Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Ismail A, Salih ZT. Chronic cervicitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cervixchroniccervicitis.html. Accessed December 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
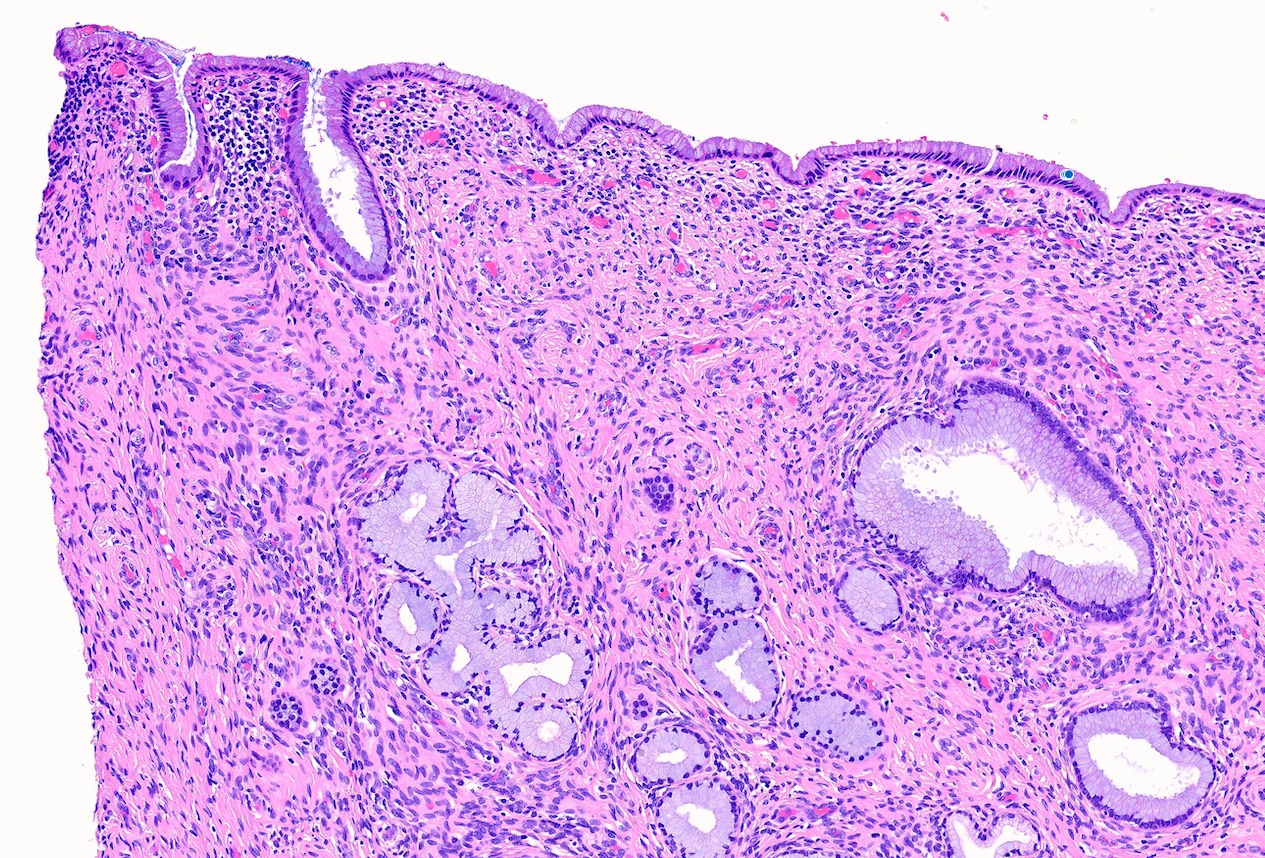
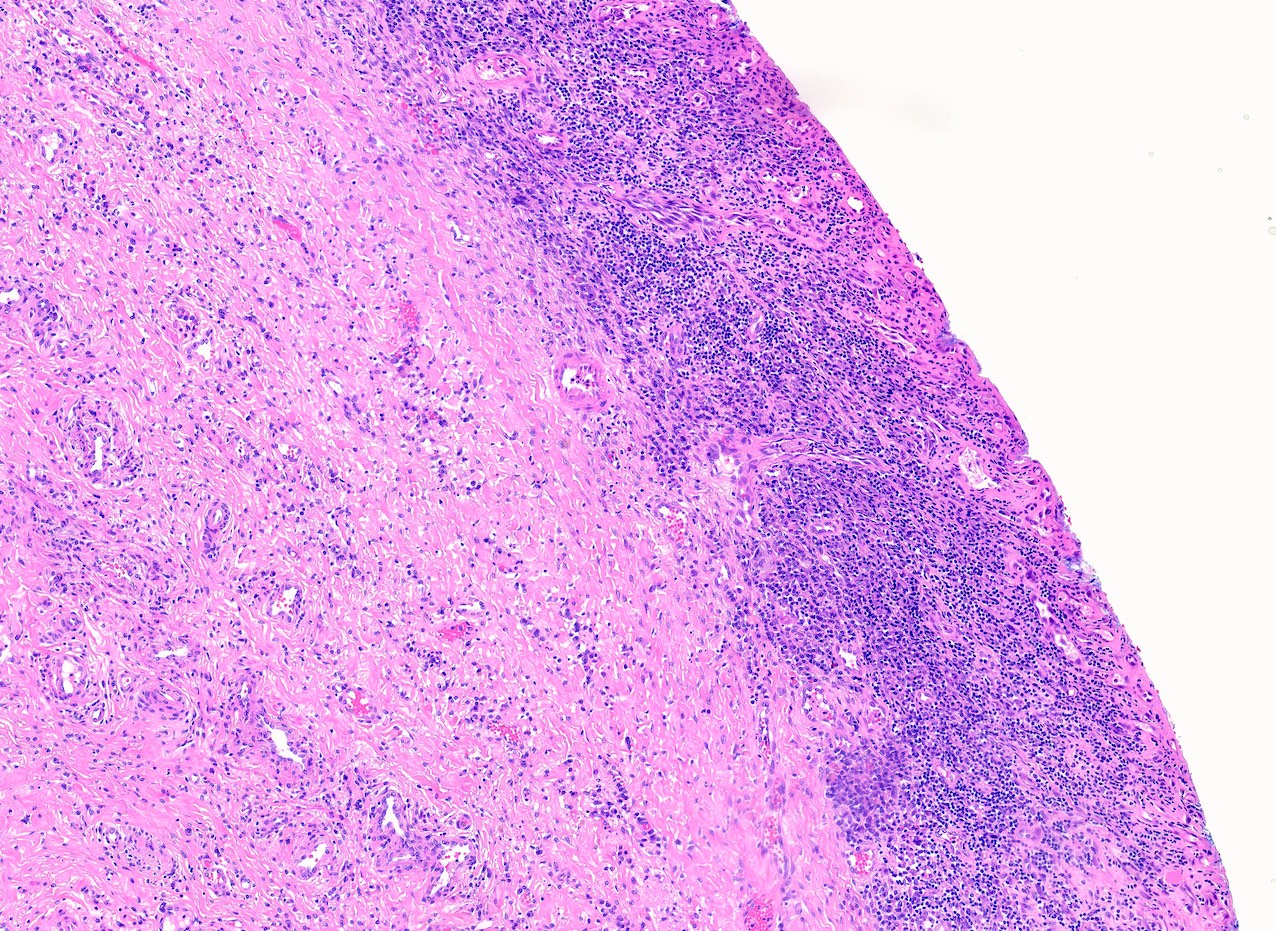
- Dense infiltrate of plasma cells and small lymphocytes with follicle formation in superficial cervical stroma, predominantly due to irritation (chemical or procedural) or infection (HSV, Chlamydia)
- Papillary endocervicitis is an endocervical inflammatory process with papillary growth pattern
Essential features
- Predominantly lymphocytic inflammation of the transformation zone of cervix
- Ulceration and necrosis suggest infective etiology
- Viral inclusions or lymphoid aggregates may point towards a chlamydia infection
Terminology
- Chronic nonspecific cervicitis, follicular cervicitis, plasma cell cervicitis, infective cervicitis
ICD coding
- ICD-10: N72 - inflammatory disease of cervix uteri
Sites
- Transformation zone of the cervix
Etiology
- Infection (chlamydia, herpes simplex virus, syphilis, Candida)
- Inflamed or traumatized Nabothian cysts
- Intrauterine device use (Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care 2014;19:187)
- Foreign bodies (tampons, diaphragms, pessaries)
- Idiopathic
Clinical features
- Majority of cases are asymptomatic
- Irregular, red and inflamed cervix on examination (Mutter: Robboy's Pathology of the Female Reproductive Tract, 2nd Edition, 2008)
- Ulceration and necrosis in infective cases (Goldblum: Rosai and Ackerman's Surgical Pathology, 11th Edition, 2017)
- May be associated with mucopurulent discharge (Mutter: Robboy's Pathology of the Female Reproductive Tract, 2nd Edition, 2008)
Diagnosis
- Redness or induration on physical examination; chronic inflammation of the cervix on pap smear or histologic evaluation
