Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Batra H, Jorns JM. Myoepithelioma and myoepithelial carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmyoepithelioma.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Myoepithelioma: bland spindle cell lesion with myoepithelial phenotype
- Myoepithelial carcinoma: very rare malignant lesion, mostly arising in association with adenomyoepitheliomas, composed of purely malignant myoepithelial cells, primarily spindle shaped to polygonal
- Associated with myoepithelioma or adenomyoepithelioma (most frequent)
- Currently classified as metaplastic carcinoma with myoepithelial differentiation
- WHO classification of breast tumors (4th edition) has included myoepithelial carcinoma under the category of metaplastic carcinoma of no special type
Essential features
- Myoepithelioma: benign lesion comprised of cells of myoepithelial derivation
- Myoepithelial carcinoma: rare, malignant tumor of the breast comprised of cells of myoepithelial derivation
Terminology
- Myoepithelioma
- Myoepitheliosis: multifocal, often microscopic proliferation of myoepithelial cells in or around small ducts; usually an incidental finding and not palpable (Am J Surg Pathol 1991;15:554)
- Myoepithelial carcinoma (not recognized by WHO):
- Malignant myoepithelioma (not recognized by WHO) (Mol Clin Oncol 2016;4:723)
- Myoepithelial rich carcinoma (not recognized by WHO) (Histopathology 1997;30:542)
- Metaplastic carcinoma with myoepithelial differentiation
- Metaplastic carcinoma of no special type
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8982/3 - malignant myoepithelioma
- ICD-11:
- Myoepithelioma:
- Myoepithelial carcinoma:
- 2C6Z - malignant neoplasms of breast, unspecified
- 2C6Y & XH43E6 - other specified malignant neoplasms of breast & myoepithelial carcinoma
- XH43E6 - myoepithelial carcinoma
Epidemiology
- Myoepithelioma: premenopausal and postmenopausal women; wide age range
- Myoepithelial carcinoma:
- Incidence is 15 per 100,000 population
- Mean age for myoepithelial carcinoma in breast: 50 years; range 45 - 86 years (Transl Cancer Res 2017;6:441)
Sites
- Breast, without specific site predilection
Pathophysiology
- Tumors that arise from the peripheral myoepithelial cell layer
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Myoepithelioma is benign but may recur locally
- Myoepithelial carcinoma may recur or metastasize to regional lymph nodes or distant sites (Eur J Surg Oncol 2004;30:357)
Diagnosis
- Histologic evaluation of tissue, typically with assistance of immunohistochemistry
Radiology description
