Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Sites | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Reisenbichler ES Spread and metastases. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantcarcinomaspread.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- See also Staging topic
- Breast carcinoma spreads by axillary, interpectoral and internal mammary lymphatic and vascular channels first to regional lymph nodes
- Regional lymph nodes for breast carcinoma include ipsilateral intramammary, internal mammary, axillary and supraclavicular lymph nodes for staging purposes (pN)
- Metastases to any other lymph nodes, including cervical or contralateral internal mammary or contralateral axillary lymph nodes, are considered distant metastases for staging purposes (pM)
- Additional sites of distant metastases vary depending on tumor type and receptor status but most often include bone, lung, brain and liver
- Circulating tumor cells or incidental tumor deposits (≤ 0.2 mm) called microscopic tumor cells do not constitute metastatic disease
Essential features
- Distant metastases typically occur earlier in triple negative tumors (within 5 years from primary diagnosis) compared with late spread in hormone receptor+ tumors (Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e2909, J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2018 Apr 19 [Epub ahead of print])
- Hormone receptor and HER2 status may change
ICD coding
- C77.3: Secondary and unspecified malignant neoplasm of axilla and upper limb lymph nodes
- C77.9: Secondary and unspecified malignant neoplasm of lymph node, unspecified
- C78.00: Secondary malignant neoplasm of unspecified lung
- C79.31: Secondary malignant neoplasm of brain
- C79.51: Secondary malignant neoplasm of bone
Sites
- Cervical, contralateral internal mammary and contralateral axillary lymph nodes are distant metastases (pM1)
- Ipsilateral axillary, intramammary, internal mammary and supraclavicular lymph nodes are considered regional nodes, not distant, and are part of pathologic nodal staging of the primary tumor (pN)
- HER2+ and triple negative (ER- / PR- / HER2-) breast tumors typically recur within 5 years of primary diagnosis (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2018 Apr 19 [Epub ahead of print])
- Basal-like tumors have higher rates of brain, lung and distant nodal metastases than liver and bone (J Clin Oncol 2010;28:3271)
- ER+ tumors often recur after long periods and have a propensity to first metastasize to bone (Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e2909)
- Malignant phyllodes tumors and primary sarcomas of the breast have a propensity to metastasize to lungs, bones and liver (Br J Cancer 2004;91:237)
Radiology description
- Imaging studies are utilized to screen for regional and distant metastases, focusing on organs most frequently involved in breast carcinoma
- Axillary ultrasound or MRI may be used for preoperative evaluation of regional lymph nodes to determine clinical stage
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines version 1.2018 for preoperative workup (NCCN: NCCN Guidelines [Accessed 24 May 2018]):
- For clinical stage I - IIB: additional studies only if clinical signs or symptoms (i.e. bone scan if bone pain or elevated alkaline phosphatase; abdominal CT or MRI if abnormal liver function tests or abdominal symptoms)
- For clinical stage IIIA (T3, N1, M0): strongly consider chest, abdominal and pelvic CT with contrast or MRI, bone scan, FDG PET / CT
Prognostic factors
- ER status and lymph node involvement are significant prognostic factors for late skeletal recurrence (Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e2909)
- Patients with bone metastases at site of first relapse have better overall survival than patients with visceral metastases at site of first relapse (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2000;59:271)
