Table of Contents
Definition / general | Sites | Pathophysiology / etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis / laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Gyure K.A. Carbon monoxide injury. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnscarbonmonoxide.html. Accessed December 4th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas resulting from incomplete combustion of fossil fuels or tobacco and is the leading cause of death by poisoning in the US (Centers for Disease Control: Carbon Monoxide Poisoning)
Sites
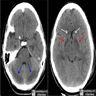
- Affects globus pallidus and white matter
Pathophysiology / etiology
- Carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin, forming carboxyhemoglobin
- This causes a decrease in the oxygen carrying capacity of the blood, leading to tissue hypoxia
- Sources of exposure to carbon monoxide include faulty or inadequately ventilated heating sources and engine exhaust
- Exposure is most commonly accidental or due to a suicide attempt
Clinical features
- Acute: headache, myalgia, dizziness, psychological impairment
- Chronic: delayed neuropsychiatric syndrome ranging from subtle personality changes or mild cognitive deficit to severe dementia, psychosis, parkinsonism
Diagnosis / laboratory
- Measurement of carboxyhemoglobin levels
Radiology description
- High signal intensity in globus pallidus bilaterally on T2 weighted MR images
- Restricted diffusion in white matter (diffusion weighted imaging [DWI], a form of MR imaging)
Case reports
- 23 year old woman and 34 year old man with delayed neuropsychiatric sequelae caused by exposure to carbon monoxide (Prim Care Companion CNS Disord 2012;14:11l01316)
- 39 year old woman with fatigue, headache, memory lapse (N Engl J Med 2009;360:1217)
- 57 year old woman with pallidoreticular lesion (Acta Neurol Taiwan 2012;21:44)
Treatment
- Administration of hyperbaric oxygen
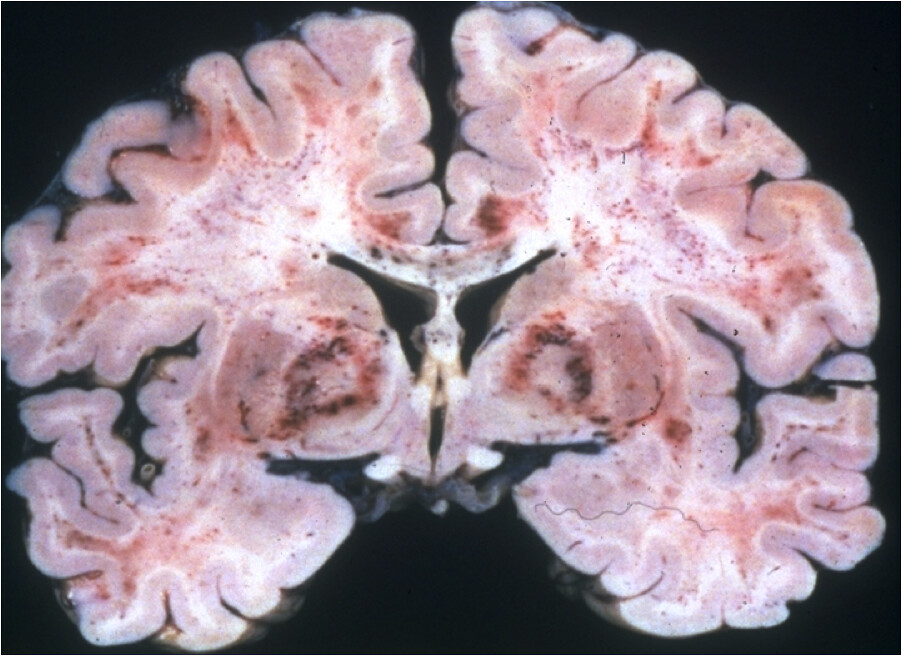
Gross description
- Acute: cherry red discoloration
- Chronic: bilateral necrosis of globus pallidus, demyelination of white matter tracts (Wikipedia: Grinker Myelinopathy)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Foci of ischemic or hemorrhagic necrosis in globus pallidus (Wikipedia: Globus Pallidus)
- Perivascular foci of demyelination in deep white matter with sparing of arcuate fibers
Differential diagnosis
- Methanol intoxication: bilateral necrosis of putamen
- Other causes of hypoxia / ischemia