Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Sites | Clinical features | Case reports | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Hemangioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colontumorangioma.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Uncommon benign vascular proliferation of the colon
Essential features
- Benign vascular proliferation
- Often related to a syndrome
- Typically a cavernous hemangioma (majority) or capillary hemangioma
Sites
- Most common site in large intestine is rectum
- More common in small intestine than large intestine
Clinical features
- Causes bleeding, melena, anemia, rarely intussusception or obstruction
- Patients are often young and may have a syndrome (blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome, Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome, etc.) (Clin Colon Rectal Surg 2011;24:193)
Case reports
- 1 year and 8 year old boys with vascular lesions of the colon (Korean J Pediatr 2014;57:245)
- 26 year old woman with hemangiomas in rectosigmoid colon and other sites (Turk J Gastroenterol 2006;17:308)
Gross description
- Well circumscribed reddish lesion
Microscopic (histologic) description
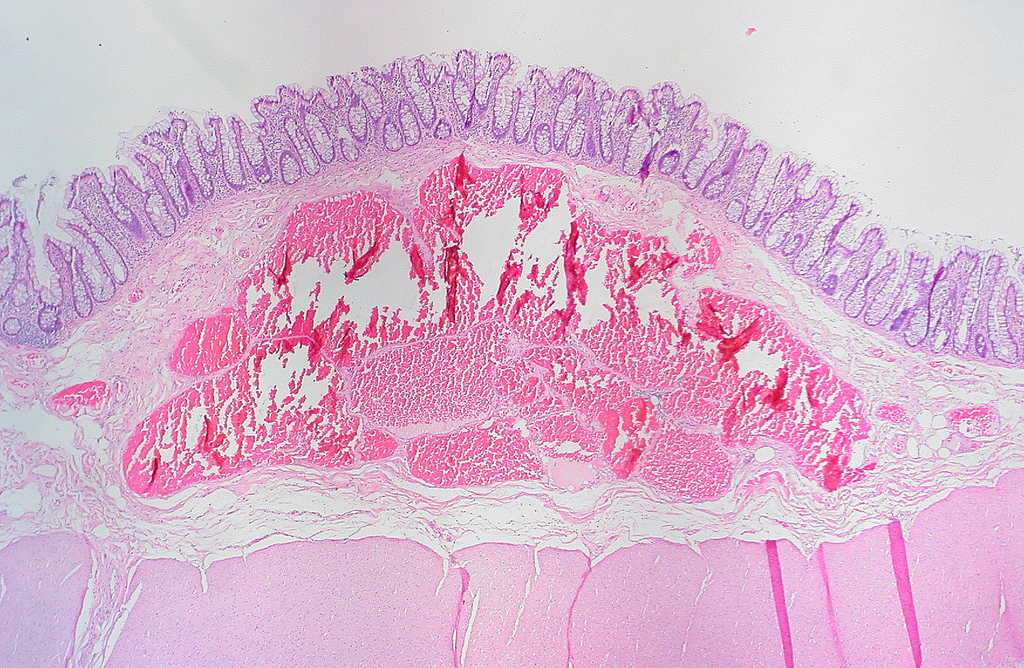
