Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Mulone D, Barresi V. Cerebellar liponeurocytoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumorcerebellarliponeurocytoma.html. Accessed April 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Cerebellar liponeurocytoma is a rare, slow growing tumor of the central nervous system with advanced neuronal or neurocytic differentiation, variable glial differentiation and lipoma-like changes
- Classified CNS WHO grade 2
- Typically occurs in the posterior cranial fossa
- To date, nearly 70 cases have been reported
Essential features
- Rare, slow growing tumor with advanced neuronal or neurocytic differentiation and focal lipoma-like changes, typically occurring in the cerebellum
- Classified as CNS WHO grade 2
- Extent of surgical resection is the main prognostic factor
- Histologically composed of monotonous neurocytic cells with rare mitoses and intermingled lipidized cells
- Diffusely positive for neuronal markers syanptophysin, NeuN and MAP2
Terminology
- Lipomatous medulloblastoma (not recommended)
- Lipidized medulloblastoma (not recommended)
- Medullocytoma (not recommended)
- Lipomatous glioneurocytoma (not recommended)
- Lipidized mature neuroectodermal tumor (not recommended)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9506/1 - cerebellar liponeurocytoma
- ICD-11: 2A00.3 & XH2GB0 - central neurocytoma of brain & cerebellar liponeurocytoma
Epidemiology
- Rare tumor, first described in 1978 (Acta Neuropathol 1978;41:261)
- ~70 cases reported (World Neurosurg 2018;120:214)
- No significant sex predilection (World Neurosurg 2018;120:214)
- Mainly affects adults between the third and fifth decade, with a mean age of 46 years (World Neurosurg 2018;120:214, Neurosurg Rev 2022;45:1747)
- Rarely reported in children (Front Oncol 2021;11:759581, Acta Neuropathol 2005;109:346, Rare Tumors 2016;8:6240)
Sites
- Mostly located in the cerebellar hemispheres (World Neurosurg 2018;120:214)
- More rarely located in the vermis, paravermian region, fourth ventricle or cerebellopontine angle (World Neurosurg 2018;120:214, Neuropathology 2022;42:169, J Neurooncol 2012;108:513)
Pathophysiology
- Supposed to originate from GABAergic neurons in the cerebellar ventricular zone, which may aberrantly differentiate into adipocyte-like tumor cells (J Neurooncol 2012;108:513)
Etiology
- Risk factors are unknown, though a possible inheritable predisposition was suggested (J Neurosurg 2016;125:57, J Clin Neurosci 2016;32:154)