- Mammography: circumscribed or irregular, noncalcified mass
- Ultrasound: hypoechoic, irregular or oval mass with microlobulated or indistinct margins
- MRI: enhancing mass with an irregular or spiculated margin and delayed washout or plateau kinetics
- References: Breast J 2007;13:203, Taehan Yongsang Uihakhoe Chi 2020;81:207
Prognostic factors
- Myoepithelioma: can recur locally
- Myoepithelial carcinoma (Eur J Surg Oncol 2004;30:357):
- Associated with aggressive course, including recurrence and metastasis
- 2 and 5 year survival is 88% and 55%
- Increased tumor size is associated with worse outcome
Case reports
- 56 year old postmenopausal woman with a palpable mass (Breast Care (Basel) 2010;5:246)
- 57 year old woman with lump in her left breast for 4 months (South Asian J Cancer 2017;6:185)
- 58 year old postmenopausal woman with a palpable lump in the left breast with calcifications on mammogram (Clin Case Rep 2019;7:930)
- 61 year old woman with an elastic hard mass measuring 2 cm in the upper central area of the left breast (Case Rep Oncol Med 2013;2013:164761)
- 67 year old woman with myoepithelial carcinoma of the breast with focal rhabdoid features (Breast J 2013;19:100)
- 71 year old woman with local recurrence (Tunis Med 2004;82:324)