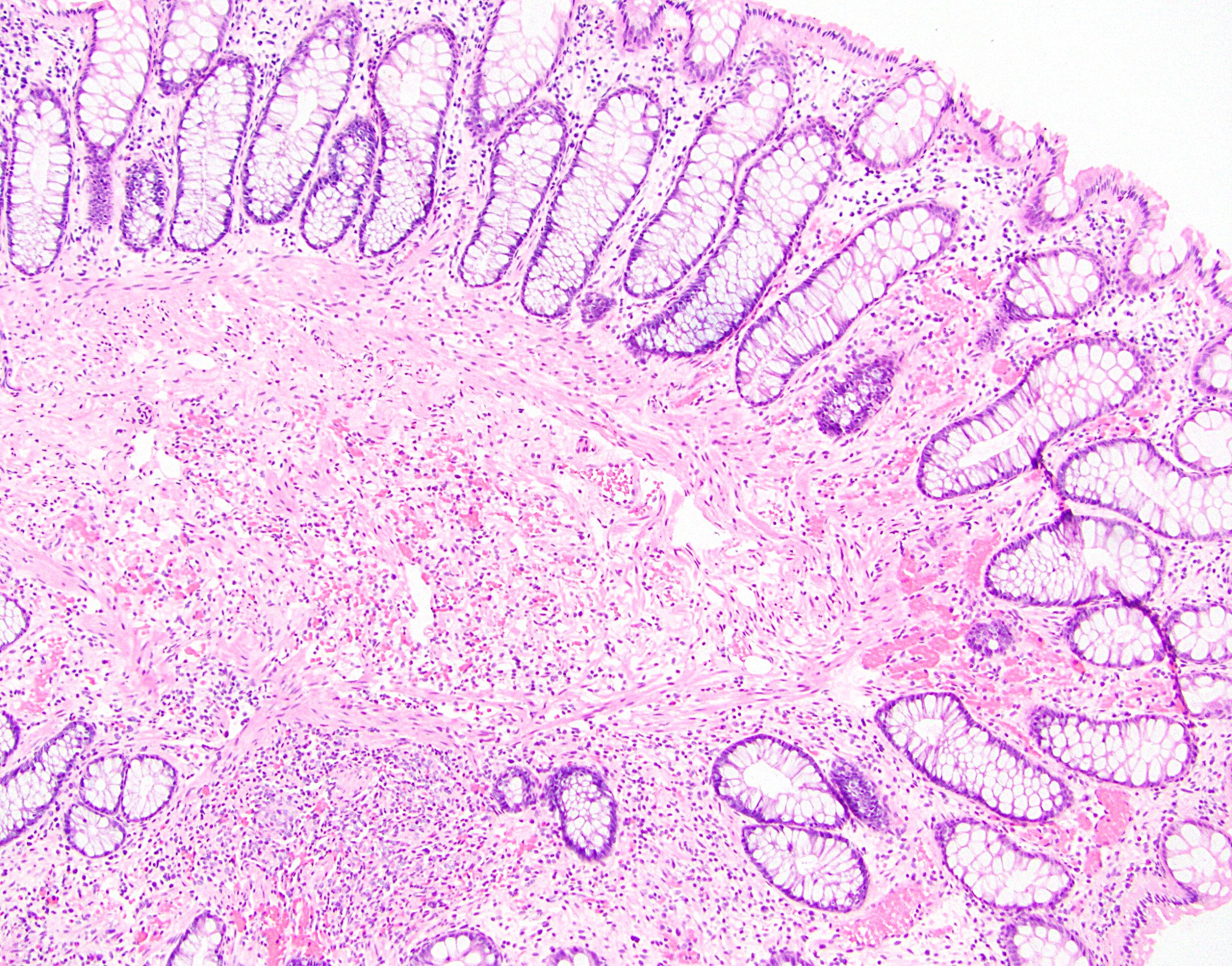
- Cavernous hemangioma: localized or diffuse; blood filled sinus-like spaces with scant connective tissue, variable smooth muscle; may be infiltrative but no other concerning features
- Capillary hemangioma: small, closely packed capillaries, rarely multifocal; no features suggestive of malignancy (Dtsch Med Wochenschr 2004;129:1970)
- Other rare variants with distinctive morphology can occur, such as anastomosing hemangioma (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1761)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Sigmoid colon, resection:
- Segment of colon with submucosal cavernous hemangioma (1.4 cm)
- Margins of resection unremarkable.
- Six benign lymph nodes.
Differential diagnosis
- Arteriovenous malformation:
- Abnormal arteries and veins; distinction from hemangiomas may be difficult
- Angiosarcoma:
- Rare; overtly malignant
- Florid vascular proliferation:
- Linked to intussusception or prolapse; spindled lesion with increased cellularity (Mod Pathol 2001;14:1114)
Board review style question #1
What is the most common subtype of hemangioma encountered in the colon?
- Anastomosing hemangioma
- Capillary hemangioma
- Cavernous hemangioma
- Glomeruloid hemangioma
Board review style answer #1