Clinical features
- Headache or other symptoms and signs of raised intracranial pressure (Neuropathology 2022;42:169, Neurochirurgie 2021;67:579)
- Cerebellar signs, including ataxia or disturbed gait (Oncol Lett 2016;11:1061, Neurochirurgie 2021;67:579)
Diagnosis
- Based on imaging (computerized tomography, magnetic resonance) / biopsy / resection specimen
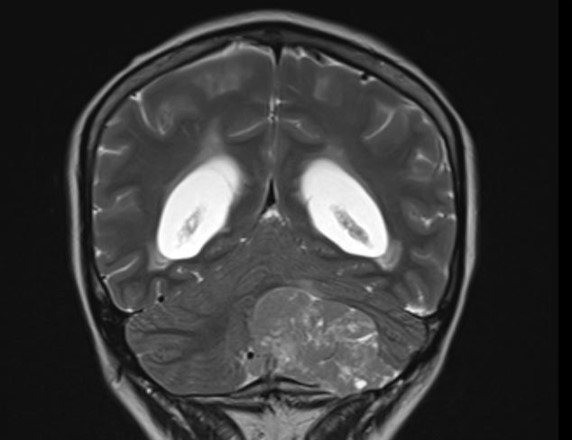
Radiology description
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan: hypodense or isodense solid mass, with focal areas of hypoattenuation corresponding to high fat density (World Neurosurg 2018;120:214, J Neurooncol 2012;108:513)
- On magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), the tumor is (World Neurosurg 2018;120:214, Neuropathology 2022;42:169)
- Well circumscribed
- Hypointense or isointense in T1 weighted sequences, with focal hyperintensity, corresponding to lipidized foci
- Hyperintense in T2 weighted sequences
- Heterogeneously contrast enhanced in most cases
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Progression free survival rates: 92.7%, 78.0% and 23.8% at 1, 5 and 10 years, respectively (Neurosurg Rev 2022;45:1747)
