Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Laboratory | Calcitonin stimulation test | Videos | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Srichomkwun P. Calcitonin. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/chemistrycalcitonin.html. Accessed April 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
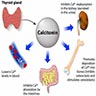
- Polypeptide hormone produced by parafollicular cells (C cells) of the thyroid gland
- Controls serum calcium level; specifically, reduces blood calcium, opposing the effects of parathyroid hormone
Essential features
- Calcitonin is a polypeptide hormone produced by parafollicular cells (C cells) of the thyroid gland to control the calcium level
- Calcitonin is a sensitive and specific tumor marker for diagnosis and follow up of C cell disorder, including C cell hyperplasia (CCH) and medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC)
- Serum calcitonin can be falsely elevated in several conditions
- Calcitonin stimulation tests may be used when the basal calcitonin level is indeterminate
Terminology
- Also known as thyrocalcitonin
Pathophysiology
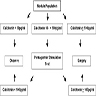
- Calcitonin (32 amino acids) is a polypeptide produced almost exclusively by parafollicular C cells of the thyroid gland
- Calcitonin results from cleavage and posttranslational processing of procalcitonin (116 amino acids, see Diagram 1), a precursor peptide derived from preprocalcitonin (141 amino acids)
- Secretion of calcitonin is stimulated by an increase in serum calcium and gastrin / pentagastrin
- Function
- Calcitonin reduces calcium level in the blood
- Major effect: inhibits osteoclasts from resorbing bone
- Minor effect: inhibits renal tubular cell and intestine from reabsorption of calcium
- Procalcitonin is a marker of systemic inflammation and can be used as a diagnostic marker of sepsis and antibiotic therapy (J Intensive Care 2017;5:51)
- See Diagram 2
- Calcitonin reduces calcium level in the blood
Diagrams / tables
Laboratory
- Immunochemiluminometric, 2 site, 2 steps assay that is highly sensitive and specific for monomeric calcitonin
Indications
- A sensitive and specific tumor marker for diagnosis and follow up of C cell disorders, including medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) and C cell hyperplasia (CCH)
- Basal serum calcitonin correlates well with tumor size and extent of metastasis of MTC (Thyroid 2015:25:567)
- To detect the presence of residual disease, a calcitonin level should be checked 3 to 6 months after the initial operation (total thyroidectomy)
- Calcitonin doubling time can be used as a prognostic factor (Clin Endocrinol 2010;72:534)
- If the doubling time is longer than 24 months, the 5 and 10 year survival rates are 100% and 100%, respectively
- When the doubling time is less than 6 months, the 5 and 10 year survival rates are 23% and 15%, respectively
- Calcitonin doubling time calculator
- Calcitonin doubling time can be used as a prognostic factor (Clin Endocrinol 2010;72:534)
- Calcitonin measurement in fine needle aspirate (FNA) washouts of thyroid nodule or suspicious neck lymph node is an additional tool if FNA biopsy findings are inconclusive (Clin Endocrinol 2014;80:135)
Limitations
- Calcitonin negative MTC (nonsecretory MTC) is rare and mostly occurs in sporadic MTC (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2016;142:2023)
- Despite the low or undetectable calcitonin serum level, many of these cases show tissue expression of calcitonin or its precursor by immunostaining or ISH (BMC Endocr Disord 2019;19:45)
- Serum calcitonin can be falsely elevated in several conditions, including chronic renal failure, autoimmune thyroiditis, large cell lung cancers, prostate cancer, mastocytosis, gastrointestinal and pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors, hyperparathyroidism and on proton pump inhibitor drugs treatment (Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2017;46:631)
- Heterophile antibodies can cause falsely elevated serum calcitonin levels (Clin Chem 2005;51:208)
