Table of Contents
Definition / general | Major updates | WHO (2019) | Microscopic (histologic) images | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Agarwal I, Blanco L. WHO classification. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantwhoclassification.html. Accessed December 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Tumor classification is a dynamic process that integrates multiple sources of recent information
- Based on current 5th edition, published in 2019
Major updates
- Includes new, renamed and removed entities from the 4th edition of WHO classification along with changes to diagnostic criteria
- Carcinomas with medullary features have been subsumed into a combined morphological subset under the category of invasive carcinoma, no special type (NST) with basal-like and medullary pattern
- Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma has been recognized as a new entity
- Characterized by cystic structures lined by tall columnar cells with abundant intracytoplasmic mucin, resembling pancreatobiliary or ovarian mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
- Tall cell carcinoma with reversed polarity has been recognized as a new entity
- Characterized by tall columnar cells with reversed nuclear polarity, arranged in solid and solid papillary patterns, often associated with IDH2 pArg172 hotspot mutations (Histopathology 2018;73:339, Am J Clin Pathol 2017;147:399)
- Neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs) harmonized with those of other organ systems incorporating uniform classification network (Mod Pathol 2018;31:1770)
- Removal of well differentiated liposarcoma as a histologic criterion for malignancy in phyllodes tumor in the absence of additional supporting features
- Abnormal adipocytes within phyllodes tumor lack MDM2 or CDK4 amplifications in contrast to extramammary well differentiated liposarcoma (Histopathology 2016;68:1040)
- Updated information on molecular pathology, expression profiling and molecular classification of breast tumors; however, focus remains on morphologic classification
- Conversion of mitotic count from a common denominator of 10 high power fields to a defined area expressed as mm2
WHO (2019)
-
Epithelial tumors
- Infiltrating duct carcinoma, NOS 8500/3
- Oncocytic carcinoma 8290/3
- Lipid rich carcinoma 8314/3
- Glycogen rich carcinoma 8315/3
- Sebaceous carcinoma 8410/3
- Lobular carcinoma, NOS 8520/3
- Tubular carcinoma 8211/3
- Cribriform carcinoma, NOS 8201/3
- Mucinous adenocarcinoma 8480/3
- Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma, NOS 8480/3
- Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of breast 8507/3
- Metaplastic carcinoma, NOS 8575/3