- Higher recurrence risk associated with incomplete surgical resection and high Ki67 (> 10%) labeling index (World Neurosurg 2018;120:214, World Neurosurg 2018;112:18, Neurosurg Rev 2022;45:1747)
- Adjuvant radiotherapy reduces the risk of recurrence after partial surgical resection (World Neurosurg 2018;120:214)
- No recurrences were observed in 6 patients receiving complete surgical resection of the tumor and adjuvant radiotherapy (World Neurosurg 2018;120:214)
Case reports
- 5 year old boy with a mass located in the cerebellar vermis and fourth ventricle (Front Oncol 2021;11:759581)
- 39 year old man with a mass in the right cerebellar hemisphere (J Med Case Rep 2018;12:170)
- 50 year old woman with a tumor in the left cerebellar hemisphere (Int J Surg Case Rep 2021;82:105937)
- 55 year old man with a tumor in the cerebellar vermis (J Neurosci Rural Pract 2019;10:360)
Treatment
- Surgery (Neurosurg Rev 2022;45:1747, World Neurosurg 2018;120:214)
- Adjuvant radiotherapy is controversial (Neurosurg Rev 2022;45:1747, World Neurosurg 2018;120:214)
Gross description
- Well circumscribed, soft, gray-pink tumor (Neurosurg Rev 2022;45:1747)
- It may lack clear demarcation and be partly attached to the surrounding tissue in some cases (World Neurosurg 2018;112:18)
Frozen section description
