Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Sites | Clinical features | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Cytology description | Immunohistochemistry & special stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Abdelzaher E. Desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma / ganglioglioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumordesmoplasticinfantileganglioglioma.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Supratentorial superficially located cystic neuroepithelial tumors of infancy characterized by prominent desmoplasia with neoplastic glial component (desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma, DIA) or neoplastic glioneuronal component (desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma, DIG)
- Corresponds to WHO grade 1
- DIA first described in 1982 by Taratuto et al. (J Neurosurg 1987;66:58)
- DIG first described in 1987 by VandenBerg et al.
- Since both lesions have similar radiological and clinical presentation, they are categorized together as desmoplastic infantile astrocytoma / ganglioglioma (DIA / DIG) in the WHO classification
Epidemiology
- Incidence: rare ( < 0.1% of CNS tumors)
- Age and sex:
- Most < 1 year
- Rare in children and young adults (Neuropathology 2005;25:150)
- Male to female ratio of 1.5:1
Sites
- Supratentorial
- Usually frontoparietal
Clinical features
- Rapidly increasing head circumference, hydrocephalus, seizures
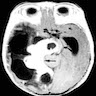
Radiology description
- Supratentorial
- Superficially located
- Large, involves more than one lobe
- Cystic with solid area / mural nodule
- Enhancing
- Desmoplastic area exhibits hypointense signal on T2
Prognostic factors
- Good prognosis
- Rarely, craniospinal seeding or metastases (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1515, Mod Pathol 1997;10:945, Australas Radiol 2005;49:433, Pediatr Blood Cancer 2005;45:986)
- Tumor progression has been reported in incompletely resected tumors or tumors with anaplastic features
Case reports
- 3 1/2 month old boy with mixed conventional and desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma (Mod Pathol 2001;14:720)
Treatment
- Gross total resection
- Chemotherapy if infiltrative or progressive
- Residual disease may not grow and may spontaneously regress (Neurosurgery 2003;53:979)
Gross description
- Large (up to 13 cm), often involves multiple lobes
- Deep macrocystic portion
- Superficial solid leptomeningeal portion, firm to hard, focally attached to overlying dura
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Well delineated from normal brain
- Desmoplastic leptomeningeal component
- Involve the subarachnoid space and extends into Virchow-Robin spaces
- Neoplastic neuroepithelial cells in desmoplastic spindled stroma arranged in fascicular and storiform patterns with pericellular reticulin deposition lending a mesenchymal appearance
- Neoplastic neuroepithelial cells:
- Astrocytic cells:
- Only component in DIA
- Spindled or gemistocytic neoplastic astrocytes
- Neuronal component:
- Seen in DIG in addition to neoplastic astrocytes
- Small ganglion cells
- Uncommonly large ganglion cells or areas resembling ganglioglioma
- Astrocytic cells:
- Immature small cell component (unclear prognostic significance)
- Hypercellular poorly differentiated neuroepithelial cells
- No desmoplasia
- May show mitoses, vascular proliferation or necrosis
- Calcification common, chronic inflammatory cells uncommon
- Exceptionally, frank anaplastic features are encountered (high mitotic rate, vascular proliferation, palisading necrosis and high proliferation index)
Cytology description
- Low cellularity
- Dispersed or variably sized clusters of large neuronal cells with abundant granular cytoplasm, eccentric hyperchromatic nuclei with undulating nuclear membranes and occasional binucleation, prominent nucleoli
- Astroglial cells with smaller cytoplasmic rim, nuclear hyperplasia and more prominent irregularities in nuclear membranes
- May have prominent degenerative changes, foamy macrophages
- No vascular structures (Cytojournal 2005;2:1)
Immunohistochemistry & special stains
- Desmoplastic component: vimentin+, GFAP+, type IV collagen+, reticulin (pericellular pattern), trichrome (stroma)
- Astrocytic cells: GFAP+, S100+
- Neuronal cells: synaptophysin+, NeuN+, neuron specific enolase+
- Poorly differentiated small cells: vimentin+, GFAP+, synaptophysin+
- Proliferation index: < 2% (higher in the poorly differentiated small cell component)
Electron microscopy description
- Astrocytic tumor cells are partly invested by pericellular basal lamina
Differential diagnosis
Additional references