- Secretory carcinoma 8502/3
- Acinar cell carcinoma 8550/3
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma 8430/3
- Polymorphous adenocarcinoma 8525/3
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma 8200/3
- Tall cell carcinoma with reversed polarity 8509/3
- Neuroendocrine tumor, NOS 8240/3
- Neuroendocrine tumor, grade 1 8240/3
- Neuroendocrine tumor, grade 2 8249/3
- Neuroendocrine carcinoma, NOS 8246/3
- Neuroendocrine carcinoma, small cell 8041/3
- Neuroendocrine carcinoma, large cell 8013/3
- Pleomorphic adenoma 8940/0
- Adenomyoepithelioma, NOS 8983/0
- Adenomyoepithelioma with carcinoma 8983/3
- Epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma 8562/3
- Atypical lobular hyperplasia
- Lobular carcinoma in situ, NOS 8520/2
- Usual ductal hyperplasia
- Columnar cell lesions including flat epithelial atypia
- Atypical ductal hyperplasia
- Sclerosing adenosis
- Apocrine adenoma 8401/0
- Microglandular adenosis
- Radial scar / complex sclerosing lesion
- Intraductal papilloma 8503/0
- Ductal carcinoma in situ, papillary 8503/2
- Encapsulated papillary carcinoma 8504/2
- Encapsulated papillary carcinoma with invasion 8504/3
- Solid papillary carcinoma in situ 8509/2
- Solid papillary carcinoma with invasion 8509/3
- Intraductal papillary adenocarcinoma with invasion 8503/3