- 73 year old postmenopausal woman with a palpable and a nontender lump in the left breast (J Clin Diagn Res 2013;7:1191)
- Renal dialysis patient with benign appearing tumor with metastatic behavior (ANZ J Surg 2004;74:1135)
Treatment
- Myoepithelioma: complete surgical excision (J Cytol 2013;30:62)
- Myoepithelial carcinoma:
- Wide local excision, segmental mastectomy or total mastectomy with regional lymph node excision and radiotherapy (Mol Clin Oncol 2016;4:723)
- Role of chemotherapy is not well defined
- Platinum analogs and paclitaxel combination has shown some efficacy in few cases reported (Oncologist 2016;21:1492)
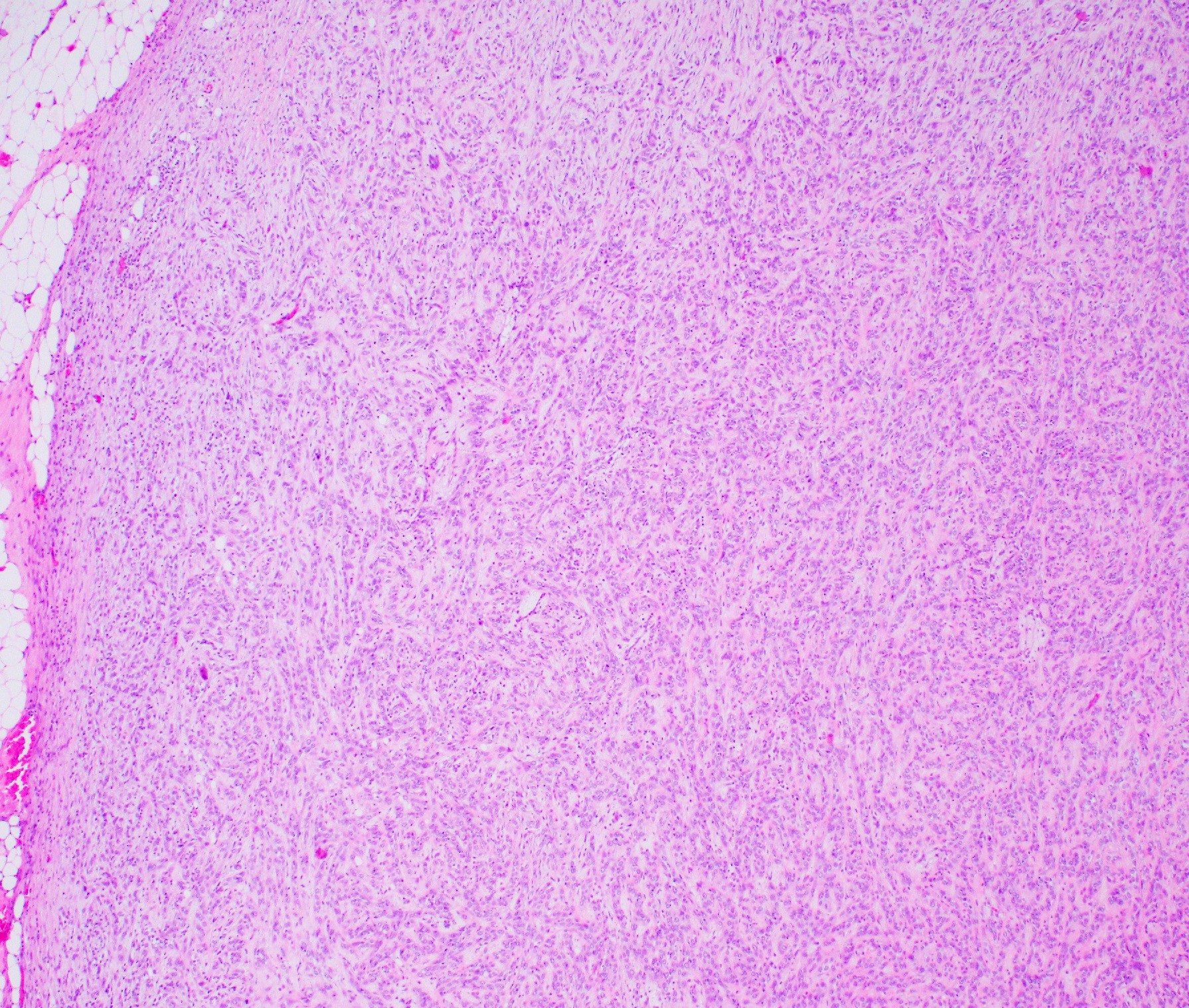
Gross description
- Well circumscribed, firm mass; irregular borders more frequent with myoepithelial carcinoma (Diagn Pathol 2008;3:7)
- Cut surface is grayish white and solid (Virchows Arch 2010;457:337)
- Larger tumors may show variable areas of cystic degeneration, hemorrhage and necrosis (myoepithelial carcinoma) (Mol Clin Oncol 2016;4:723)
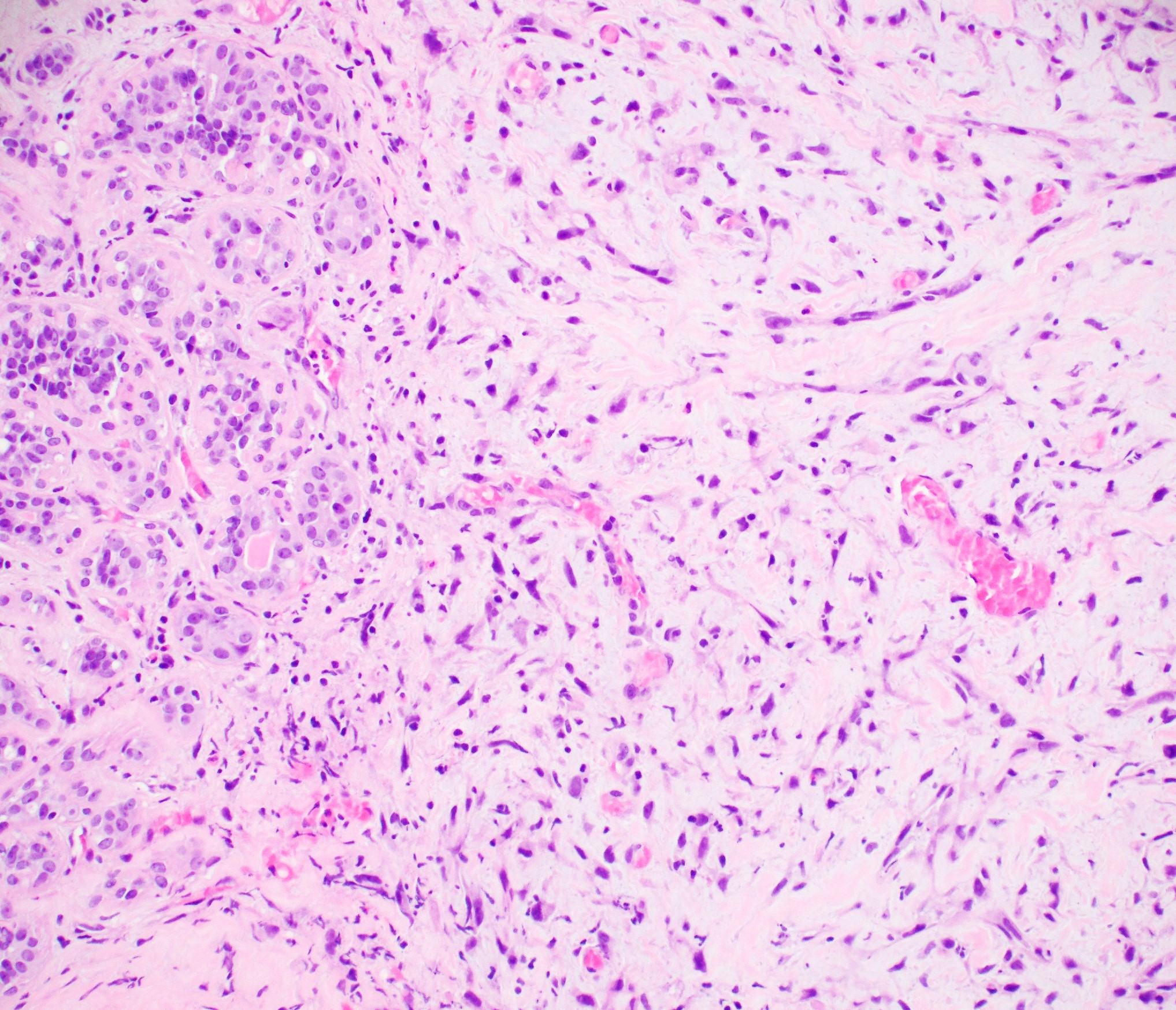
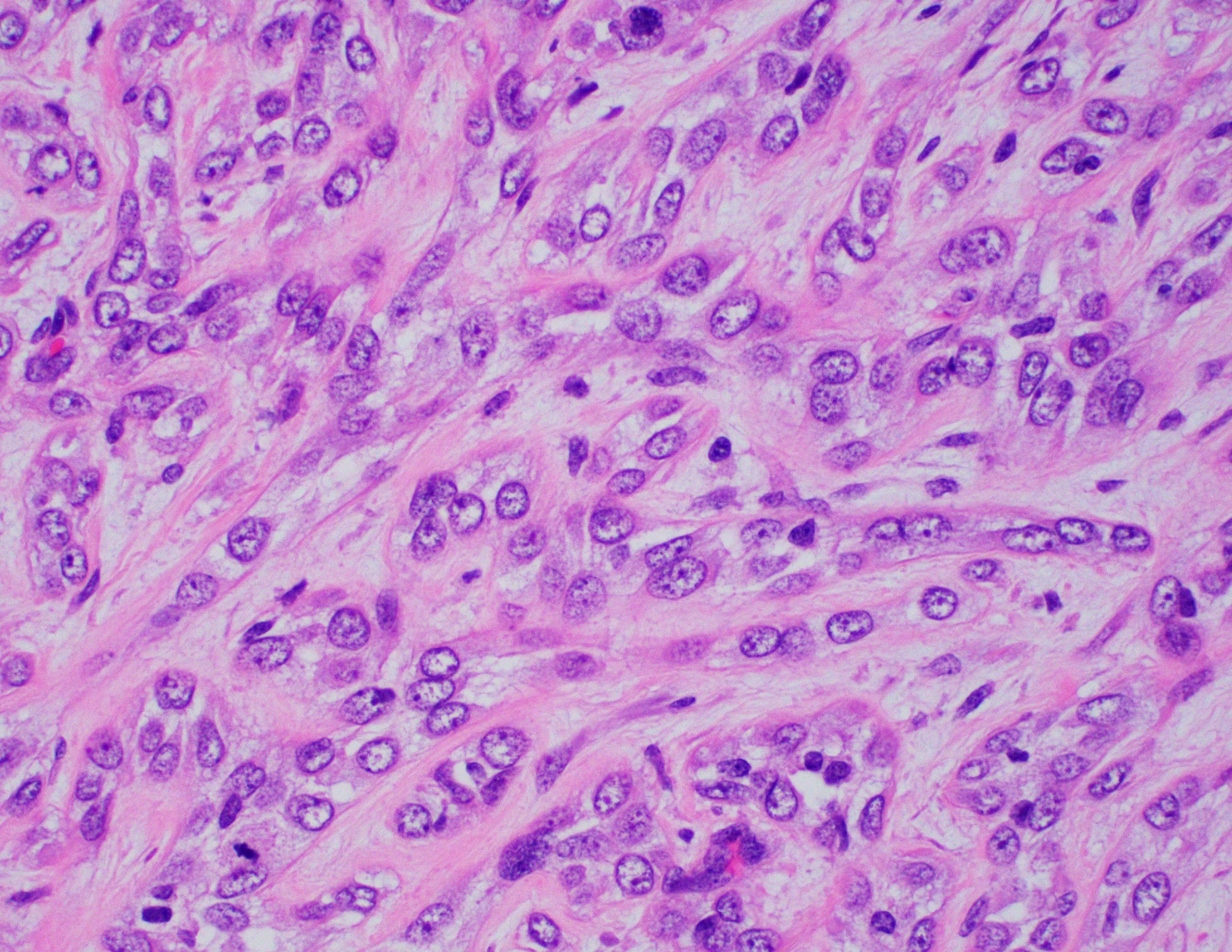
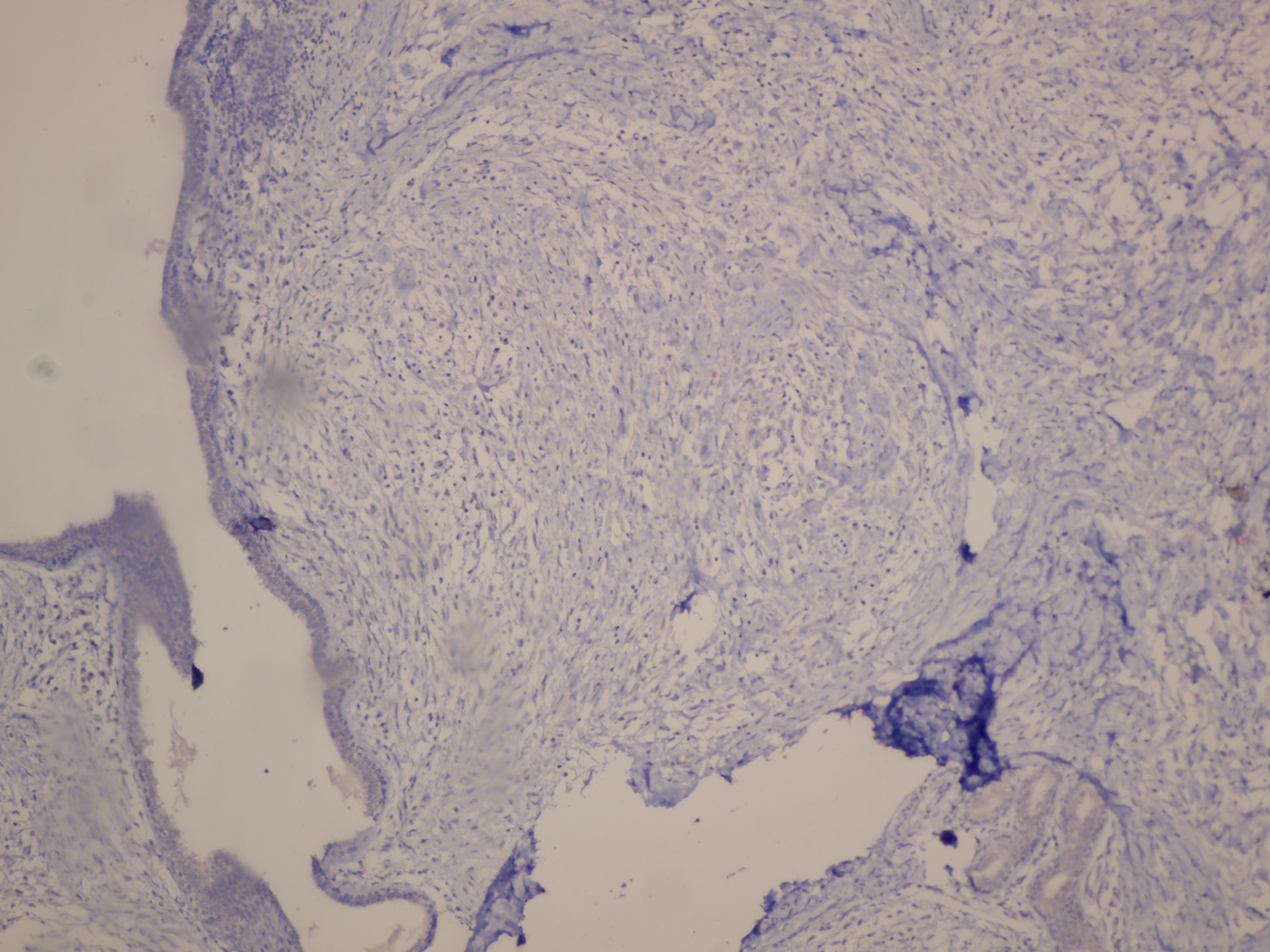
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Myoepithelioma:
- Dense spindle cell neoplasm; may be arranged in storiform pattern (J Cytol 2013;30:62)
