Table of Contents
Definition / general | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Parra-Herran C. Mesonephric rests and mesonephric hyperplasia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cervixmesonephrichyper.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Remnants of the mesonephric duct are commonly seen in resection specimens, particularly in the cervical stroma of cone and LEEP excisions (Am J Surg Pathol 1990;14:1100)
- Usually an incidental finding; rarely it can present as an area of induration or nodularity, being as large as 2.5 cm (Am J Surg Pathol 1990;14:1100)
- Mean age 38 to 47 years, range 21 to 81 years
- Benign (Int J Gynecol Pathol 1995;14:293)
Case reports
- Patients with squamous cell carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 1994;18:1265, Cesk Patol 2004;40:109)
- Patient with atypical mesonephric rests associated with cervical osteosarcoma (Cancer 1988;62:1594)
Microscopic (histologic) description
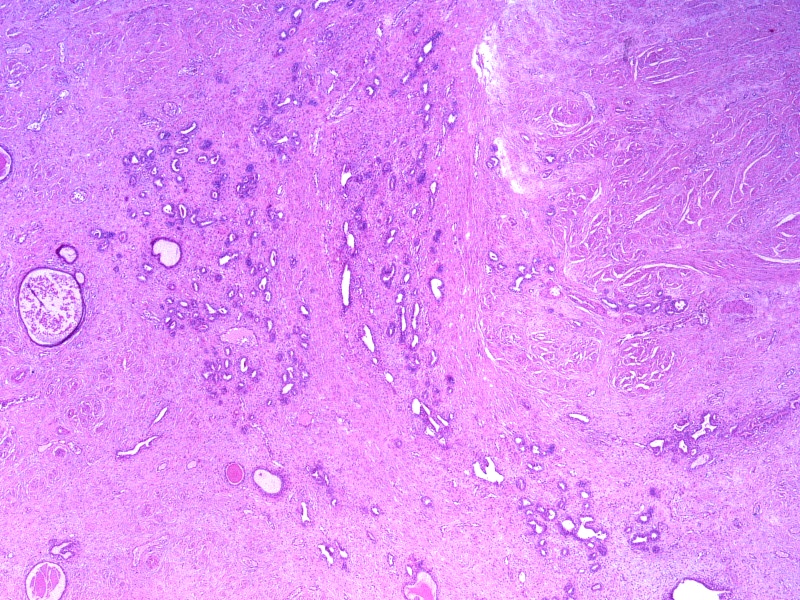
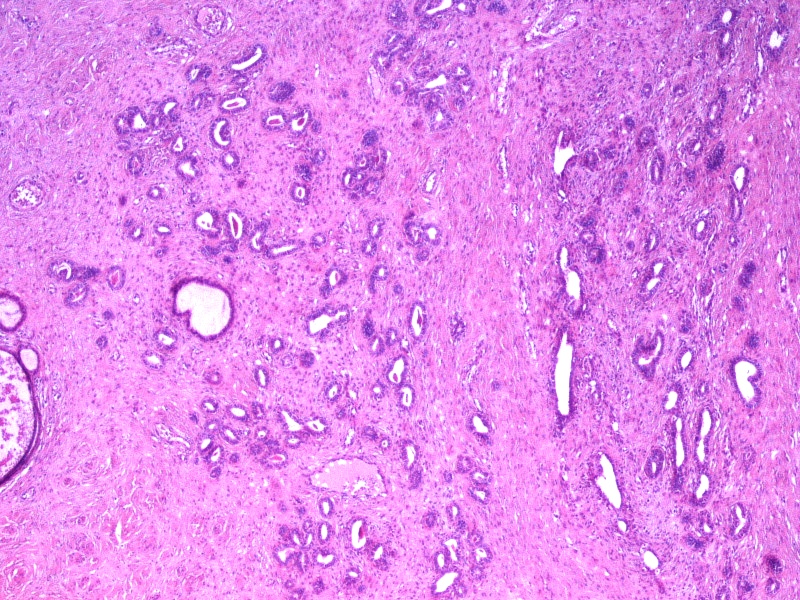
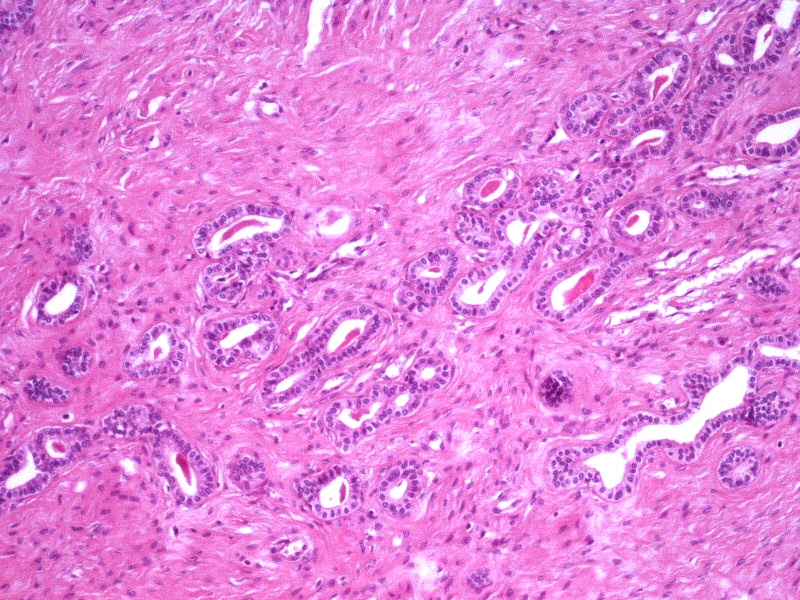
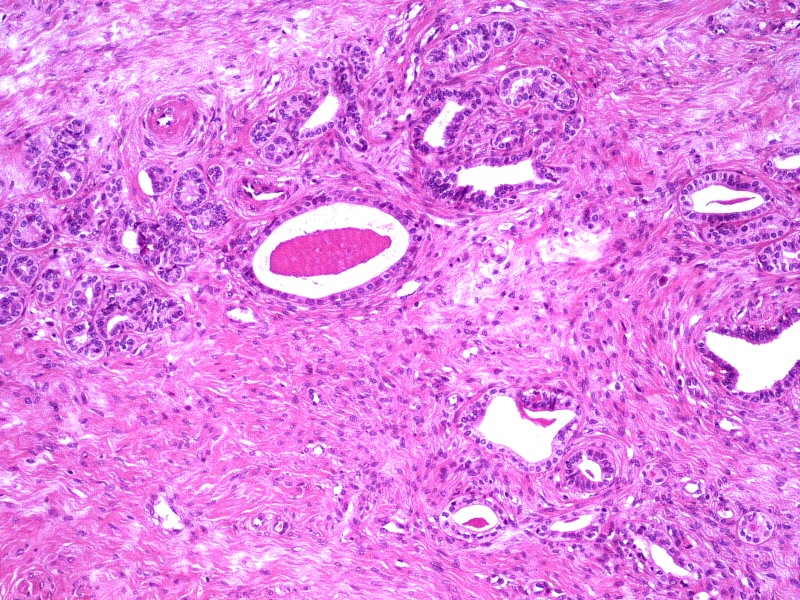
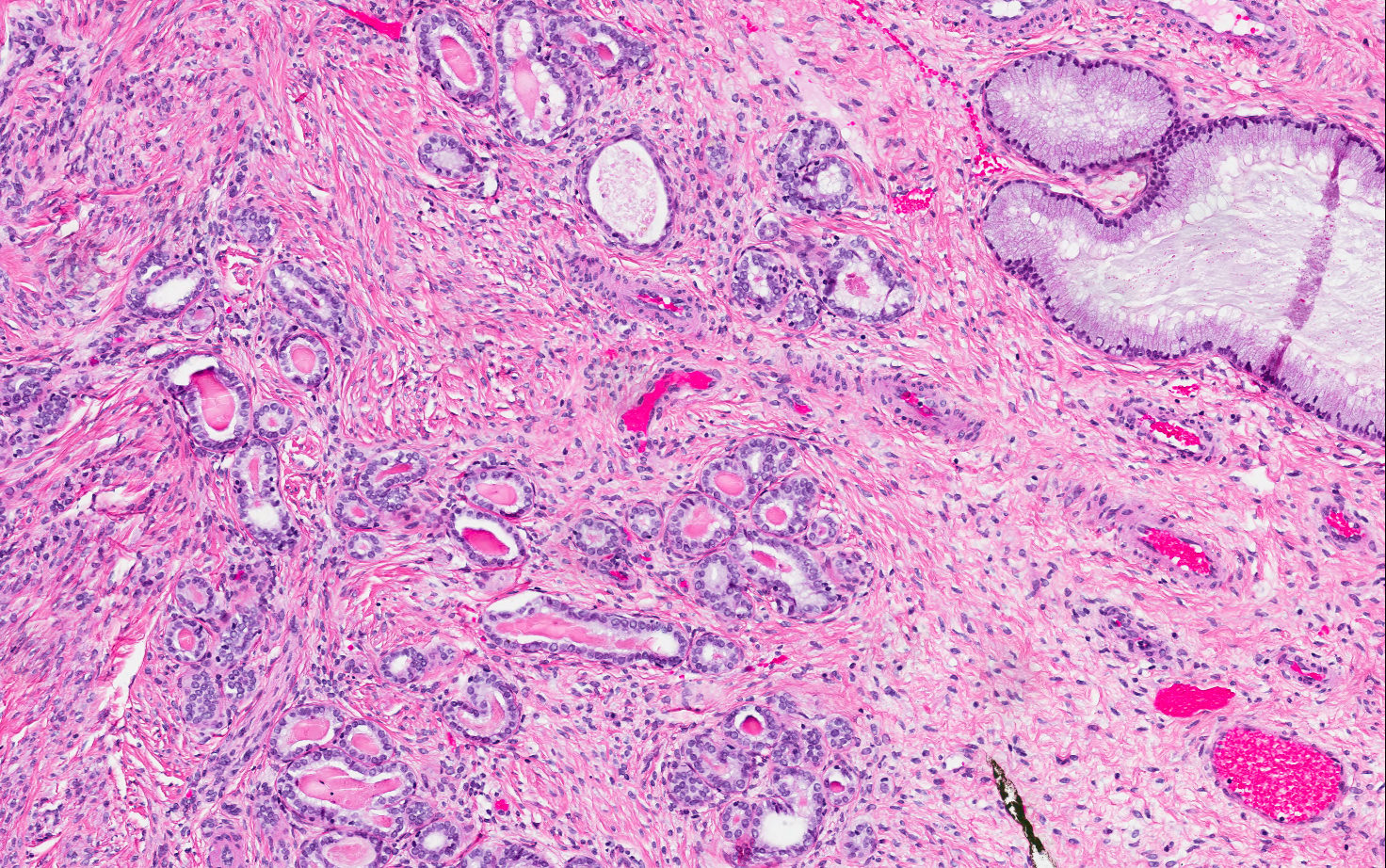
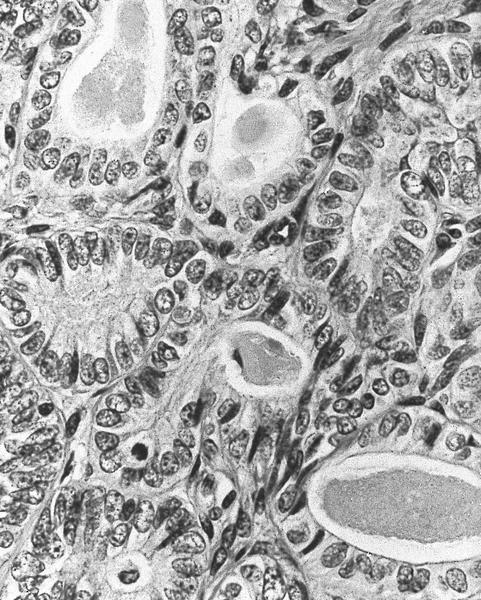
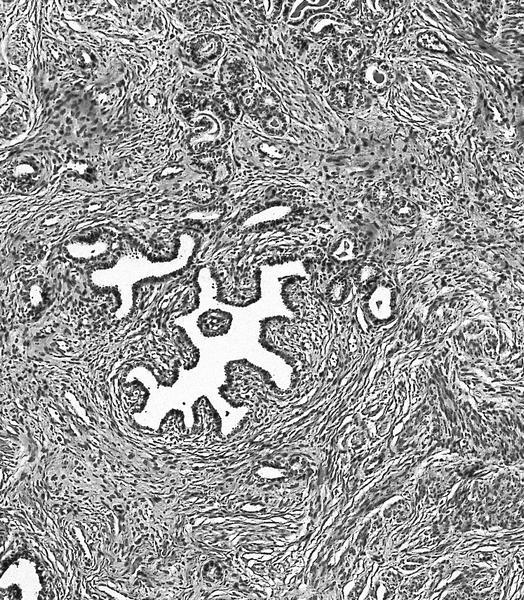
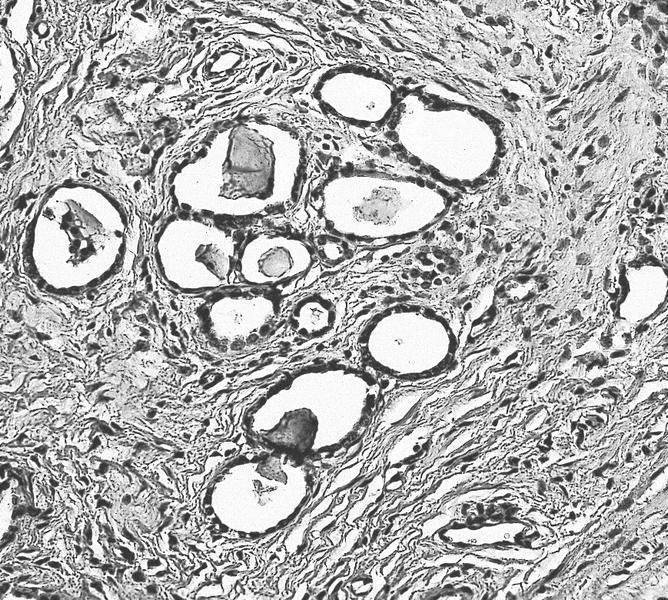