Case reports
- 22 year old woman with chronic cervicitis (J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2019;32:342)
- 67 year old woman with a large cervical tumor (Obstet Gynecol 1993;82:646)
- Postmenopausal woman with follicular cervicitis (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2004;47:271)
Treatment
- Infectious cervicitis requires antimicrobial treatment
- Noninfectious cervicitis generally does not require treatment
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Transformation zone of the cervix predominantly involved
- Dense lymphoplasmacytic inflammation of the cervix, with or without lymphoid follicle formation (Goldblum: Rosai and Ackerman's Surgical Pathology, 11th Edition, 2017)
- Ulceration and necrosis may suggest infective etiology (Goldblum: Rosai and Ackerman's Surgical Pathology, 11th Edition, 2017)
- Dense plasmacytic inflammation is suggestive of Treponema pallidum infection (Nucci: Gynecologic Pathology - A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series, 2nd Edition, 2020)
- Multinucleated cells with ground glass chromatin seen in viral induced cases; cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection shows evidence of large, basophilic intranuclear inclusions, which affect some of the epithelial cells; herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection shows ground glass chromatin with peripheral margination and Cowdry type A nuclear inclusions (Mutter: Robboy's Pathology of the Female Reproductive Tract, 2nd Edition, 2008)
- Mild lymphocytic inflammation of the cervix may represent normal histology (Goldblum: Rosai and Ackerman's Surgical Pathology, 11th Edition, 2017)
- Papillary endocervicitis:
- Chronic cervicitis with papillary architecture at surface
- Papillae are short and edematous, often with lymphoid aggregates, covered by simple columnar epithelium with reactive nuclear changes