- Tumor cells have eosinophilic cytoplasm, oval and regular nuclei (J Cytol 2013;30:62)
- May have polygonal cells with clear cytoplasm and hyperchromatic nuclei (J Cytol 2013;30:62)
- May infiltrate fat or surround normal ducts (J Cytol 2013;30:62)
- Few mitotic figures, no necrosis, no atypia (J Cytol 2013;30:62, Tunis Med 2004;82:324)
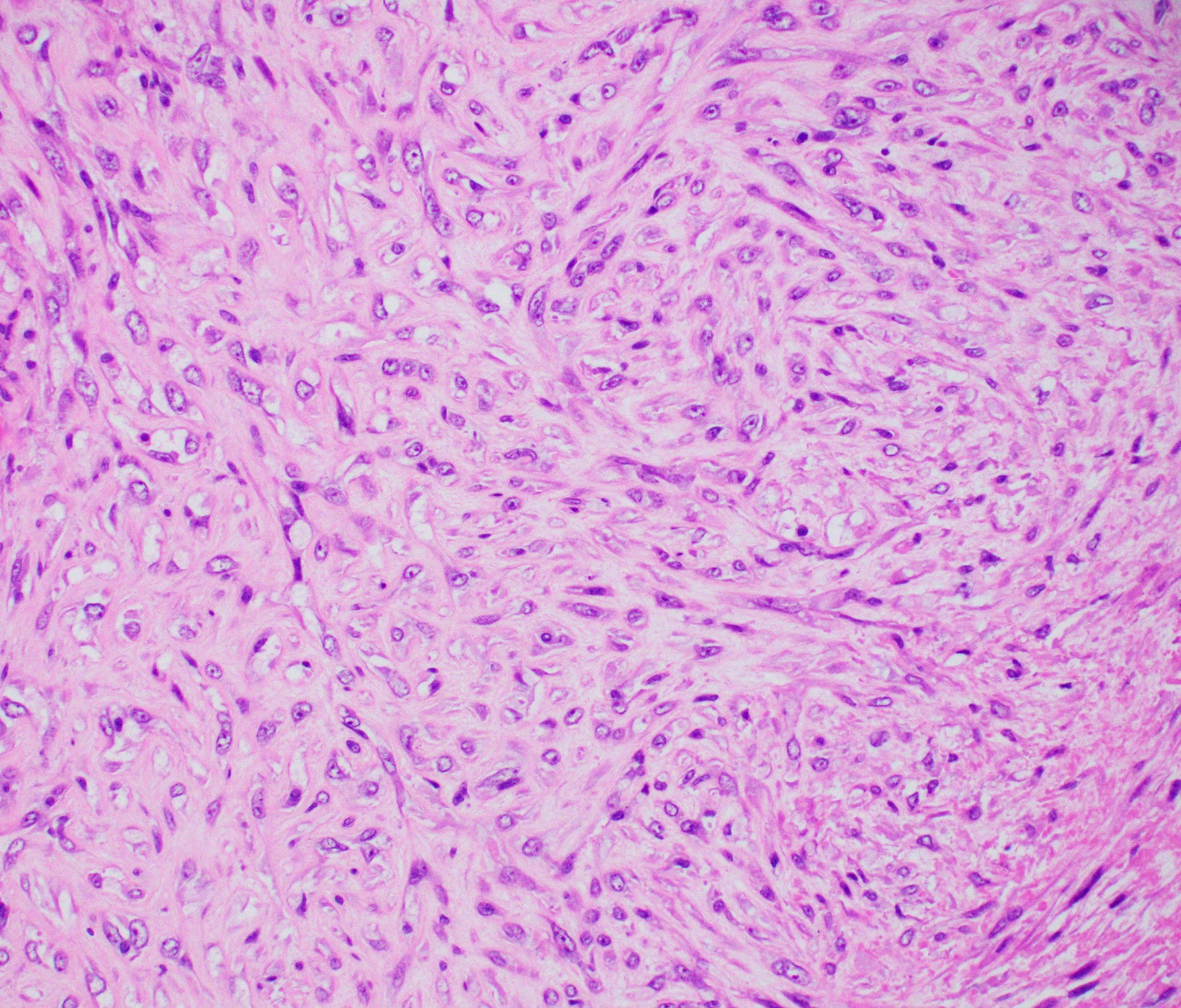
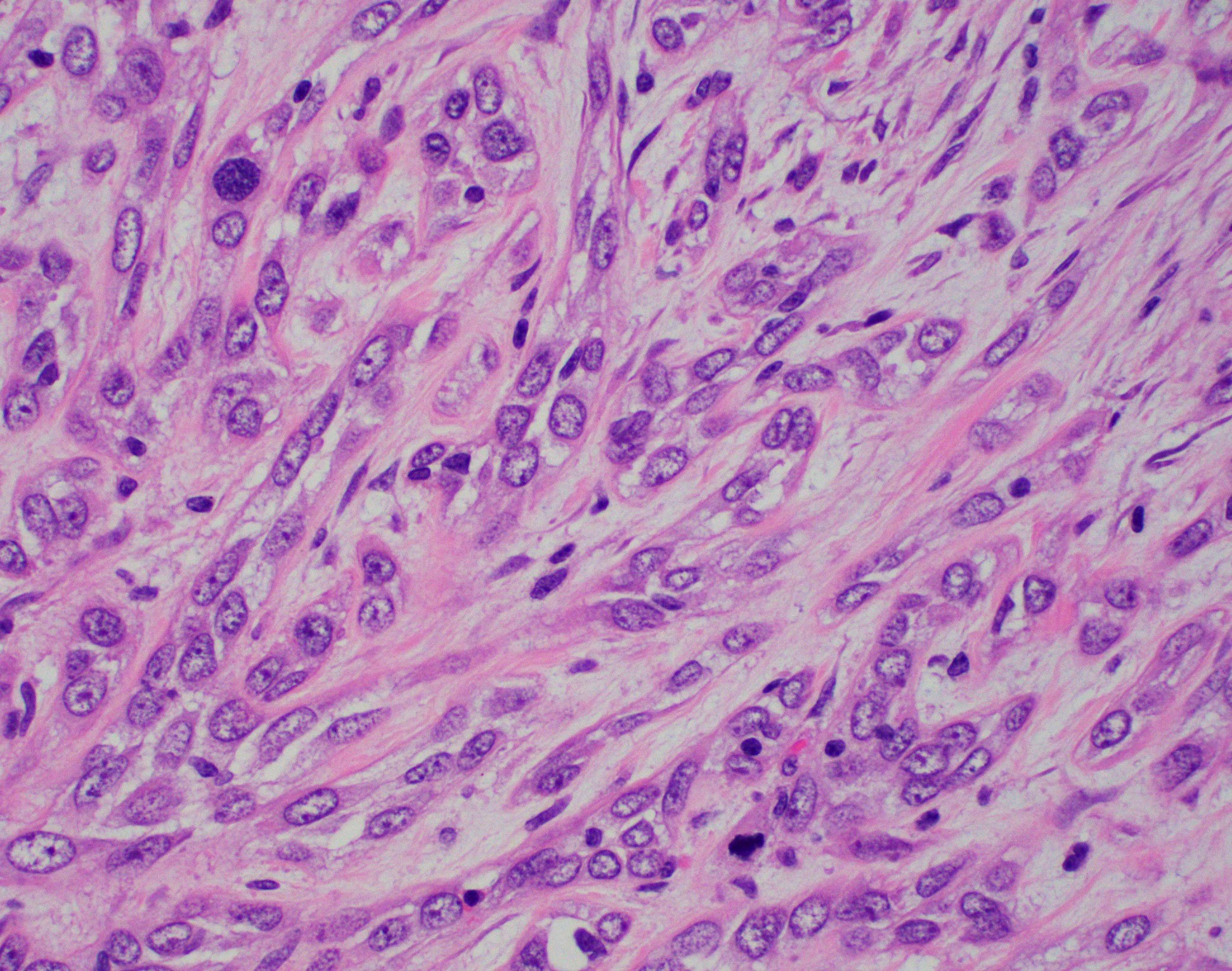
- Myoepithelial carcinoma:
- Plump, atypical spindle cells with readily identifiable mitotic figures (Breast Care (Basel) 2010;5:246)
- Mitotic activity ranges from 0 to 9 mitoses per 10 high power fields (Virchows Arch 2010;457:337)
- Variable amount of necrosis and cystic degeneration (Case Rep Oncol Med 2013;2013:164761)
- Clear cell and plasmacytoid variants (very rare) (Breast 2004;13:506)
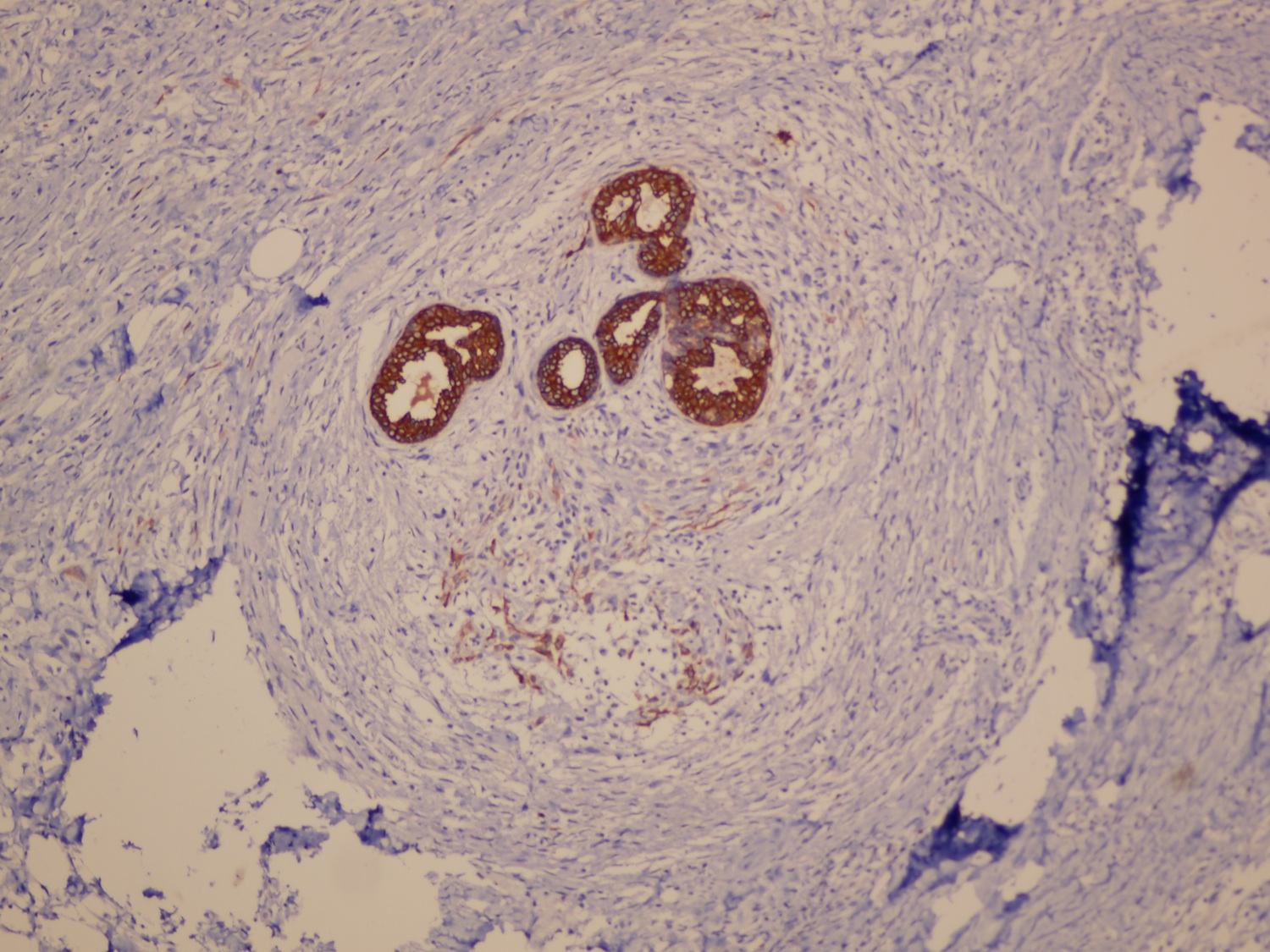
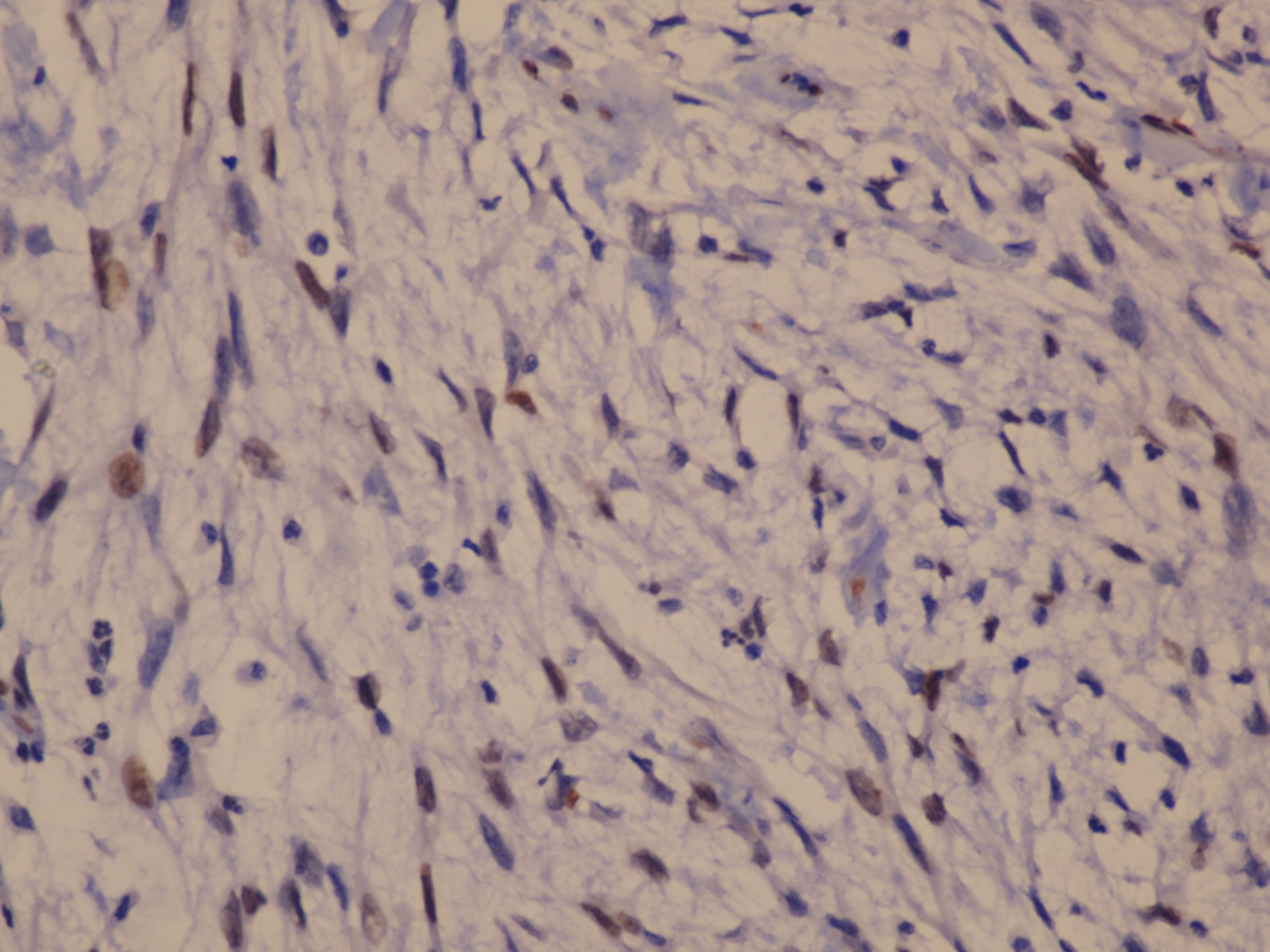
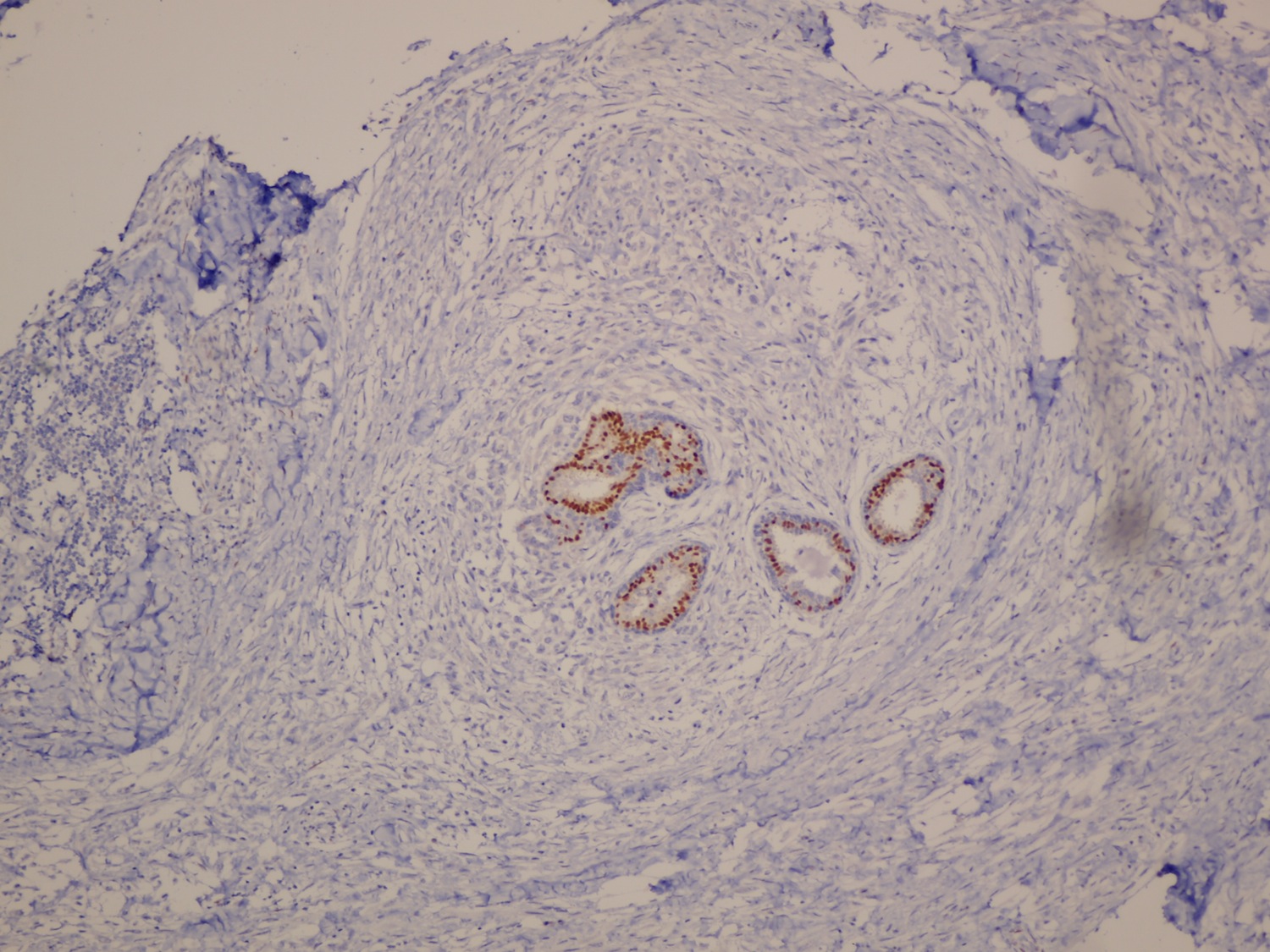
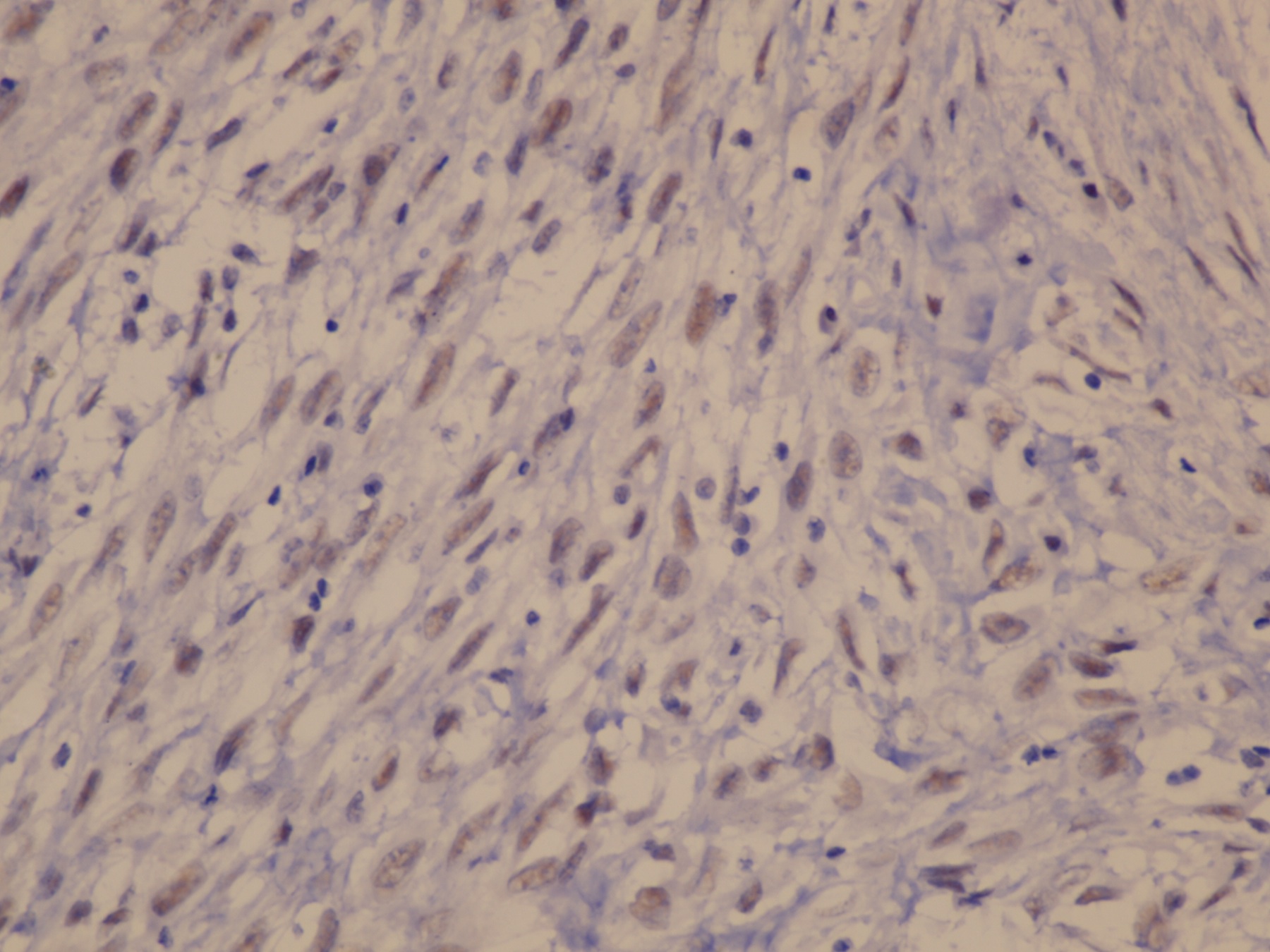
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Cellular smears showing single spindle or polymorphic, polygonal cells with dense blue cytoplasm and admixed groups of benign ductal epithelial cells and lymphocytes (Virchows Arch 2010;457:337, Cytojournal 2007;4:3)
- Granular metachromatic stromal component in the background (Cytojournal 2007;4:3)