- Tumor composed of small, roundish, uniform cells (World Neurosurg 2018;112:18)
- Infrequent mitoses
- Microvascular proliferation and necrosis are typically absent
- Neuropil matrix around vessels may simulate perivascular pseudorosettes of ependymoma
- Lipid accumulation can be demonstrated using oil red O staining (Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 1993;19:95)
Frozen section images
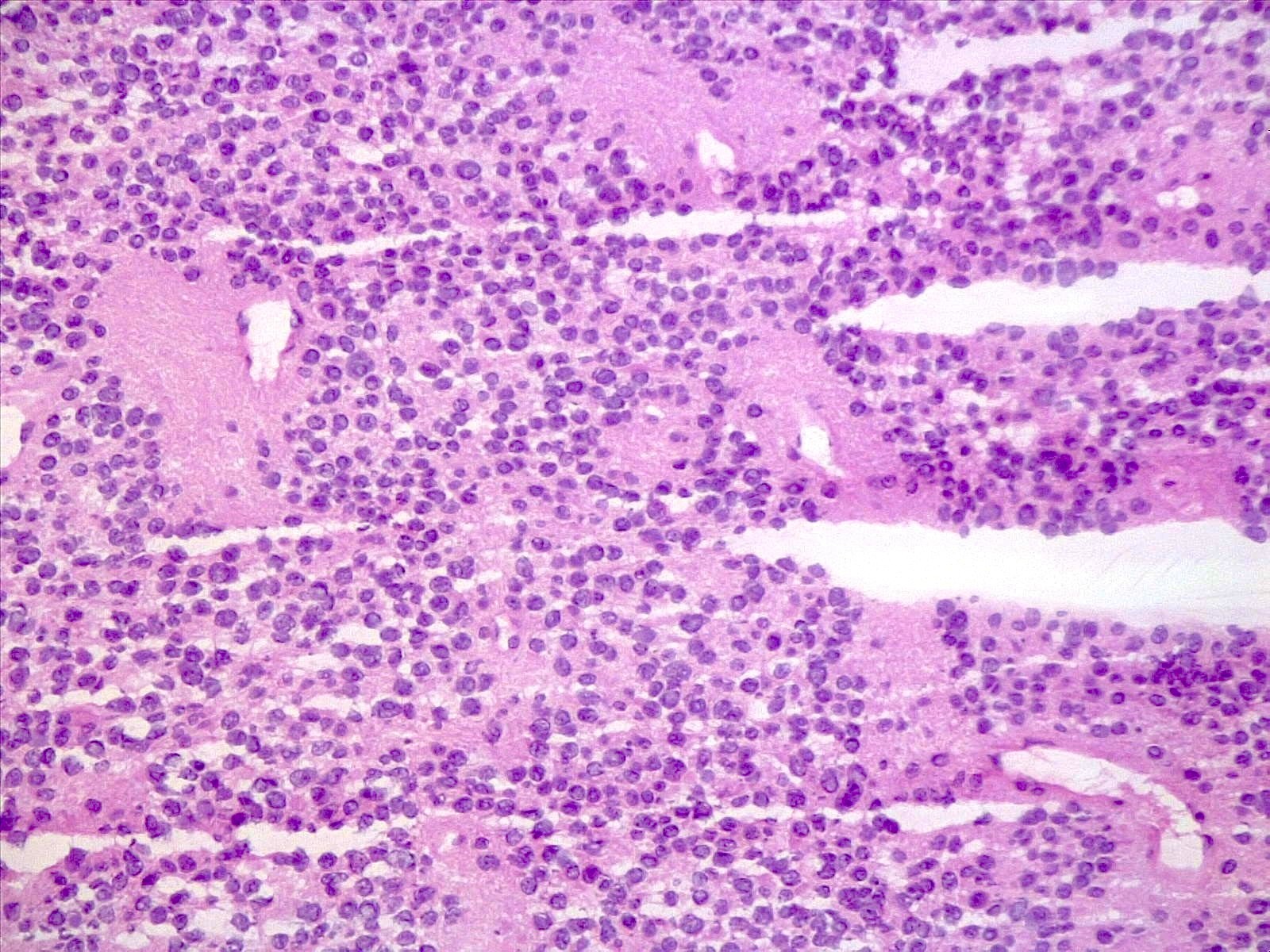
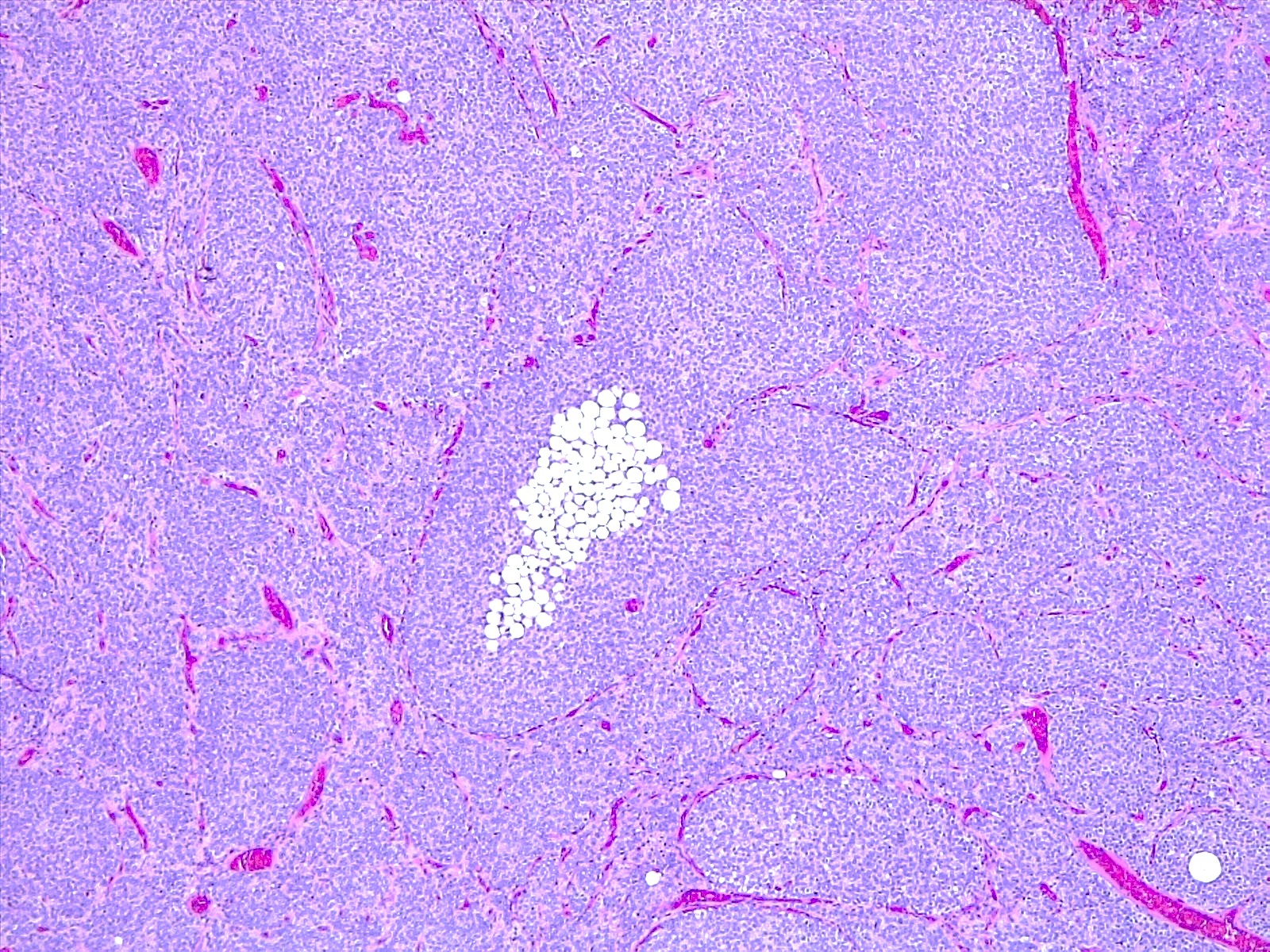
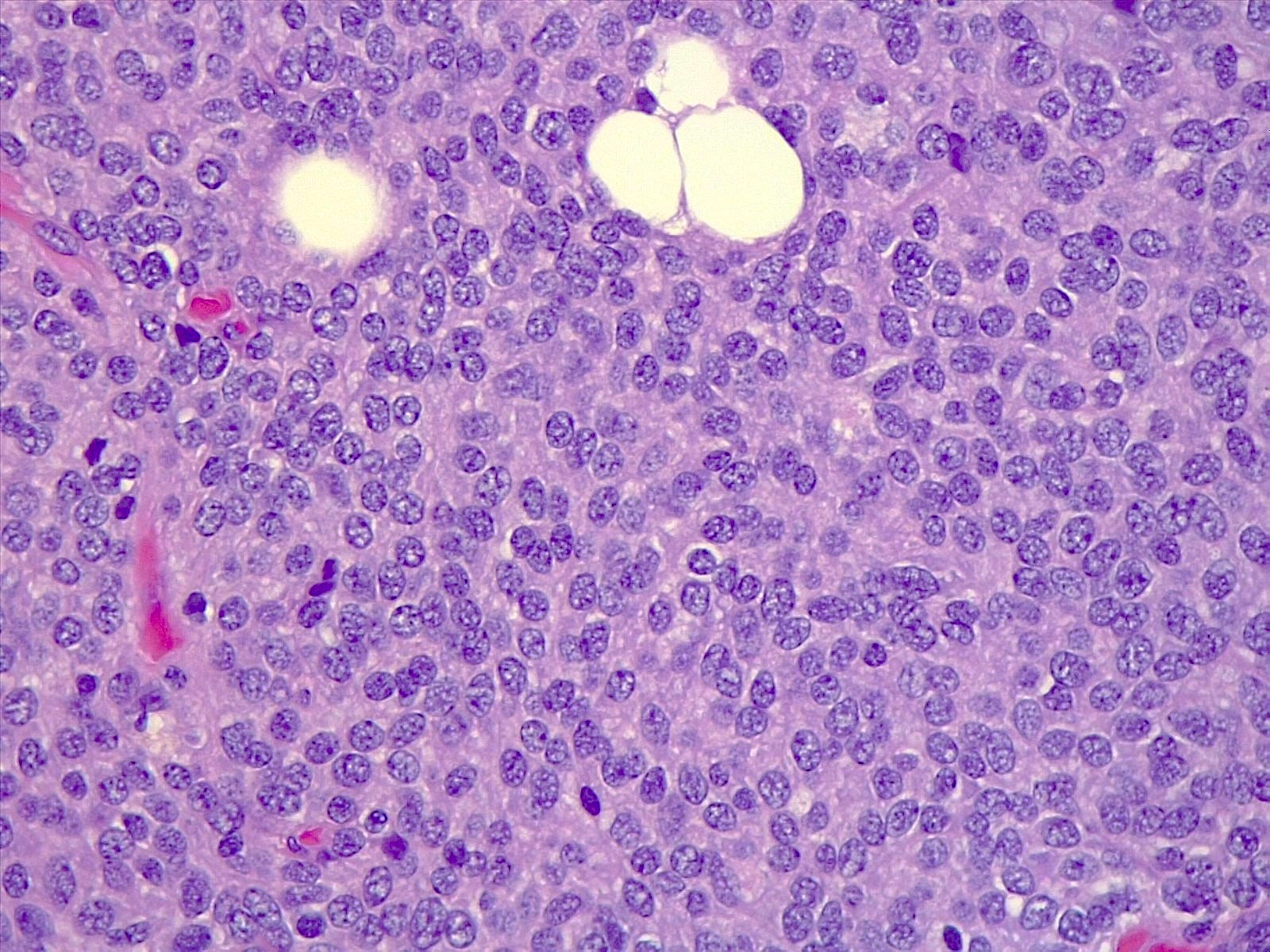
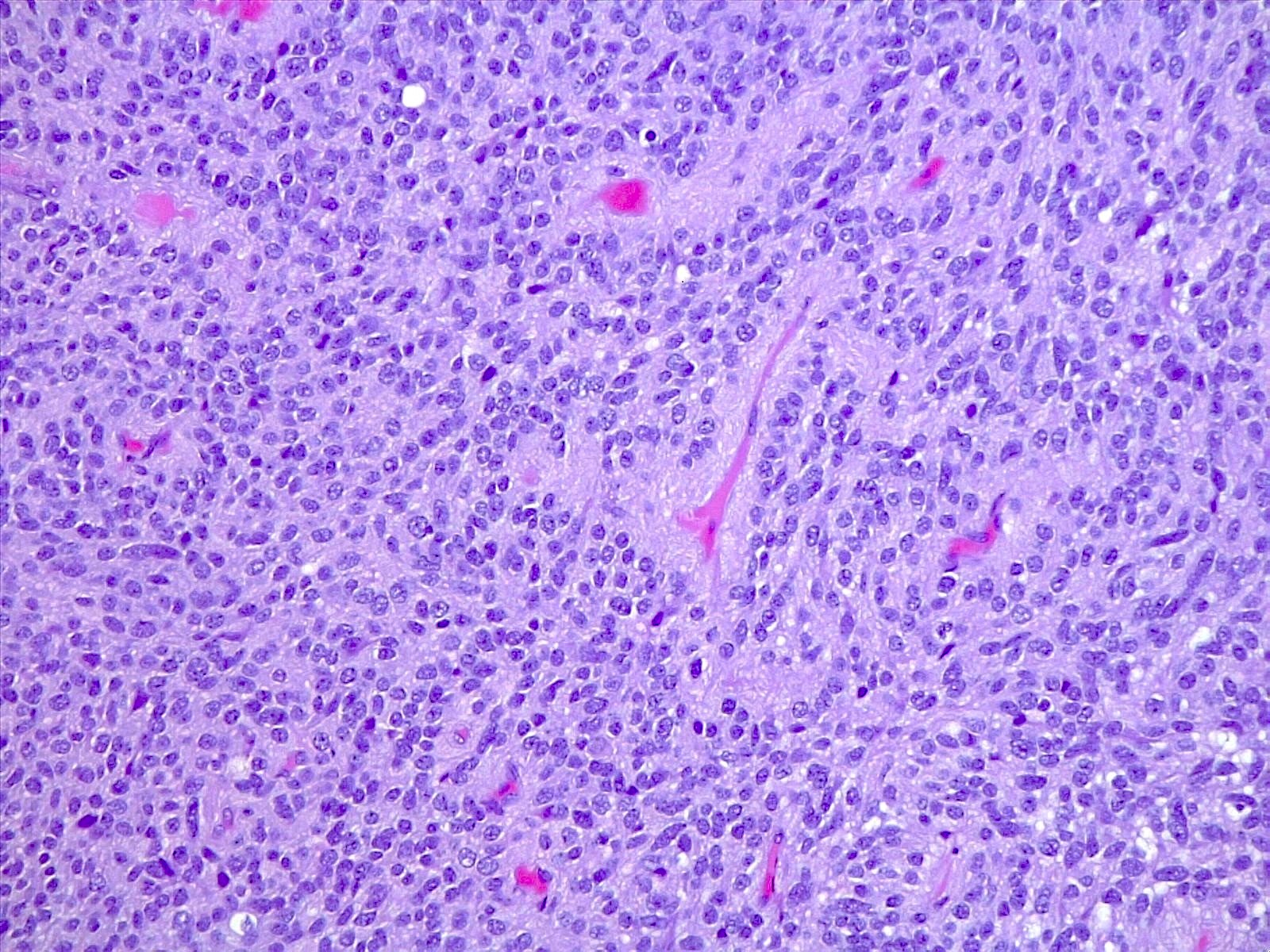
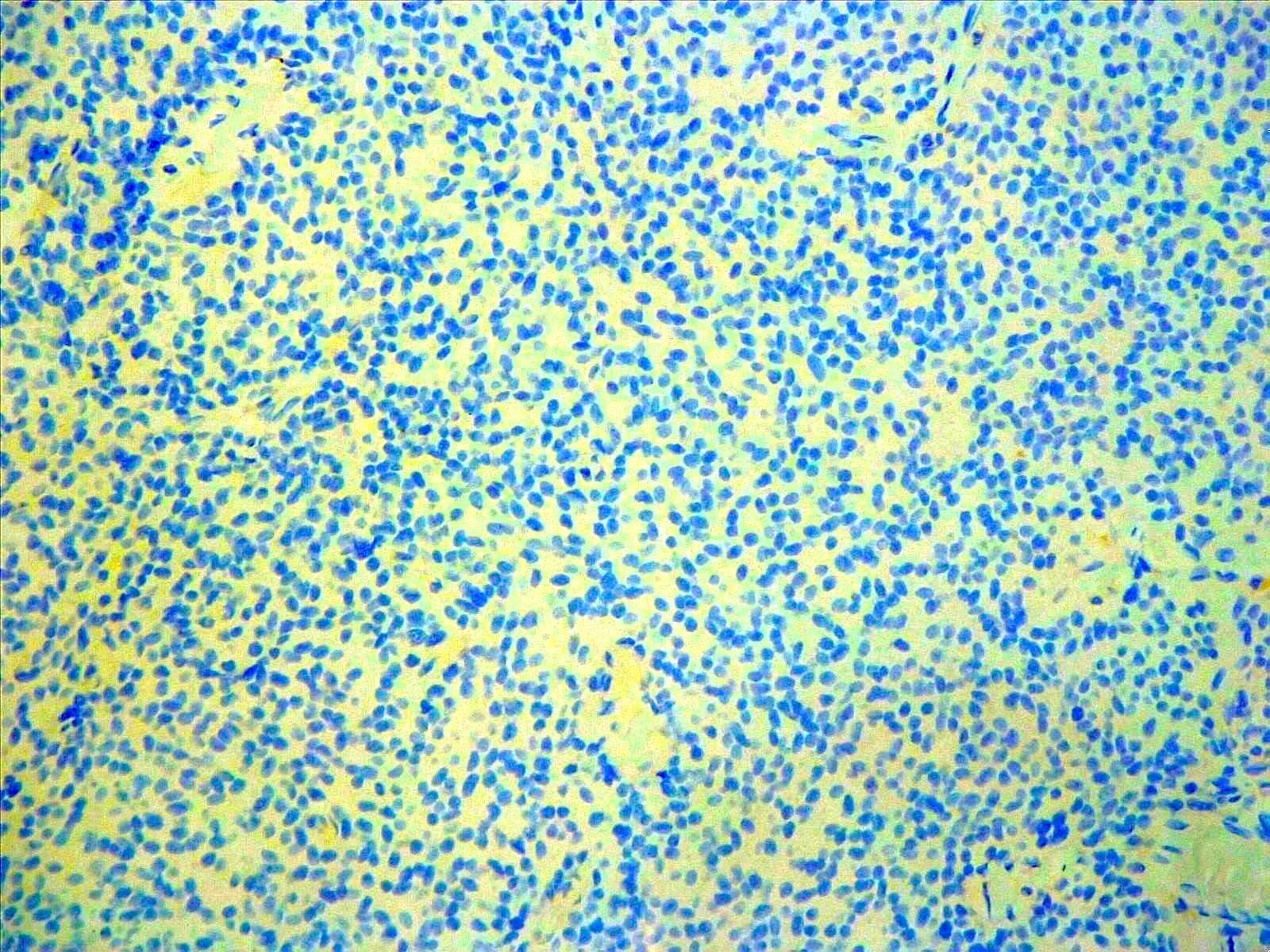
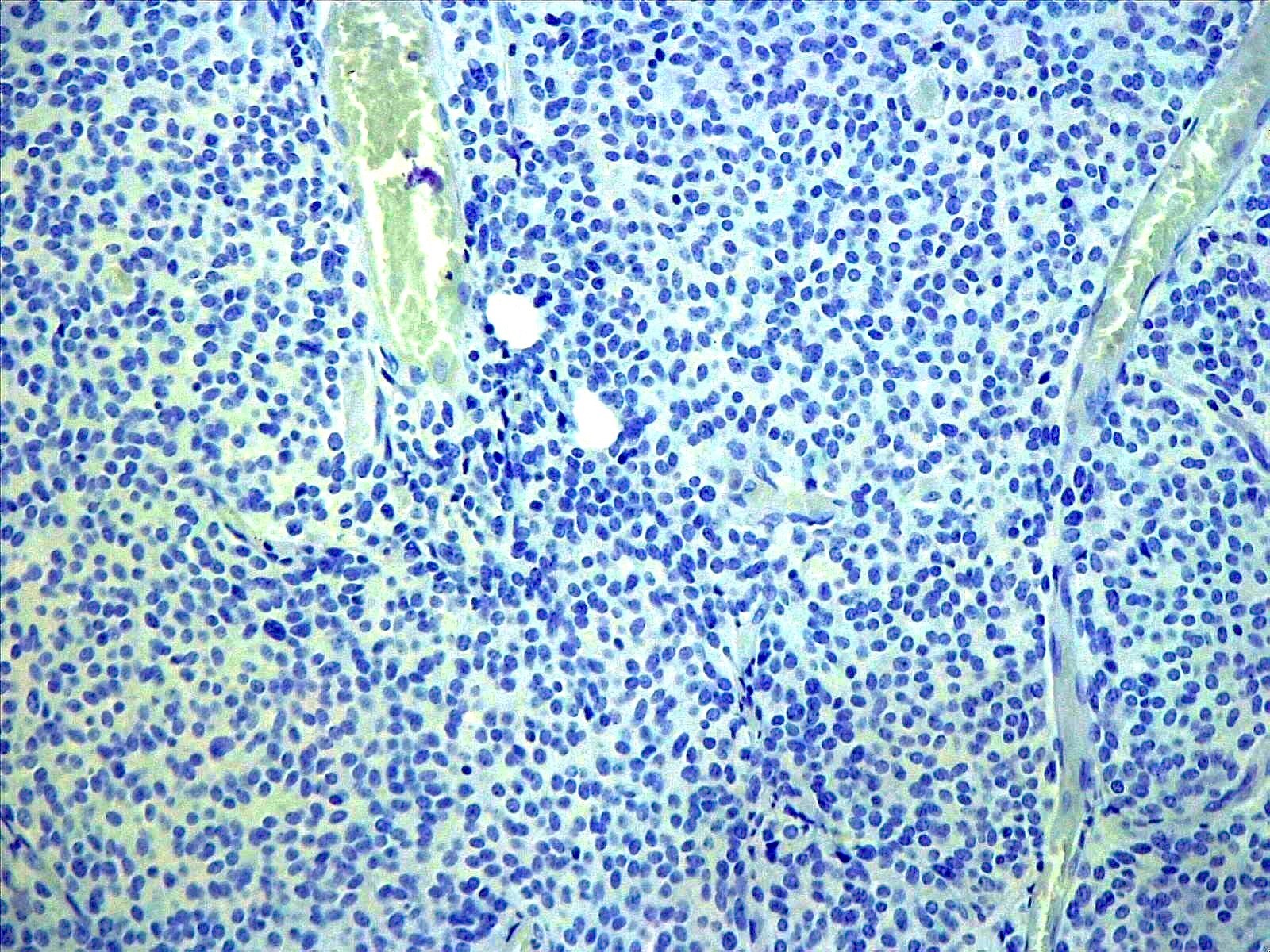
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Tumor composed of small and uniform neurocytic cells with round to oval nuclei, clear cytoplasm and indistinct cell membrane, arranged in sheets or lobules (Front Oncol 2021;11:759581, Neuropathology 2022;42:169, Brain Tumor Pathol 2017;34:28)
- Presence of lipidized cells in groups or scattered throughout the tumor (Front Oncol 2021;11:759581, Neuropathology 2022;42:169, Brain Tumor Pathol 2017;34:28, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:965)
- Few mitoses
- Absent necrosis and microvascular proliferation
