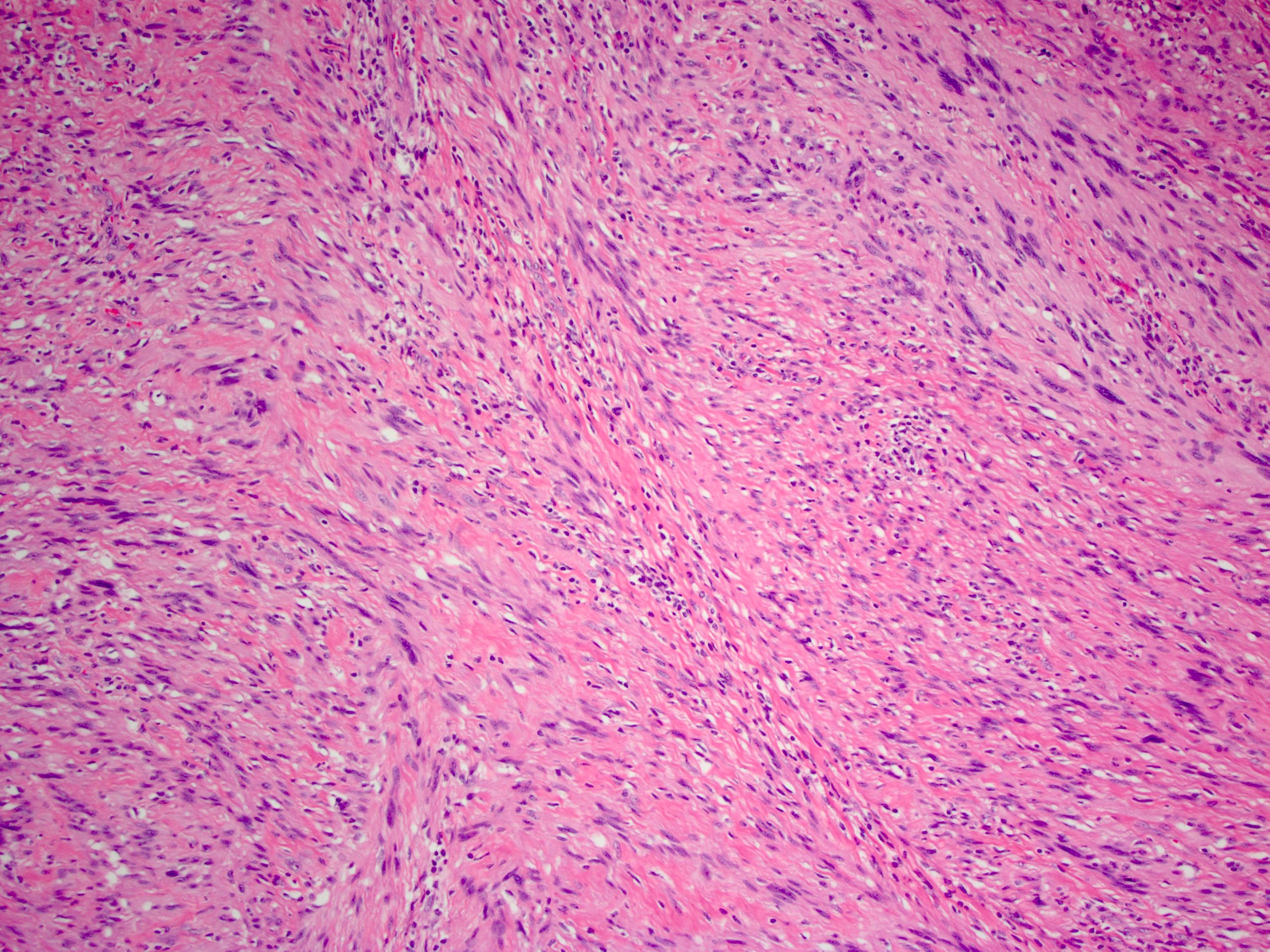
- Bland spindle cells with elongated, pointed nuclei; no or indistinct Verocay bodies and no prominent nuclear palisading
- Stroma may be myxoid and contain prominent collagen bands
- Surrounded by lymphoid cuff
- May have microcystic or reticular features or may be epithelioid (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1080)
- May have focal nuclear atypia; mitotic figures rare
- Usually no vascular hyalinization or xanthoma cells
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- S100, GFAP
- May have PAS positive needle shaped crystalloids (Hum Pathol 1997;28:304)
Negative stains
Sample pathology report
- Rectosigmoid colon, resection:
- Schwannoma (4.1 cm) (see comment)
- Margins of resection unremarkable.
- Three benign lymph nodes.
- Comment: An immunohistochemical stain for S100 is positive.
Differential diagnosis
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is a common feature of gastrointestinal schwannomas?
- Artifactual cytoplasmic vacuoles
- Dense cellularity and high mitotic rate
- Epicenter in the muscularis mucosae
- Peripheral lymphoid cuff
- Verocay bodies and thick walled vasculature
Board review style answer #1