- Cells have finely stippled chromatin and prominent nucleoli
- Mitotic figures may be present but no atypia
- No infiltrative pattern
- Often mast cells (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2004;47:178)
Cytology description
- Inflammatory changes include pale uniform chromatin and perinuclear halos
- Lymphocytes of varying stages of maturation along with tingible body macrophages (DeMay: Practical Principles of Cytopathology, 1st Edition, 2007)
- Scattered plasma cells may be seen
- Pap smear considered unreliable for diagnosis of chlamydia infection (DeMay: Practical Principles of Cytopathology, 1st Edition, 2007)
Sample pathology report
- Cervix, biopsy:
- Squamous mucosa with nonspecific chronic inflammation
- Cervix, biopsy:
- Squamocolumnar junction mucosa with dense inflammation, ulceration and epithelial viral cytopathic changes consistent with herpes simplex infection
Differential diagnosis
- Lymphoma:
- Monomorphic lymphoid population, large lymphoid cells seen in cases with diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Negative for viral immunohistochemical stains
- Most are B cell lymphomas and express pan-B cell markers
- Clonal IGH rearrangements
- Florid reactive lymphoid hyperplasia:
- Superficial aggregates of large lymphoid cells with admixed small lymphocytes, macrophages and germinal center formation
- Negative for viral immunohistochemical stains
- Mixture of B cells, T cells and polytypic plasma cells
- May show clonal IGH rearrangements (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:161)
Board review style question #1
Which of the following causes of chronic cervicitis is associated with multinucleated cells with ground glass chromatin with eosinophilic nuclear inclusions?
- Adenocarcinoma in situ
- Arias-Stella reaction
- Atrophy
- High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV) cervicitis
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2