- Tubular adenoma, NOS 8211/0
- Lactating adenoma 8204/0
- Duct adenoma, NOS 8503/0
- Hemangioma, NOS 9120/0
- Angiomatosis
- Atypical vascular lesion 9126/0
- Postradiation angiosarcoma 9120/3
- Angiosarcoma 9120/3
- Nodular fasciitis 8828/0
- Myofibroblastoma 8825/0
- Desmoid type fibromatosis 8821/1
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor 8825/1
- Schwannoma, NOS 9560/0
- Neurofibroma, NOS 9540/0
- Granular cell tumor, NOS 9580/0
- Granular cell tumor, malignant 9580/3
- Leiomyoma, NOS 8890/0
- Leiomyosarcoma, NOS 8890/3
- Lipoma, NOS 8850/0
- Angiolipoma, NOS 8861/0
- Liposarcoma, NOS 8850/3
- Fibroadenoma, NOS 9010/0
- Phyllodes tumor, NOS 9020/1
- Periductal stromal tumor
- Phyllodes tumor, benign 9020/0
- Phyllodes tumor, borderline 9020/1
- Phyllodes tumor, malignant 9020/3
- Hamartoma
- Nipple adenoma 8506/0
- Syringoma, NOS 8407/0
- Paget disease of the nipple 8540/3
- Diffuse large B cell lymphoma, NOS 9680/3
- Burkitt lymphoma, NOS / acute leukemia, Burkitt type 9687/3
- Breast implant associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma 9715/3
- Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma 9699/3
- Follicular lymphoma, NOS 9690/3
- Gynecomastia
- Carcinoma
- Invasive carcinoma 8500/3
- In situ carcinoma 8500/2
Invasive breast carcinoma
Rare and salivary gland type tumors
Neuroendocrine neoplasms