- Lipidized cells may be reduced or absent in recurrent tumors
Microscopic (histologic) images
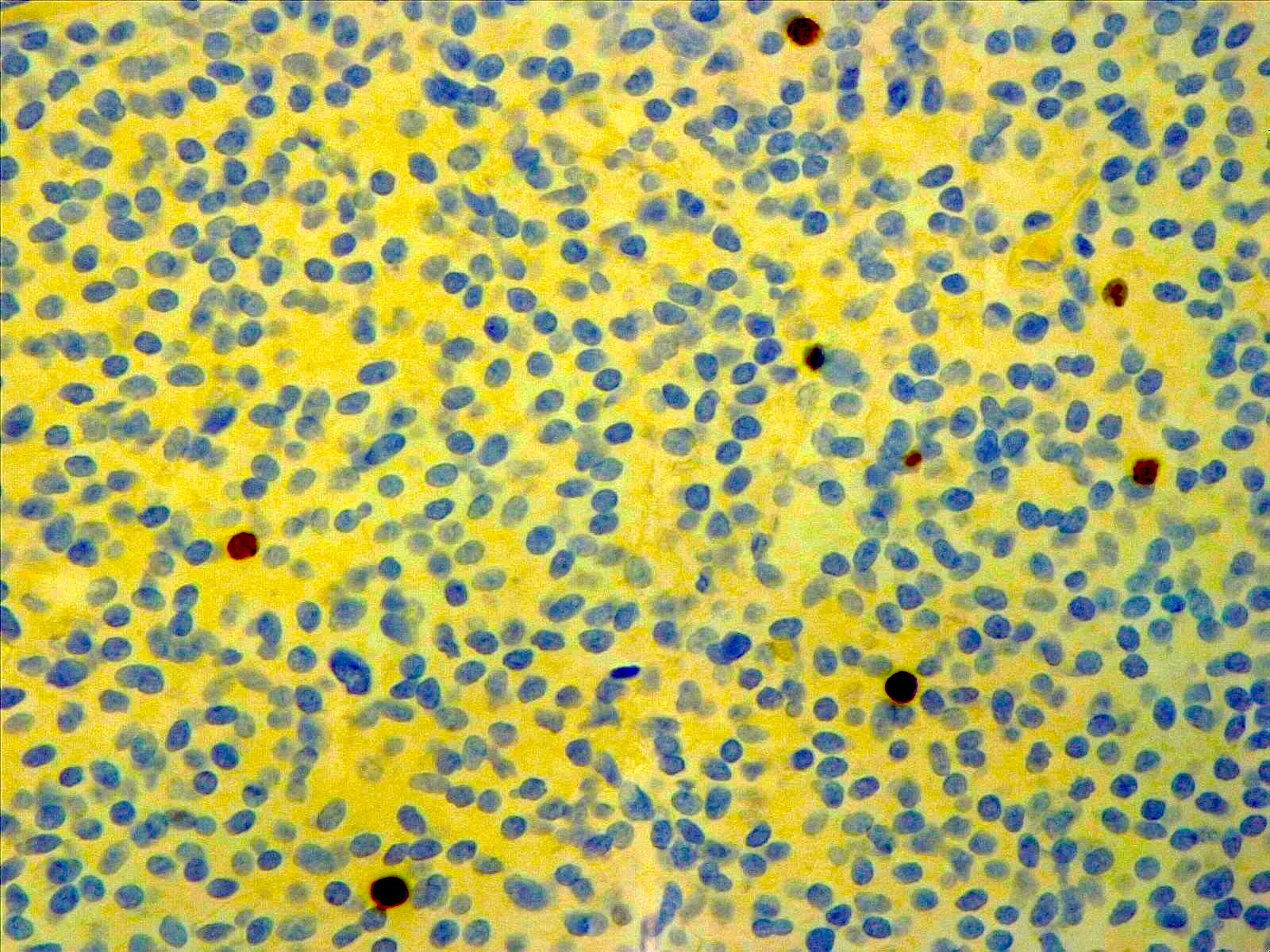
Cytology description
- Small, uniform cells with rounded to oval nuclei showing salt and pepper chromatin and scant cytoplasm
- Some cells show a single, large cytoplasmic vacuole displacing the nucleus to the periphery of the cell, similar to adipocytes (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:965)
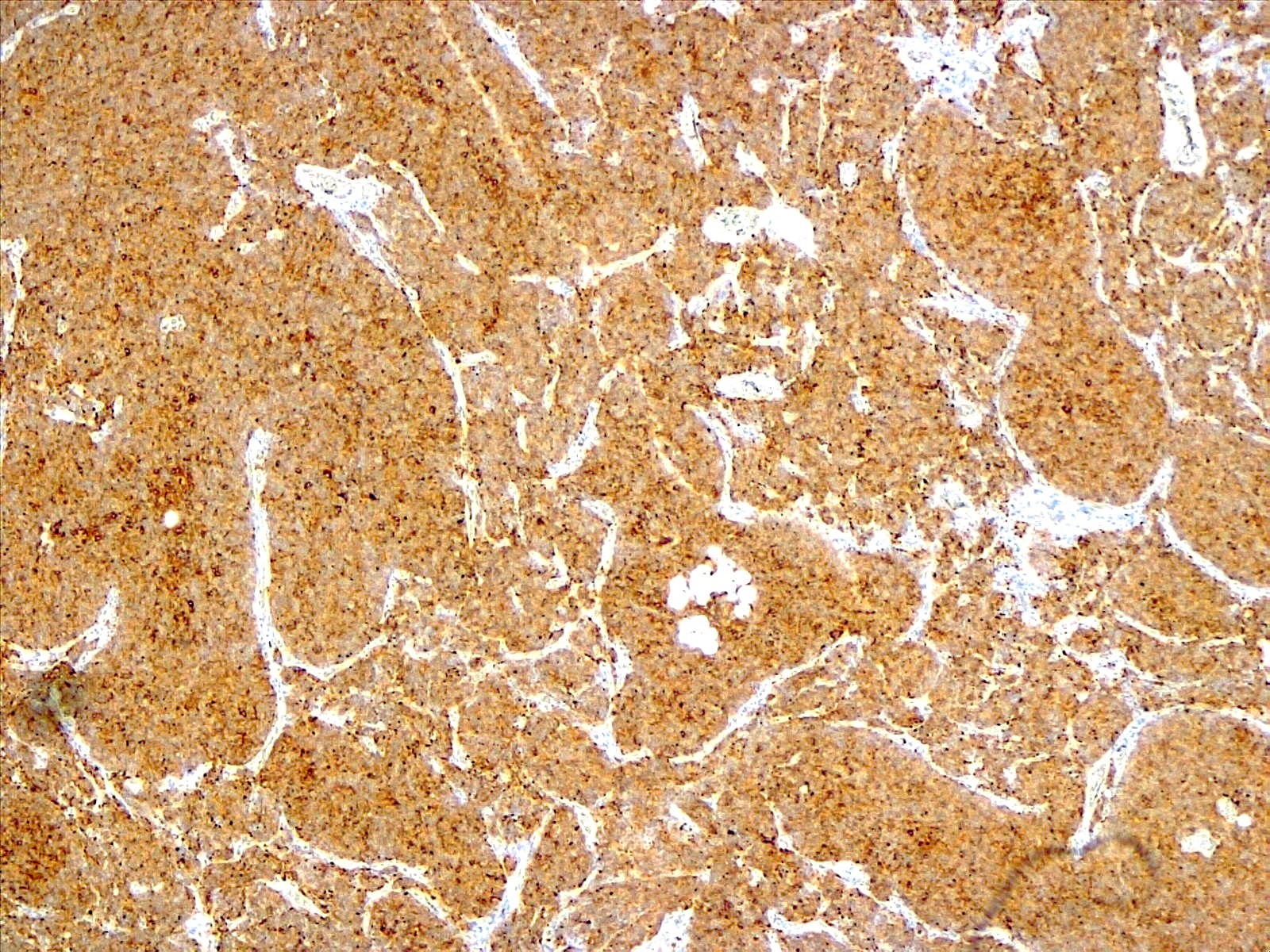
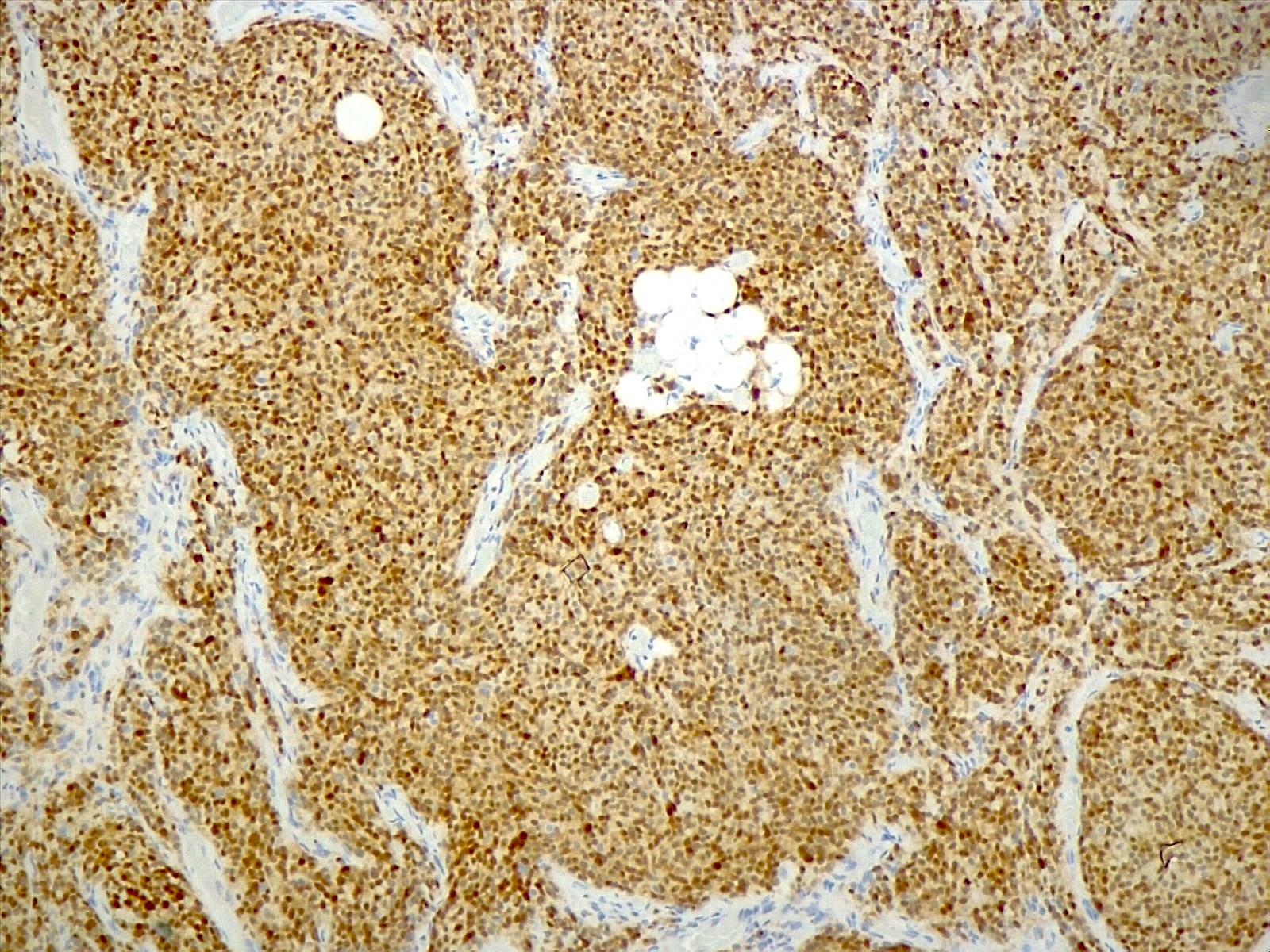
Positive stains
- Synaptophysin (~98%) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:965, World Neurosurg 2018;120:214)
- MAP2 (100%) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:965, World Neurosurg 2018;120:214)
- NSE (100%%) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:965, World Neurosurg 2018;120:214)
- NeuN (100%) (Neuropathology 2022;42:169)
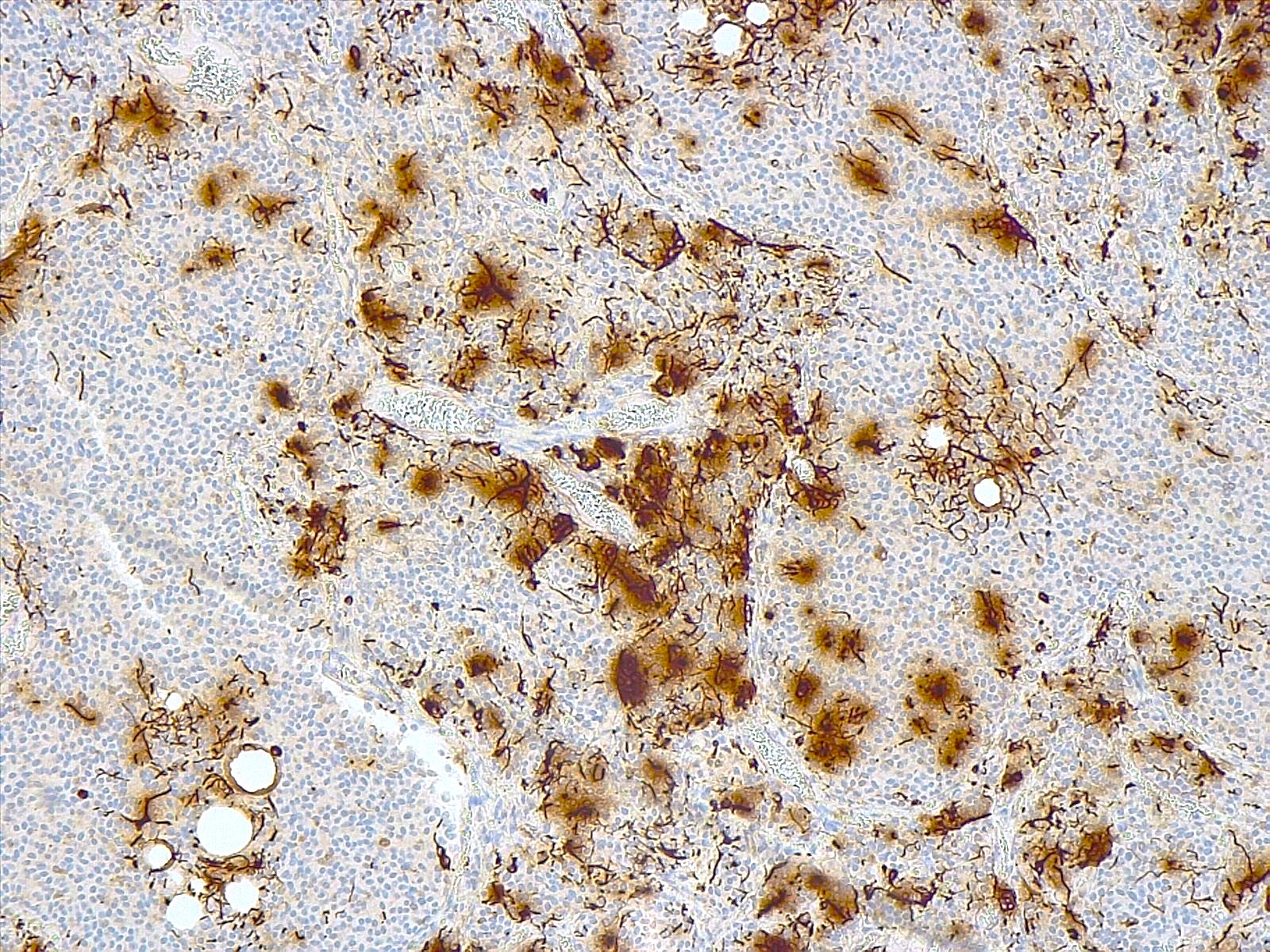
- GFAP (~85%) and S100 (~82%): expressed by reactive astrocytes and few tumor cells (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:965, World Neurosurg 2018;120:214)
- Chromogranin A (~55%) (Neuropathology 2022;42:169, World Neurosurg 2018;120:214)
- Ki67 (MIB1): usually 1 - 3% (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:965)
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Lipidized cells display large, nonmembrane bound lipid deposits within the cytoplasm and retain features of neuronal differentiation, including dense core neurosecretory granules (J Neurosurg 2001;95:700, Ultrastruct Pathol 2015;39:419)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- TP53 missense mutations in 20% of cases (Brain Pathol 2004;14:281)
- Lack of isochromosome 17 or mutations in APC, CTNNB and PTCH, which helps rule out medulloblastoma (Brain Pathol 2004;14:281)
- Recurrent focal losses of chromosomes 2p and 14 (Acta Neuropathol 2018;136:181)
- Unique DNA methylation profile (Clin Neuropathol 2022;41:12)
Sample pathology report
- Cerebellum, tumor resection:
- Cerebellar liponeurocytoma, CNS WHO grade 2 (see comment)
- Comment: The tumor is composed of monotonous neurocytic cells, with round nuclei, small nucleoli and scant cytoplasm, disposed in a diffuse growth pattern and showing foci of lipidized cells. Only scattered mitoses are present. Necrosis is absent. On immunohistochemistry, tumor cells are diffusely positive for synaptophysin and MAP2 and negative for Olig2 and EMA. Ki67 labeling index is < 5%.