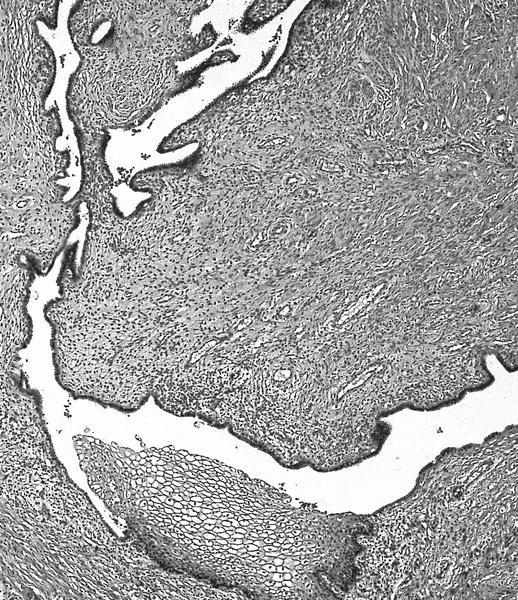
- Mesonephric duct remnants appear as groups of round glands and tubules, lined by simple flat to low cuboidal epithelium
- Glandular lumen is usually filled with a dense eosinophilic PAS positive, diastase resistant material; mucinous or ciliated cells are not identified
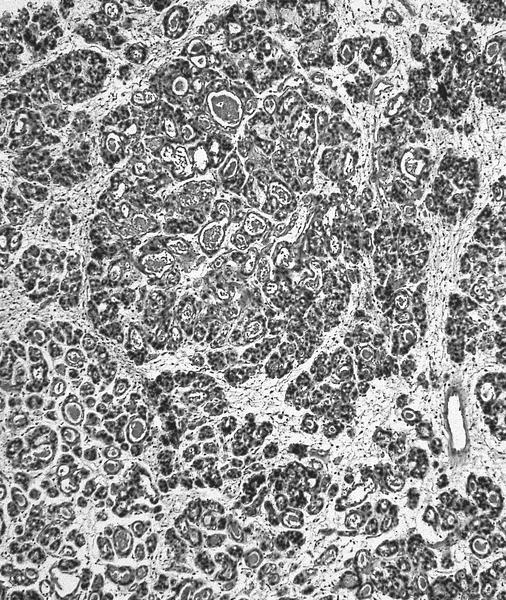
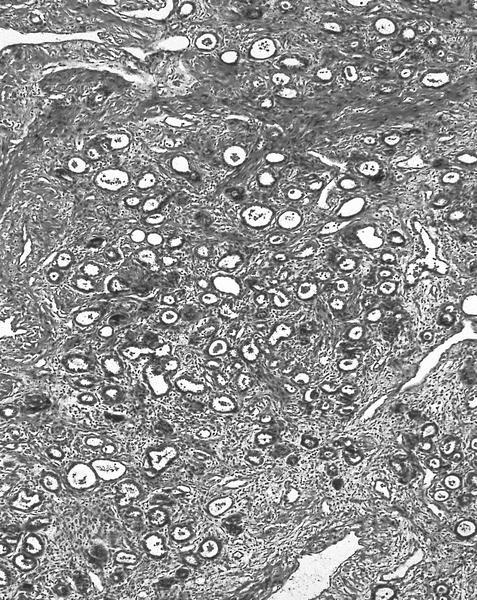
- Hyperplasia of mesonephric ducts is characterized by a glandular population similar to mesonephric remnants but larger, more irregular and haphazardly distributed with increase in lobule size and extensive involvement of the cervix
- Either lobular, diffuse (bland glands, no stromal reaction) or ductal patterns (large, dilated or irregular ducts in wall of cervix with micropapillary budding of pseudostratified epithelial cells without atypia); lobular is the most frequent
- Small round mesonephric tubules are often deep within cervical wall and extend to cervical surface
- May appear infiltrative
- No back to back glandular crowding, no nuclear atypia, no angiolymphatic invasion, no perineural invasion
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- May cause abnormal pap smears (Cytopathology 2005;16:240, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2003;22:121)
- Abnormal glandular cells in loose clusters with cuboidal outlines and no significant anisocytosis
Positive stains
Differential diagnosis
- Clear cell carcinoma
- Lobular endocervical glandular hyperplasia:
- Presence of intra and extracellular mucin
- Mesonephric adenocarcinoma:
- Mass related symptoms, frankly infiltrative borders, significant nuclear atpua, solid and confluent growth, lymphovascular invasion
- Tunnel clusters:
- Presence of intra and extracellular mucin
- Well differentiated endocervical adenocarcinoma:
- Cytologic atypia with hyperchromasia and apical mitoses, mucinous differentiation at least focally, no eosinophilic secretions
Additional references