Positive stains
- Myoepithelioma: broad spectrum keratin AE1 / AE3, EMA, alpha smooth muscle actin, calponin, caldesmon, vimentin, CD10, p63, S100
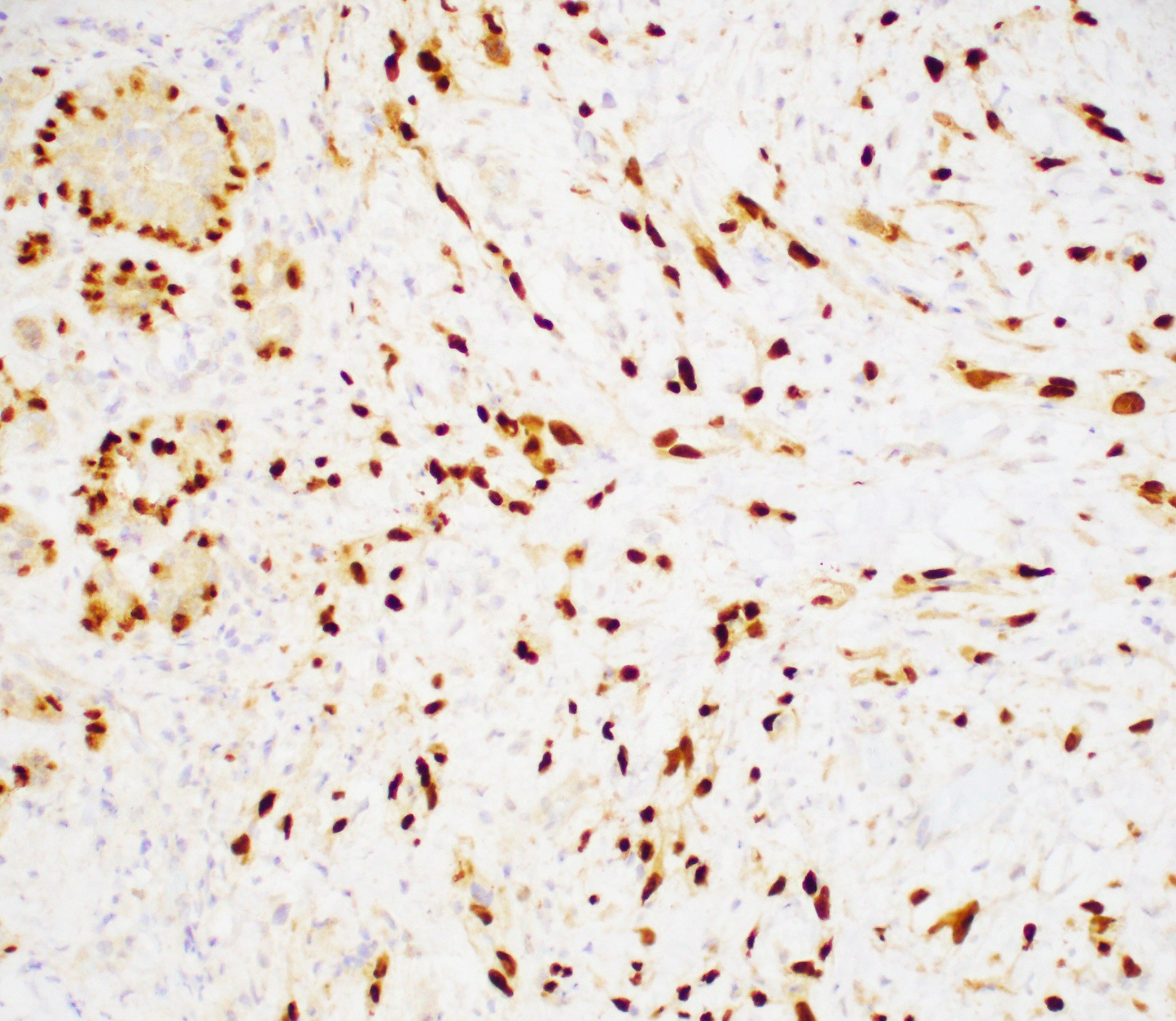
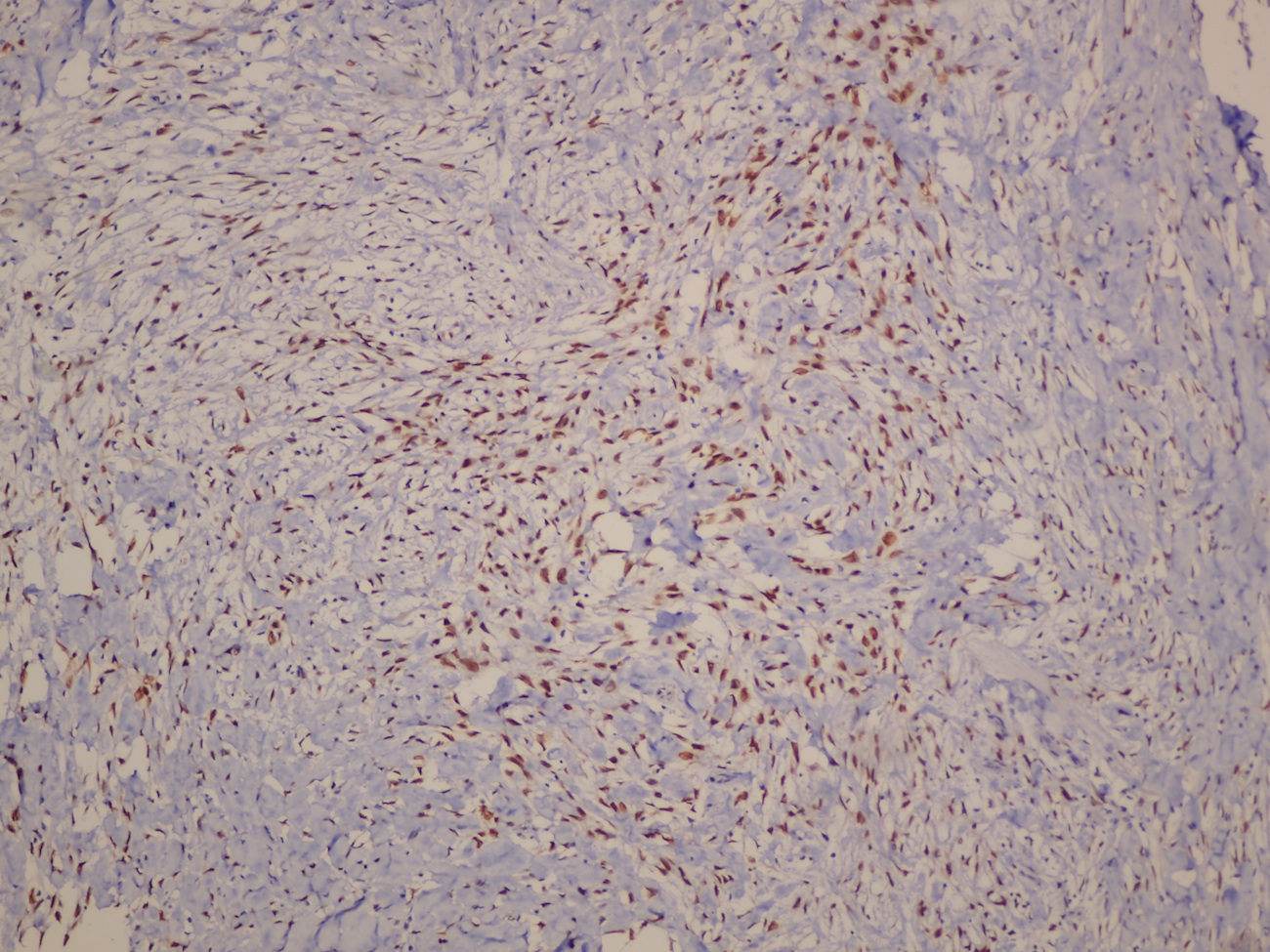
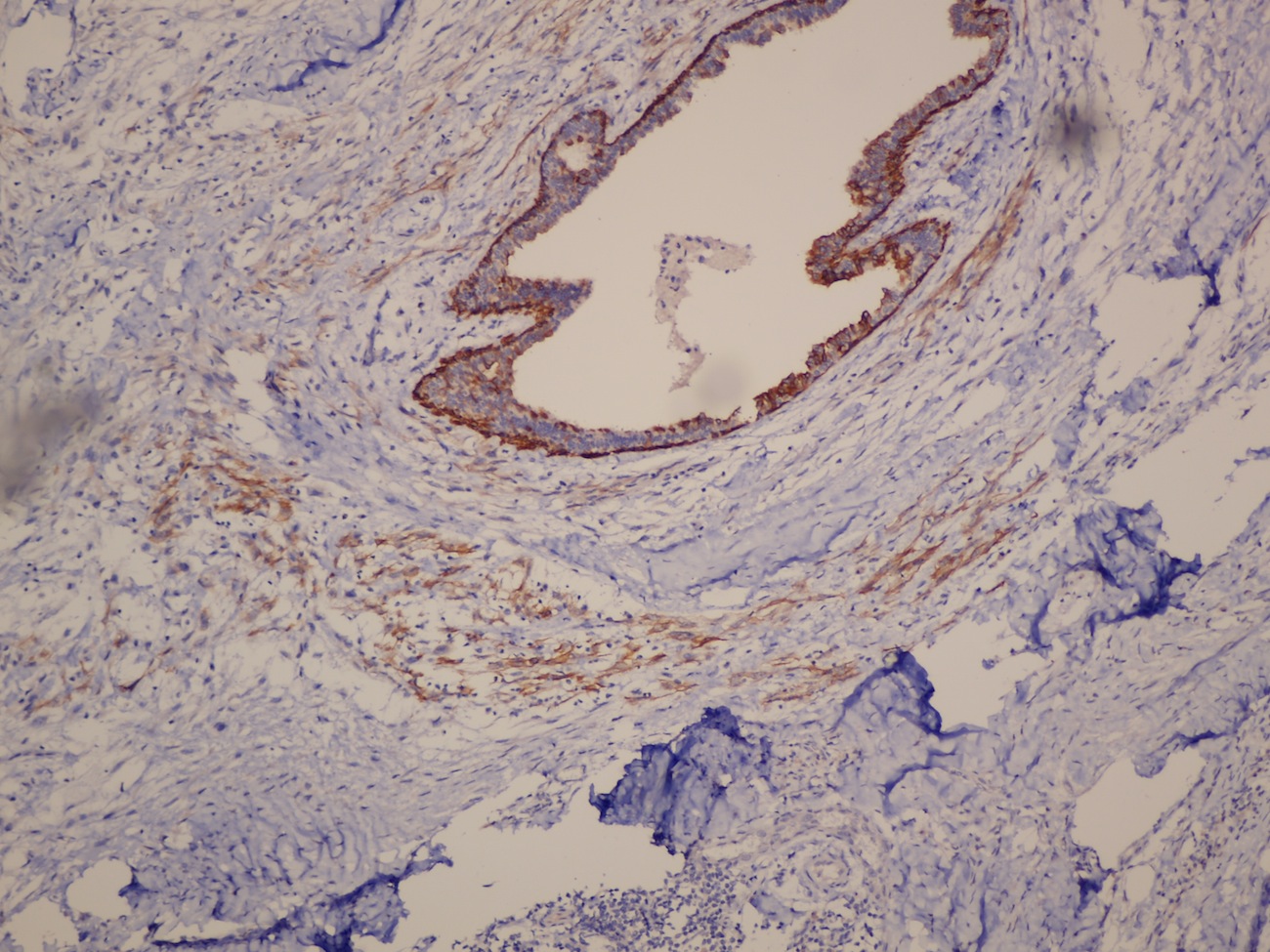
- Myoepithelial carcinoma:
- Strong and diffusely positive for p63, CD10, CK903 and CK5/6 (Virchows Arch 2010;457:337)
- Focal weak to diffuse positivity for calponin, S100 and SMA (Virchows Arch 2010;457:337)
- Strong positivity for EGFR (Virchows Arch 2010;457:337)
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Curvilinear bundles of tonofilaments (about 8 - 10 nm in diameter) usually located in perinuclear areas or centrally located in cytoplasmic extensions (Ultrastruct Pathol 1985;8:1)
- Subplasmalemmal bundles of microfilaments (about 5 - 7 nm in diameter) in cytoplasm of many spindle cells (Ultrastruct Pathol 1985;8:1)
- Tumor cells also show pinocytic vesicles, intermediate junctions, dense plaques (hemidesmosomes) and are poorly connected by desmosomes (Ultrastruct Pathol 1985;8:1)
- Dense bodies in the microfilament bundles (Ultrastruct Pathol 1985;8:1)
- Spindle cells show fragmented external lamina (Ultrastruct Pathol 1985;8:1)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Loss of 16q (3/10 cases), 17p (3/10), 11q (2/10) and 16p (2/10) (Lab Invest 2000;80:831)