- Conversion from negative to positive ER or PR or remaining receptor negative is significantly worse than patients remaining receptor positive (Cancer 2012;118:4929)
- ER or PR conversion from positive in the primary breast tumor to negative in distant metastases is a poor prognostic indicator (Cancer 2012;118:4929)
Case reports
- 47 year old woman with breast cancer metastases to the gastrointestinal tract, mimicking hyperplastic polyps (Surg Case Rep 2018;4:23)
- 51 year old woman with menorrhagia, found to have an undiagnosed invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast, metastatic to the endometrium (Am J Case Rep 2018;19:494)
- 65 year old woman with lobular breast carcinoma, metastatic to anorectum (BMC Res Notes 2018;11:268)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Metastatic tumors often resemble the morphology of the primary tumor
- Only the stromal component of a malignant phyllodes tumor will metastasize and morphologically resembles a primary sarcoma
- Receptor status in distant metastases often changes from the original primary tumor receptor status (J Natl Cancer Inst 2018 Jan 5 [Epub ahead of print]):
- Estrogen receptor (ER):
- 22.5% positive primary to negative in the metastasis
- 21.5% negative primary to positive in the metastasis
- Progesterone receptor (PR):
- 49.4% positive primary to negative in the metastasis
- 15.9% negative primary to positive in the metastasis
- HER2:
- 21.3% positive primary to negative in the metastasis
- 9.5% negative primary to positive in the metastasis
- Estrogen receptor (ER):
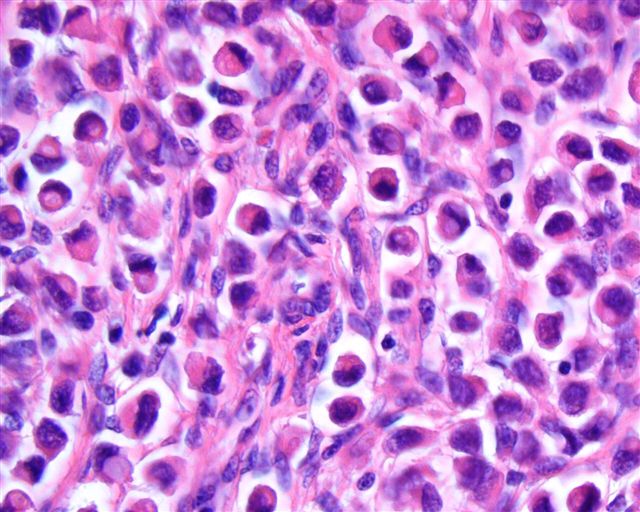
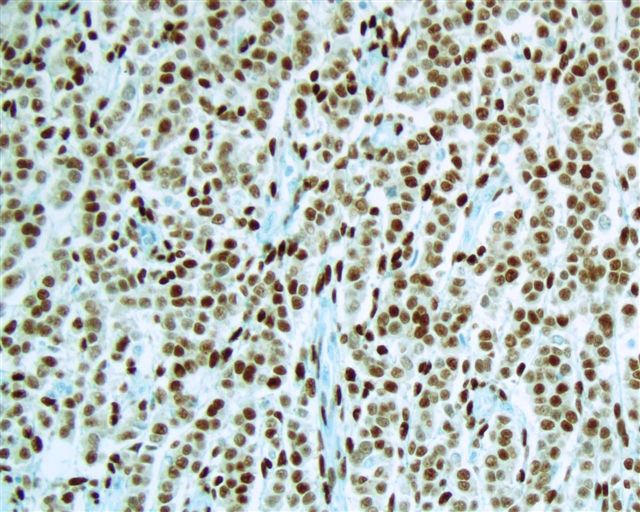
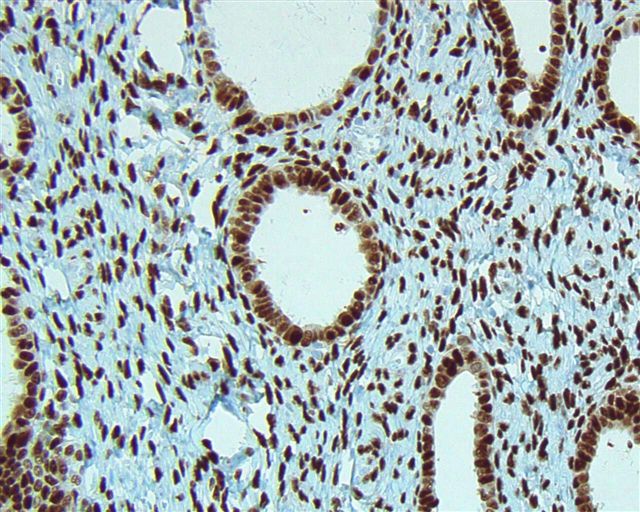
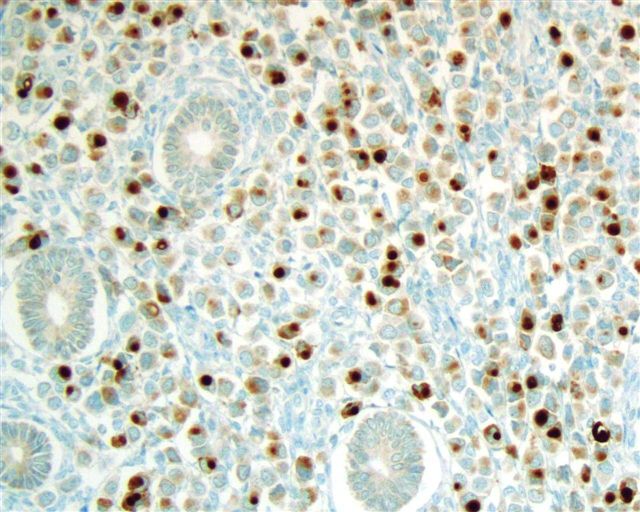
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Emily S. Reisenbichler, M.D.
Case #125
Positive stains
- GATA3: 96% of non triple negative tumors and 63 - 87% of triple negative tumors, depending on antibody clone (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2016;24:609)
- CK7
- GCDFP-15: 69% of non triple negative tumors and 10% of triple negative tumors
- Mammaglobin A: 61% of non triple negative tumors and 17% of triple negative tumors
- SOX10: 38% of triple negative tumors; rarely positive in non triple negative tumors (Hum Pathol 2017;67:205, Int J Surg Pathol 2021;29:470, Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:293)
Differential diagnosis
- Benign glandular inclusions in axillary lymph nodes, such as endosalpingiosis, may mimic metastatic breast cancer (Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:21)
- Morphology differences from the primary breast carcinoma and the presence of p63+ myoepithelial cells support a diagnosis of benign glandular inclusions
- Sarcoidosis may mimic metastatic breast cancer (Clin Breast Cancer 2007;7:804)
Board review style question #1
What is the most likely combination of the site of breast carcinoma metastasis, tumor type and timing of metastases from primary diagnosis?
- ER+ / PR+ / HER2- metastasis to bone 10 years after primary diagnosis
- ER- / PR- / HER2- metastasis to bone 10 years after primary diagnosis
- ER+ / PR+ / HER2- metastasis to brain 2 years after primary diagnosis
- ER- / PR- / HER2- metastasis to ovary 10 years after primary diagnosis
Board review style answer #1
A. ER+ / PR+ / HER2- metastasis to bone 10 years after primary diagnosis.
Hormone receptor+ (estrogen receptor+ / progesterone receptor+) tumors are more likely to metastasize after long periods and the most frequent site of first distant metastases is the bone. Triple negative (estrogen receptor- / progesterone receptor- / HER2-) tumors typically metastasize within 5 years of primary diagnosis.
Comment Here
Reference: Spread and metastases
Comment Here
Reference: Spread and metastases