- Owing to variability in calcitonin measurements among different commercial assays, individual patient samples should be evaluated using the same assay whenever possible
- Different assays may use antisera that recognize different epitopes of the calcitonin molecule
Reference ranges
- Gender differences and age related changes in normal calcitonin level exist but no significant ethnic differences observed
- Adults
- Males: < 19 ng/L
- Females: < 14 ng/L
- Children: (Clin Chem 2004;50:1828)
- < 6 months: < 40 ng/L
- 6 months to 3 years: < 15 ng/L
- Older children same as adults
Conversion factor
- Multiply by 0.293 to convert from ng/L to pmol/L
Interpretation
- Screening or diagnosis of MTC
- < 10 ng/L: normal
- 10 - 100 ng/L: indeterminate (need calcitonin stimulation test)
- > 100 ng/L: suspected MTC (see Diagram 3)
- Follow up monitoring and prognostic assessment
- < 10 ng/L: no residual tumor tissue
- 10 - 150 ng/L: possible local disease (i.e. neck)
- > 150 ng/l: possible distant metastases (see Diagram 4)
- Reference: Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2009;5:35
Calcitonin stimulation test
Indications
Methodology
Interpretation
Adverse effects
- Early diagnosis of neoplastic CCH or micro MTC in RET mutation carriers
- Differentiation MTC from CCH, the preoperative recognition of which should avoid unnecessary thyroidectomies
- Identifying the possible coexistence of nonthyroidal neuroendocrine tumors of the foregut, pancreas, prostate and lung that can be distinguished from a C cell disease by the absence of response to the stimulation test
- Reference: J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2014;99:1656
Methodology
- 2 ways to stimulate calcitonin secretion for diagnostic testing:
- Calcium stimulation test: give 2.5 mg of elemental calcium/kg bodyweight of 10% calcium gluconate (1 ml = 9 elemental calcium) IV at rate of 5 ml/min for a minimum of 3 minutes
- Pentagastrin stimulation test: give 0.5 μg/kg body weight of pentagastrin IV for 10 seconds (pentagastrin is now unavailable in many countries)
- Blood is taken at time 0, 2, 5 and 10 or 15 minutes after administration of stimulants to determine calcitonin levels (see Diagram 5)
Interpretation
- Calcium stimulation test and pentagastrin stimulation test show similar diagnostic value in MTC after thyroidectomy (Neuro Endocrinol Lett 2016;37:485)
- Peak stimulated calcitonin (Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2009;5:35)
- < 10 ng/L: absence of C cell disease
- 10 - 100 ng/L: indeterminate (probable false positive result)
- 101 - 500 ng/L: probable CCH
- 501 - 1,000 ng/L: probable MTC
- > 1,000 ng/L: MTC
Adverse effects
- Nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramping, urgency to micturate, warm feeling, altered gustatory sensation, extremity or facial paresthesia, tachycardia, bradycardia, substernal discomfort and dizziness (Endocrine 2014;46:549)
- Testing is contraindicated in patients older than 60 years old and those with hypertension or coronary artery disease
- Calcium stimulation test is better tolerated than pentagastrin stimulation test
Videos
Regulation of blood calcium via PTH and calcitonin
Customizing imaging based on calcitonin levels in medullary thyroid cancer
Board review style question #1
A 30 year old male without a history of underlying disease or medication presented with right thyroid nodule, 3 cm. Fine needle aspiration cytology showed atypical cells suspicious for medullary thyroid carcinoma. His calcitonin level was 30 ng/L (normal < 10 ng/L). What is the most appropriate management of this patient?
- Check CEA level
- Consult surgeon for thyroidectomy
- CT chest / abdomen screening for metastasis
- Perform calcium stimulation test
- Repeat fasting calcitonin
Board review style answer #1
D. Perform calcium stimulation test. Calcitonin level is indeterminate (10 - 100 ng/L). After excluding other causes of falsely high calcitonin, calcium or pentagastrin test should be performed in this patient.
Comment Here
Reference: Calcitonin
Comment Here
Reference: Calcitonin