- Basal specific microRNAs such as miR-126, miR-127-3p, miR-143, miR-145 and miR-199a-3p are upregulated (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2011;130:735)
- Luminal specific miR-200c and miR-429 are significantly lower expressed compared to luminal A, luminal B and basal-like breast cancer (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2011;130:735)
Sample pathology report
- Left breast, core biopsy:
- Spindle cell neoplasm (see comment)
- Comment: Histologic sections show a spindle cell neoplasm arranged in storiform pattern. The tumor cells have vesicular nuclei, prominent nucleoli, variable nuclear atypia and eosinophilic cytoplasm. Mitoses are readily identifiable (with up to 4 mitoses/10 high power fields). Focal areas of cystic degeneration and necrosis are seen. Immunohistochemistry shows tumor cells to be positive for p63 and cytokeratins 5/6 and 903 and negative for cytokeratin 7, desmin, ER, PR and HER2 / neu. Overall, findings are suggestive of metaplastic carcinoma, spindle cell type or myoepithelial carcinoma.
Differential diagnosis
- Metaplastic carcinoma:
- Variable group of breast carcinomas with mesenchymal differentiation
- Myoepithelial carcinoma is considered a subtype by WHO
- Spindle cell sarcoma:
- Negative for myoepithelial markers
- Leiomyosarcoma:
- Blunt ended nuclei with abundant cytoplasm
- Positive for desmin
- Fibromatosis:
- Infiltrative fibroblastic and myofibroblastic proliferation
- Minimal pleomorphism with no mitosis
- Positive for actin, desmin and S100
- Negative for cytokeratins
- Adenomyoepithelioma:
- Biphasic, circumscribed tumor composed of variable number of myoepithelial cells surrounding epithelial lined spaces
- Myofibroblastoma:
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
C. Myoepithelial carcinoma. The biopsy shows an atypical proliferation with plump spindle cells and readily identifiable mitoses. p63 positivity supports myoepithelial differentiation. The morphology is malignant, arguing against adenomyoepithelioma and myoepithelioma. Adenomyoepithelioma and adenoid cystic carcinoma additionally have a biphasic composition, making these answers incorrect. In this case, tumor cells are of uniform myoepithelial differentiation, making the best diagnosis myoepithelial carcinoma, which is considered a metaplastic carcinoma of no special type by the WHO.
Comment Here
Reference: Myoepithelioma and myoepithelial carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Myoepithelioma and myoepithelial carcinoma