Differential diagnosis
- Medulloblastoma:
- Mainly affects children and young adults
- Lacks lipidized cells
- Shows high mitotic index and Ki67 labeling index
- May show necrosis
- May occasionally have foamy macrophages that mimic lipomatous differentiation of cerebellar liponeurocytoma
- Classic subtype is composed of small blue round cells with hyperchromatic nuclei of various shapes
- Desmoplastic / nodular subtype features reticulin free zones surrounded by densely packed, poorly differentiated, highly proliferative cells with moderately pleomorphic nuclei
- Large / anaplastic subtype is composed of markedly pleomorphic cells
- Harbors isochromosome 17q
- May harbor PTCH, CTNNB and APC mutations
- Clear cell ependymoma:
- Shows perivascular pseudorosettes and rosettes
- Lacks lipidized cells
- Positive for EMA (dot-like)
- Diffusely positive for GFAP
- Negative for synaptophysin
- Oligodendroglioma, IDH mutant and 1p / 19q codeleted:
- Rare in the posterior fossa
- Lacks lipidized cells
- Positive for Olig2
- Negative for synaptophysin
- IDH1 / 2 mutated
- 1p / 19q codeleted
Board review style question #1
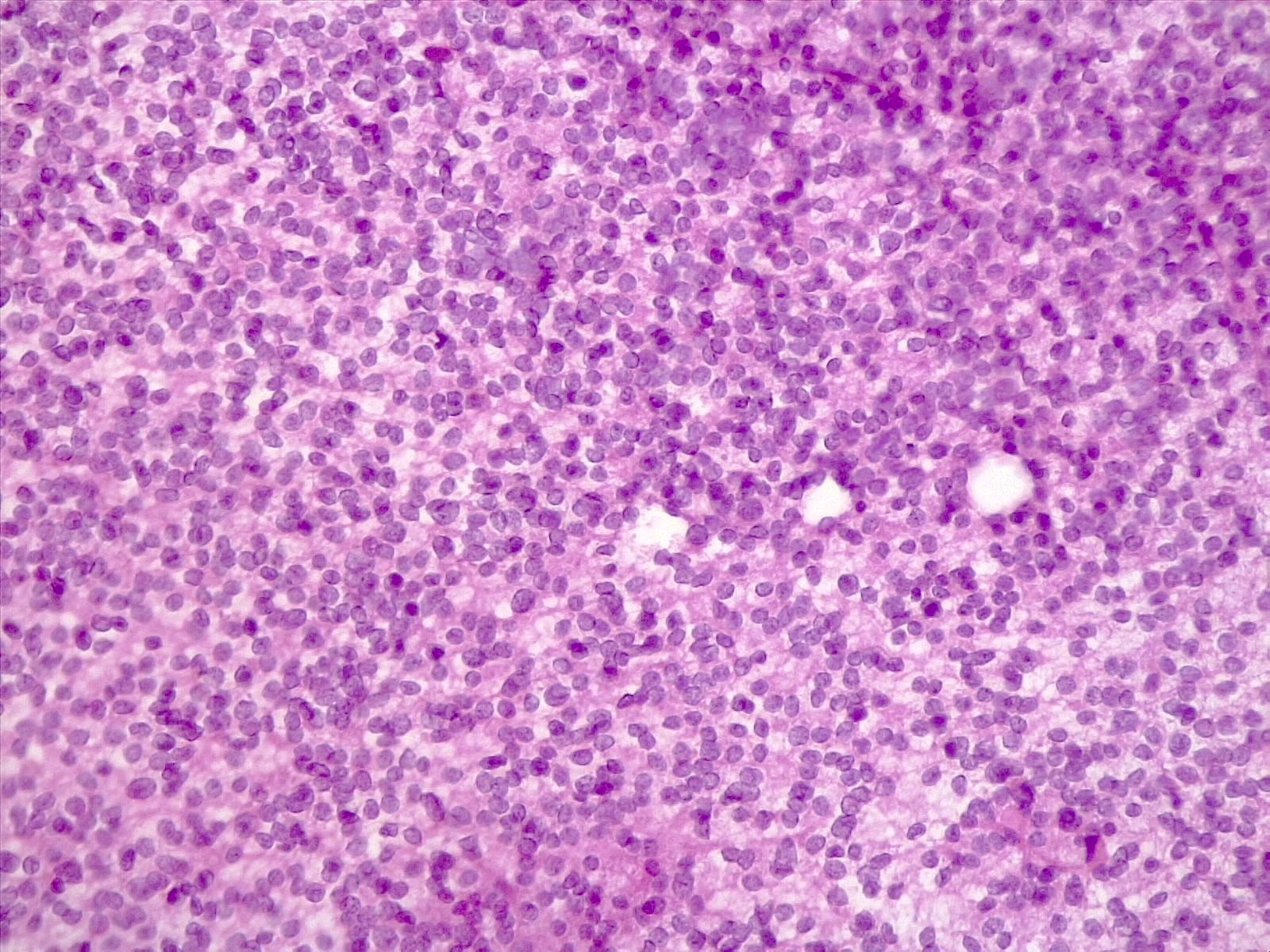
The tumor shown above was found in the left cerebellar hemisphere of a 45 year old woman. Only rare mitoses are present. It shows diffuse immunostaining for synaptophysin, focal immunostaining for GFAP and is negative for Olig2 and EMA. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Cerebellar liponeurocytoma
- Ependymoma
- Medulloblastoma
- Oligodendroglioma
Board review style answer #1
A. Cerebellar liponeurocytoma. This tumor is by definition located in the cerebellum. It is composed of small neurocytic cells with focal lipidized cells, is positive for synaptophysin and has a low mitotic index. Answer C is incorrect because medulloblastoma is not characterized by lipidized cells and it has a high mitotic index. Answer B is incorrect because ependymoma is GFAP positive and features EMA dot-like staining. Answer D is incorrect because oligodendroglioma is diffusely positive for Olig2 and negative for synaptophysin.
Comment Here
Reference: Cerebellar liponeurocytoma
Comment Here
Reference: Cerebellar liponeurocytoma