Epithelial myoepithelial tumors
Noninvasive lobular neoplasia
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
Benign epithelial proliferations and precursors
Adenosis and benign sclerosing lesions
Papillary neoplasms
Adenomas
Mesenchymal tumors
Vascular tumors
Fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors
Peripheral nerve sheath tumors
Smooth muscle tumors
Adipocytic tumors
Other mesenchymal tumors and tumor-like conditions
Fibroepithelial tumors
Tumors of the nipple
Malignant lymphoma
Metastatic tumors
Tumors of the male breast
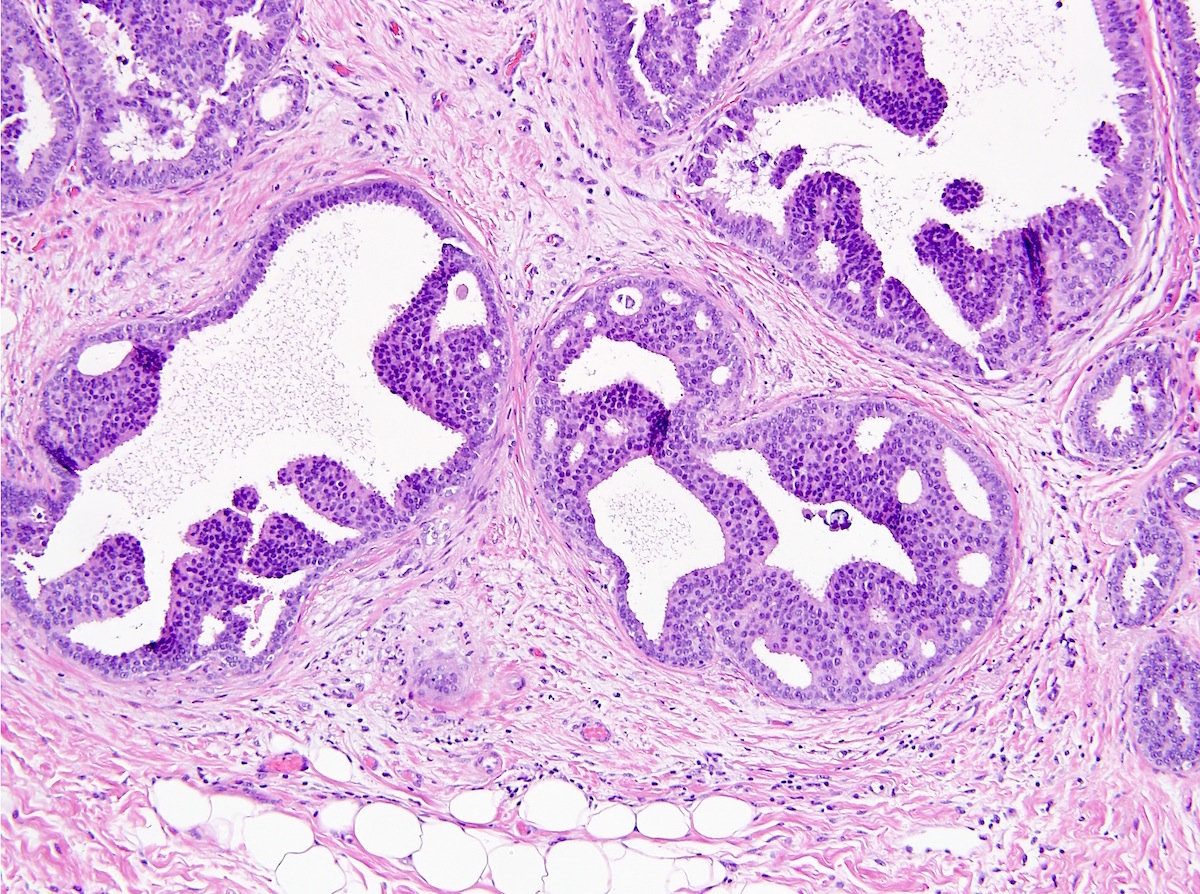
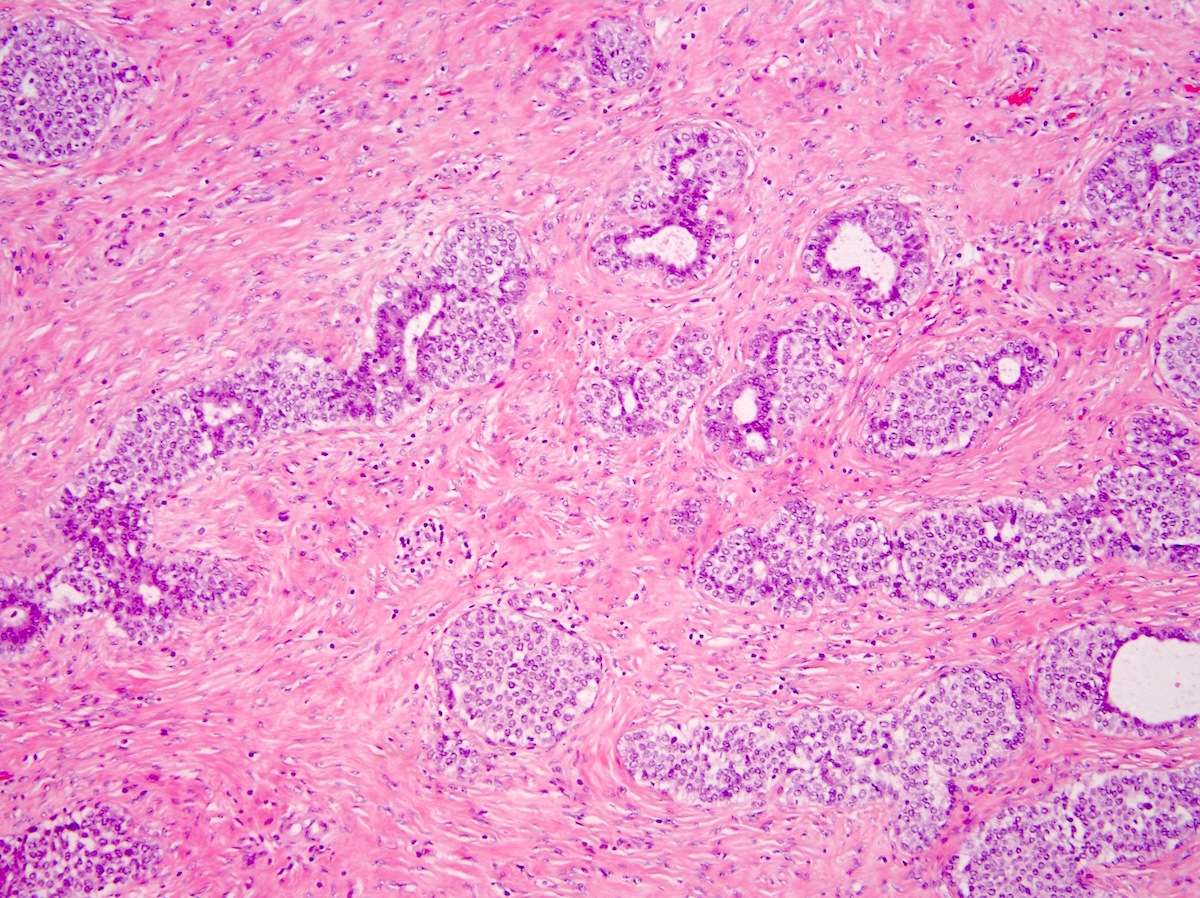
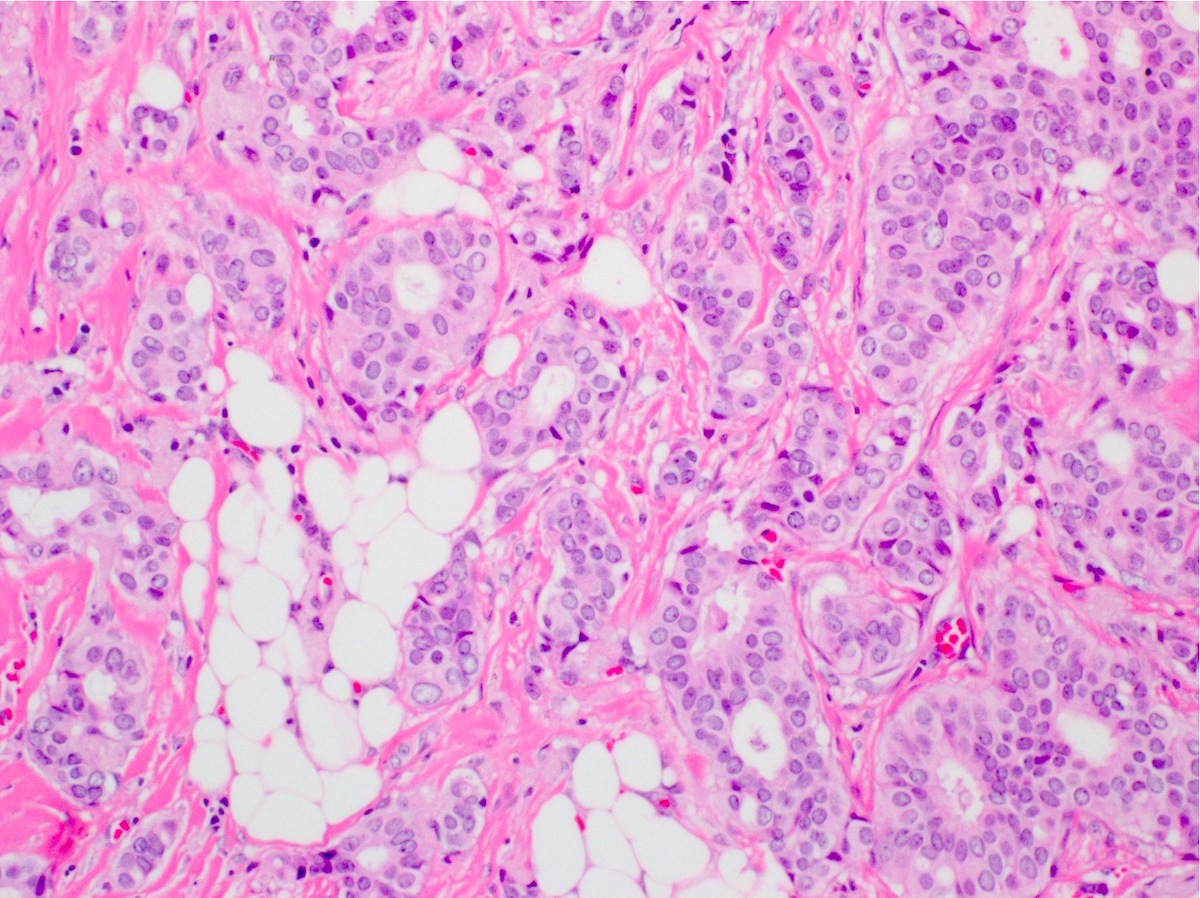
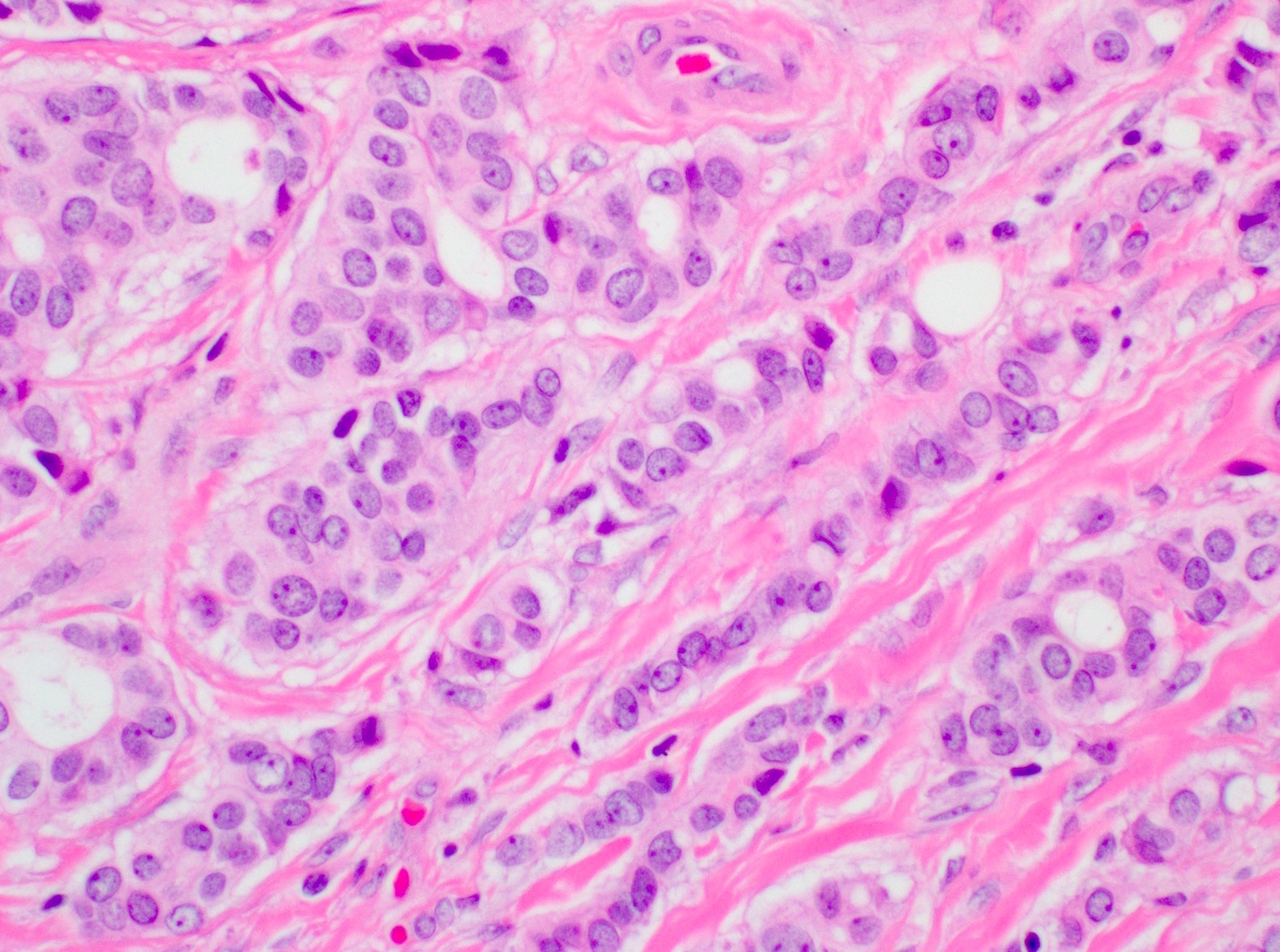
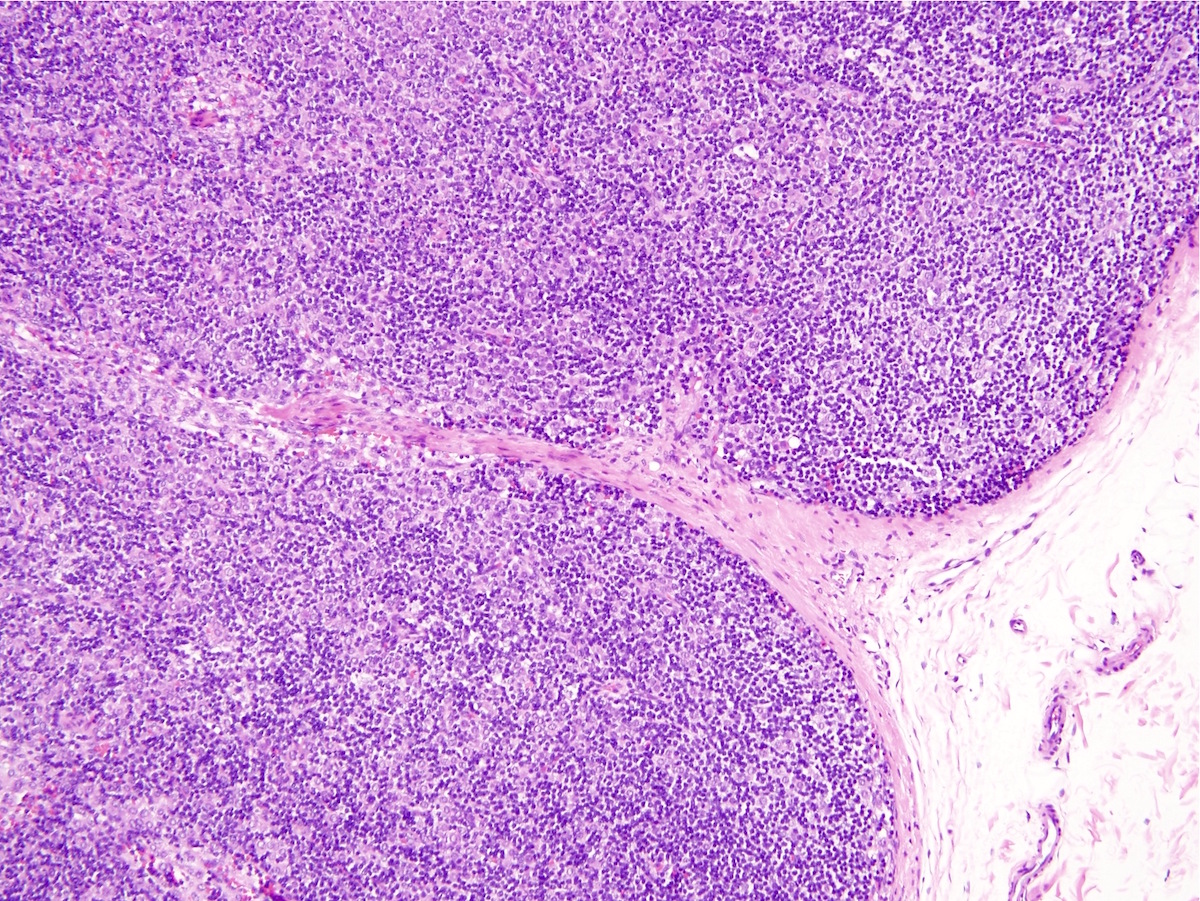
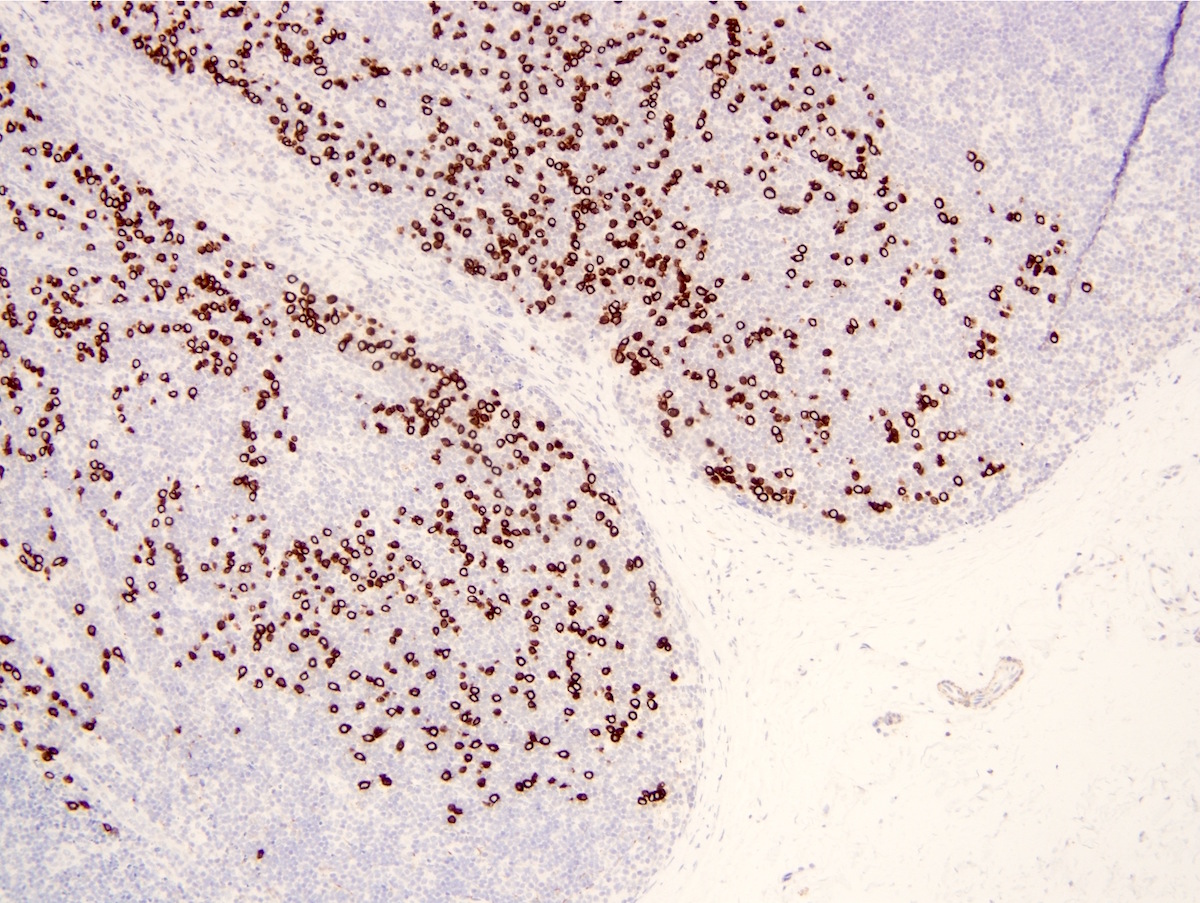
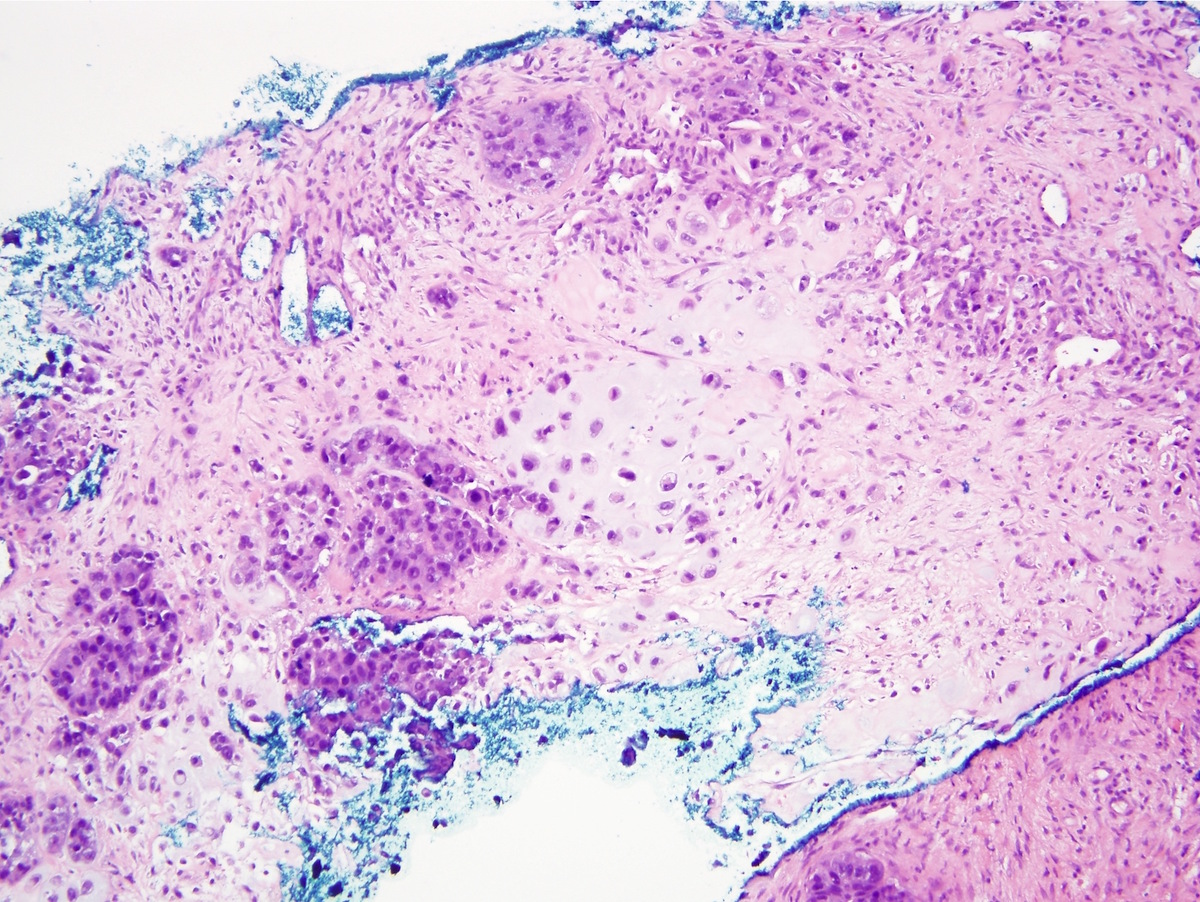
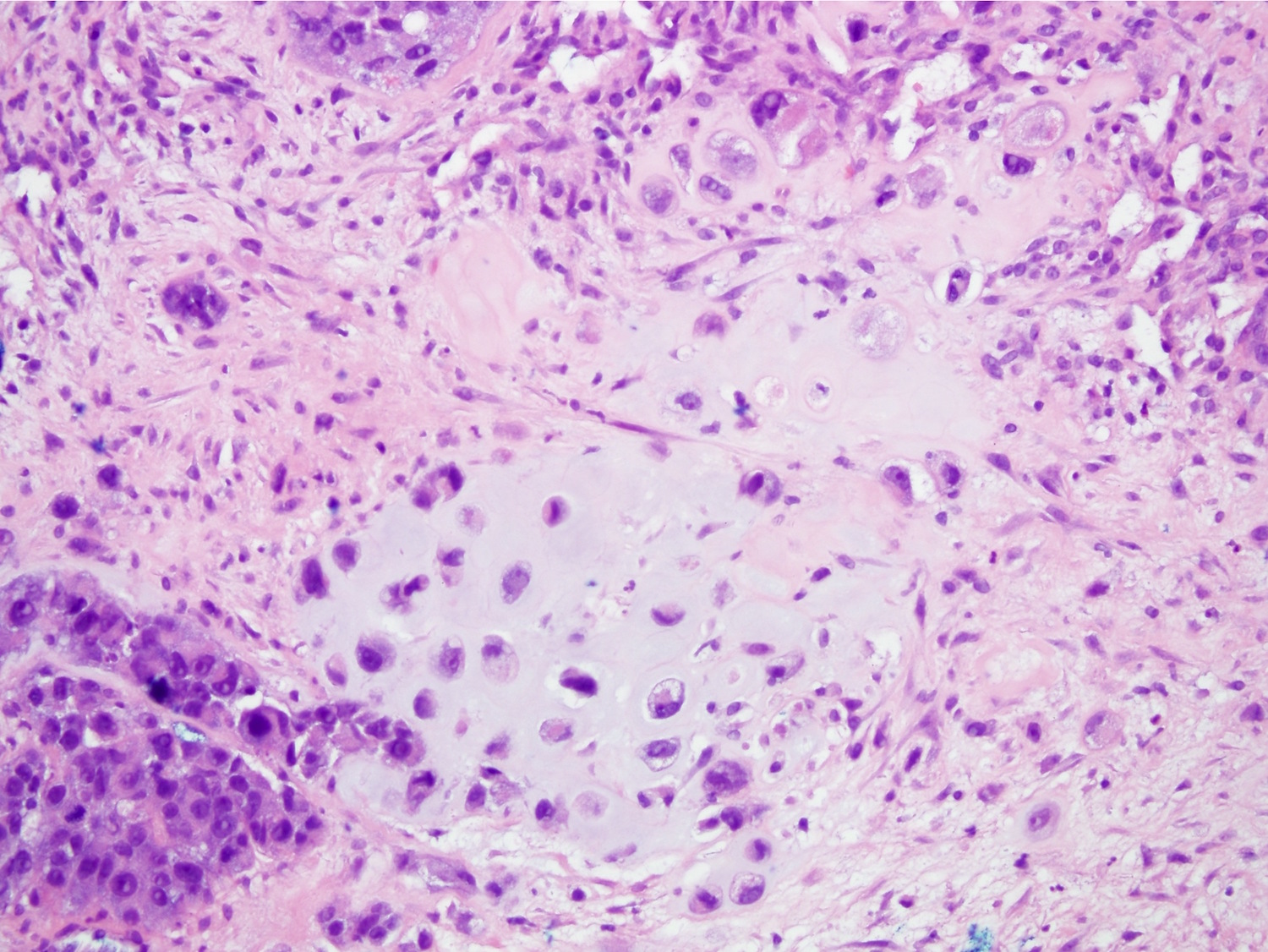
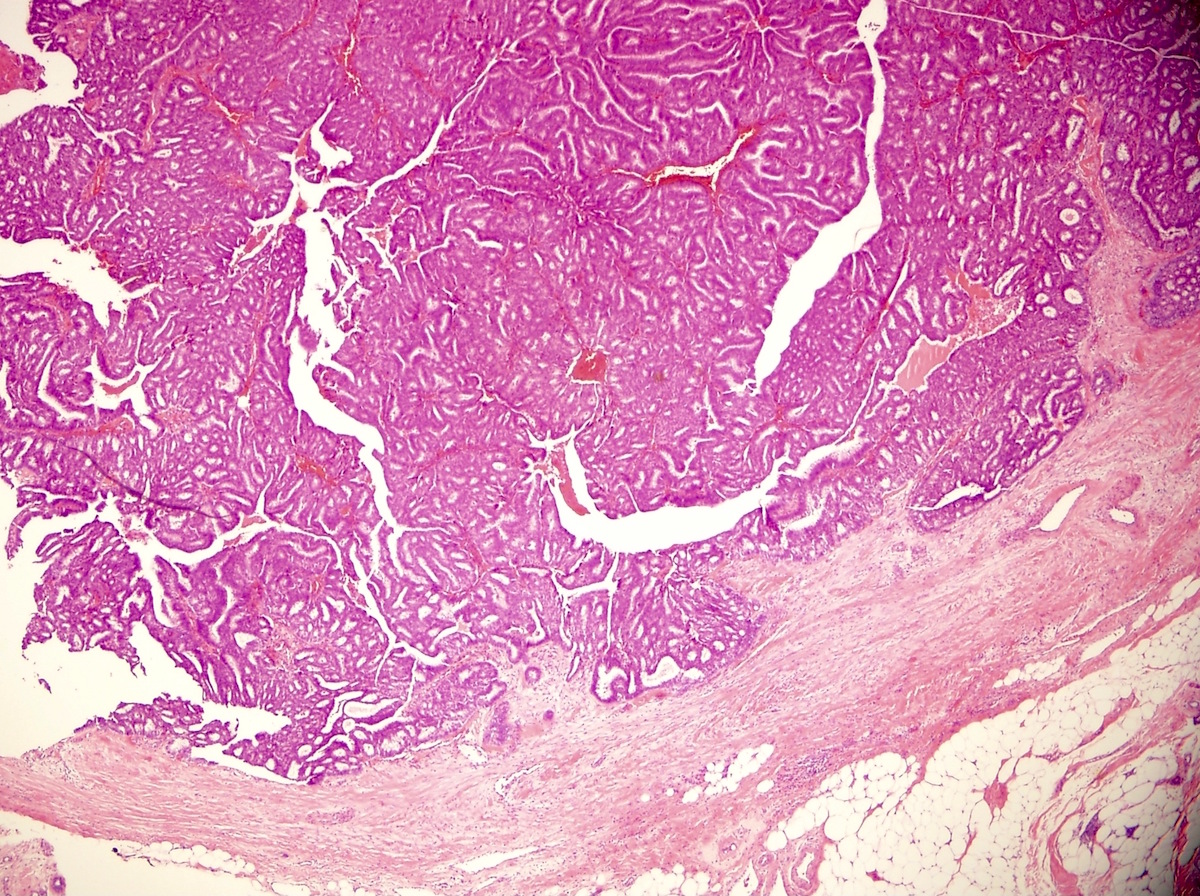
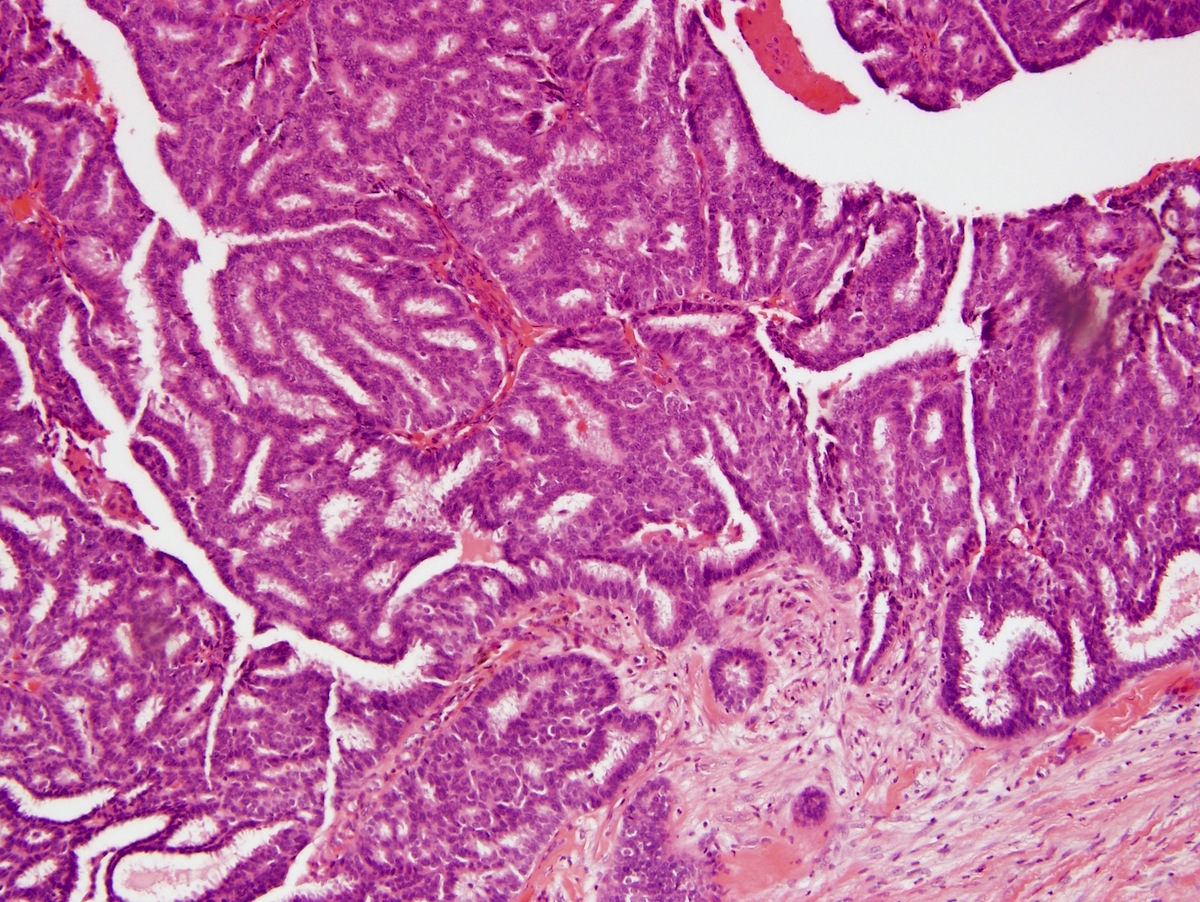
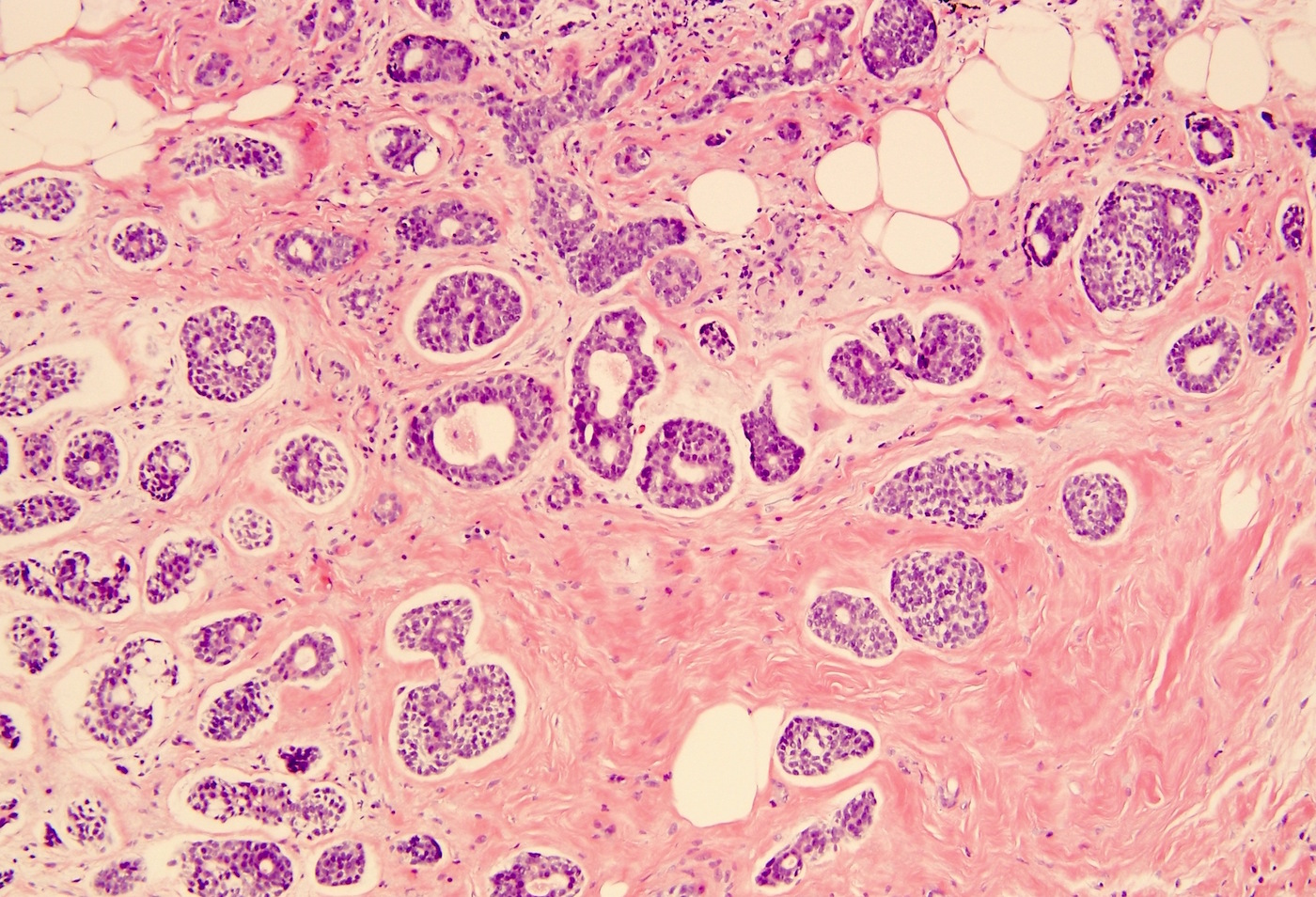
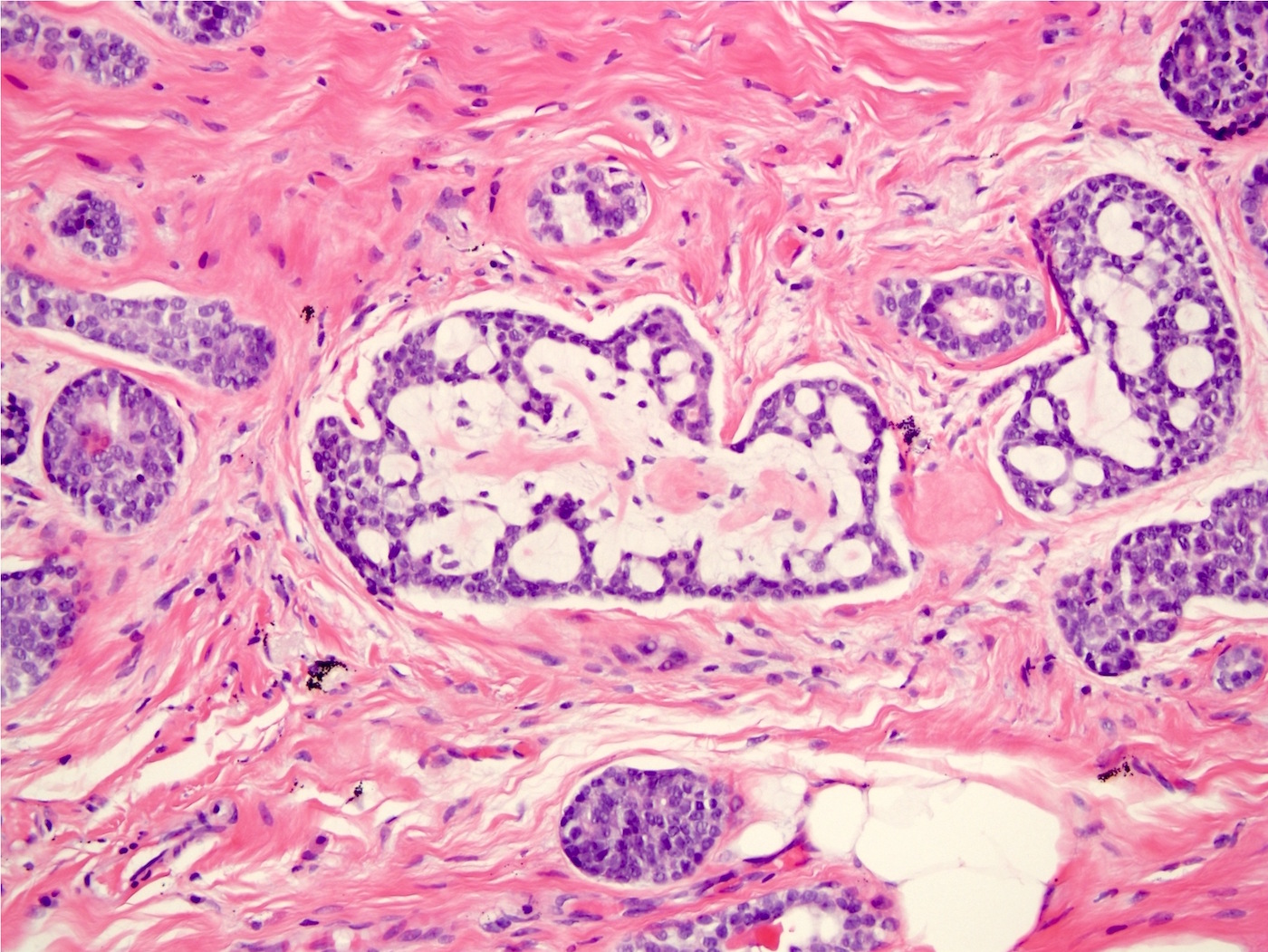
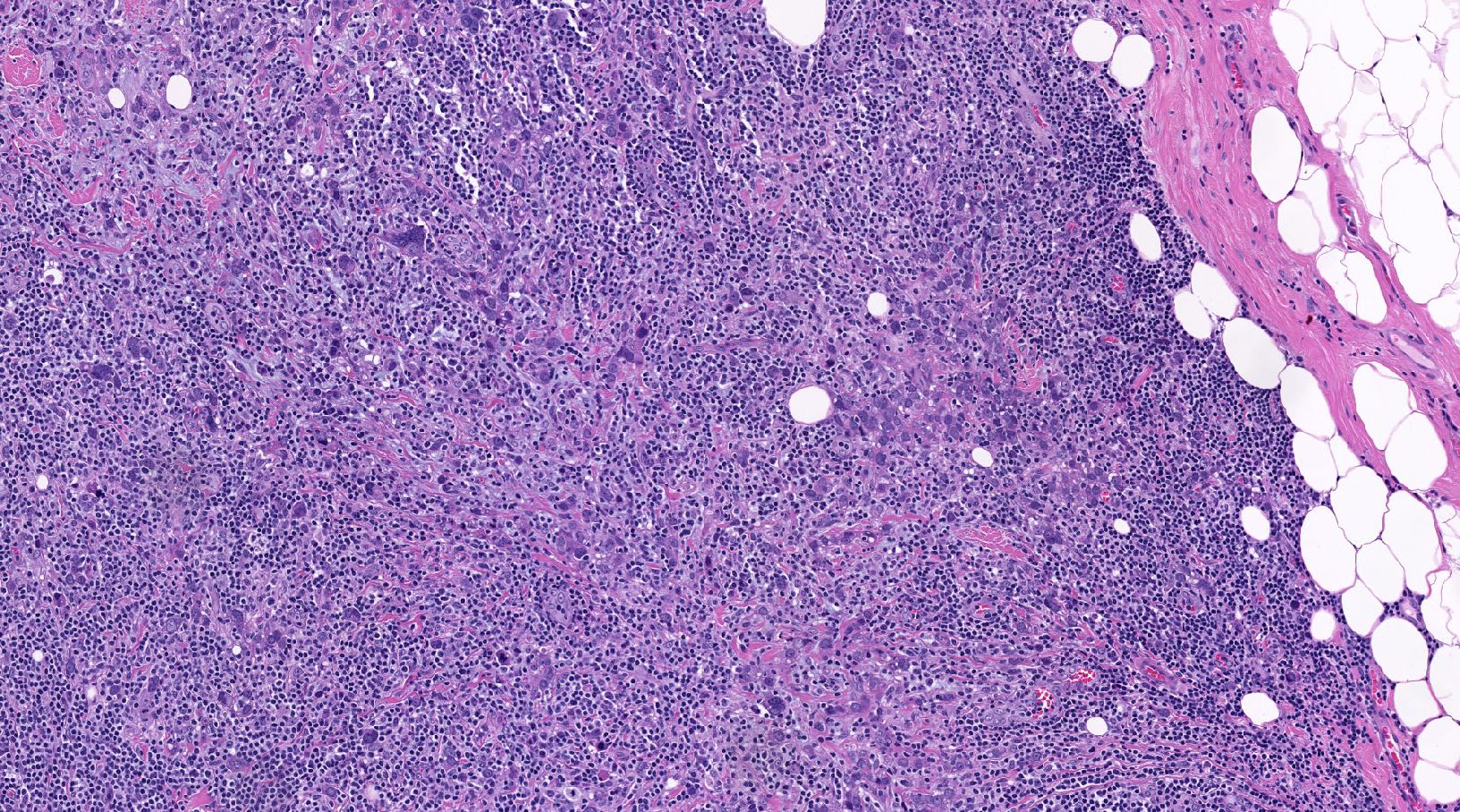
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Indu Agarwal, M.D., Mirna B. Podoll, M.D. and Julie M. Jorns, M.D.
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is a new entity in the WHO Classification of Breast Tumours, 5th edition, published in 2019?
- Malignant phyllodes tumor with well differentiated liposarcomatous differentiation alone
- Medullary carcinoma
- Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
- Solid papillary carcinoma
Board review style answer #1
C. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma.
Tall cell carcinoma with reversed polarity (TCCRP) and mucinous cystadenocarcinoma, NOS are 2 new entities. TCRRP is a rare subtype of invasive breast carcinoma characterized by tall columnar cells with reversed nuclear polarity, arranged in solid and solid papillary patterns and most commonly associated with IDH2 p.Arg172 hotspot mutations. Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast is an invasive breast carcinoma characterized by cystic structures lined by tall columnar cells with abundant intracytoplasmic mucin, resembling pancreatobiliary or ovarian mucinous cystadenocarcinoma.
Answer A is incorrect because liposarcomatous differentiation has been removed as a histologic criterion for malignancy in phyllodes tumor in the absence of additional supporting features. Answer B is incorrect because tumors previously called as medullary carcinoma, atypical medullary carcinoma and invasive carcinoma with medullary features have been subsumed into a combined morphologic subset under the category of invasive carcinoma, NST with basal-like and medullary pattern, regarding them as a part of a spectrum of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes rich breast carcinomas. Answer D is incorrect because encapsulated papillary carcinoma and solid papillary carcinoma have been previously present in prior WHO editions.
Comment Here
Reference: Breast - WHO classification
Answer A is incorrect because liposarcomatous differentiation has been removed as a histologic criterion for malignancy in phyllodes tumor in the absence of additional supporting features. Answer B is incorrect because tumors previously called as medullary carcinoma, atypical medullary carcinoma and invasive carcinoma with medullary features have been subsumed into a combined morphologic subset under the category of invasive carcinoma, NST with basal-like and medullary pattern, regarding them as a part of a spectrum of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes rich breast carcinomas. Answer D is incorrect because encapsulated papillary carcinoma and solid papillary carcinoma have been previously present in prior WHO editions.
Comment Here
Reference: Breast - WHO classification
Board review style question #2
Tall cell carcinoma with reversed polarity (TCCRP) is a new entity in the WHO Classification of Breast Tumours, 5th edition, published in 2019, that has what typical prognosis and estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and HER2 / neu (HER2) profile?
- Good prognosis, ER / PR negative, HER2 negative
- Good prognosis, ER / PR positive, HER2 negative
- Poor prognosis, ER / PR negative, HER2 negative
- Poor prognosis, ER / PR positive, HER2 negative
Board review style answer #2
A. Good prognosis, ER / PR negative, HER2 negative. Tall cell carcinoma with reversed polarity (TCCPR) is a rare subtype of invasive breast carcinoma characterized by tall columnar cells with reversed nuclear polarity, arranged in solid and solid papillary patterns and most commonly associated with IDH2 p.Arg172 hotspot mutations. Despite the good prognosis and indolent course of TCCRP, this tumor typically expresses low and high molecular weight keratins, including CK5/6 and is ER / PR and HER2 negative, thus part of a group of rare good prognosis triple negative breast carcinoma (TNBC), which also includes some salivary gland type tumors (e.g., adenoid cystic carcinoma) and variants of metaplastic carcinoma (e.g., low grade fibromatosis-like carcinoma). Answers B and D are incorrect because TCCRP is not ER / PR positive. Answers C and D are incorrect because it is not a poor prognosis breast cancer subtype.
Comment Here
Reference: Breast - WHO classification
Comment Here
Reference: Breast - WHO classification