Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Jorns JM. Adenomyoepithelial adenosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastadenomyoepithelialadenosis.html. Accessed December 18th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Uncommon variant of adenosis with proliferation of epithelial and myoepithelial cells
Essential features
- Lobulocentric proliferation of both epithelial and myoepithelial components
- Prominent myoepithelial cells, 1 - 3 layers
Terminology
- Tubular variant of adenomyoepithelioma (Schnitt: Biopsy Interpretation of the Breast, 3rd Edition, 2017)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- No known associations
- Wide age range but most frequent in third to fourth decades (WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board: Breast Tumours, 5th Edition, 2019)
Sites
- Lobulocentric but otherwise no specific location within the breast
Pathophysiology
- Unknown
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- May present with a palpable mass
- May be a precursor to benign adenomyoepithelioma, malignant adenomyoepithelioma or invasive duct carcinoma (Am J Clin Pathol 1988;89:308, Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 1984;405:55, Springerplus 2013;2:50)
Diagnosis
- Histologic examination of tissue with or without immunohistochemistry
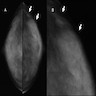
Radiology description
- No specific features
- May show asymmetry, architectural distortion or mass with irregular margins, with or without microcalcifications
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Unknown but progression to malignancy may be associated with older age (> 50 years) and mass on imaging (Springerplus 2013;2:50)
Case reports
- 17 year old girl with a palpable lump (Turk Patoloji Derg 2017;33:240)
- 35 year old woman with adenomyoepithelial adenosis associated with breast cancer (Springerplus 2013;2:50)
- 46 year old woman with a palpable mass (Breast Care (Basel) 2008;3:427)
- Malignant progression of adenomyoepithelial adenosis of breast (Pathol Int 1994;44:475)
Treatment
- Excision recommended due to possibility of recurrence and association with malignancy
- Best predictors of recurrence are initial incomplete excision and close margins
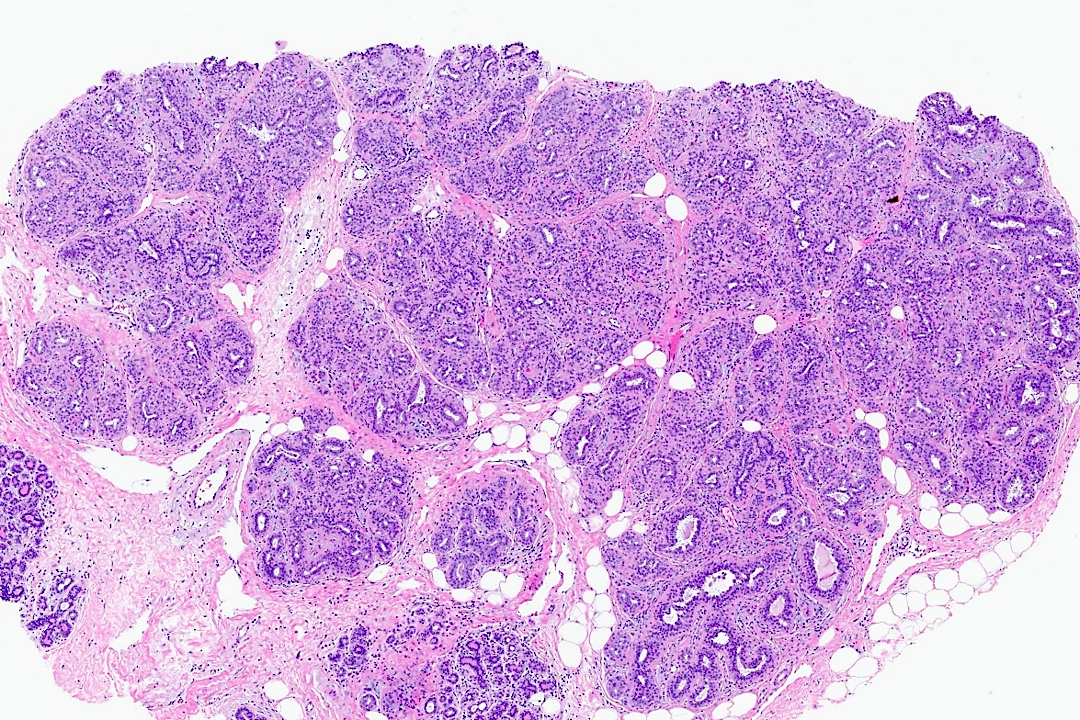
Gross description
- May form a firm mass with circumscribed or ill defined borders or may be grossly indistinguishable from surrounding fibrotic breast tissue
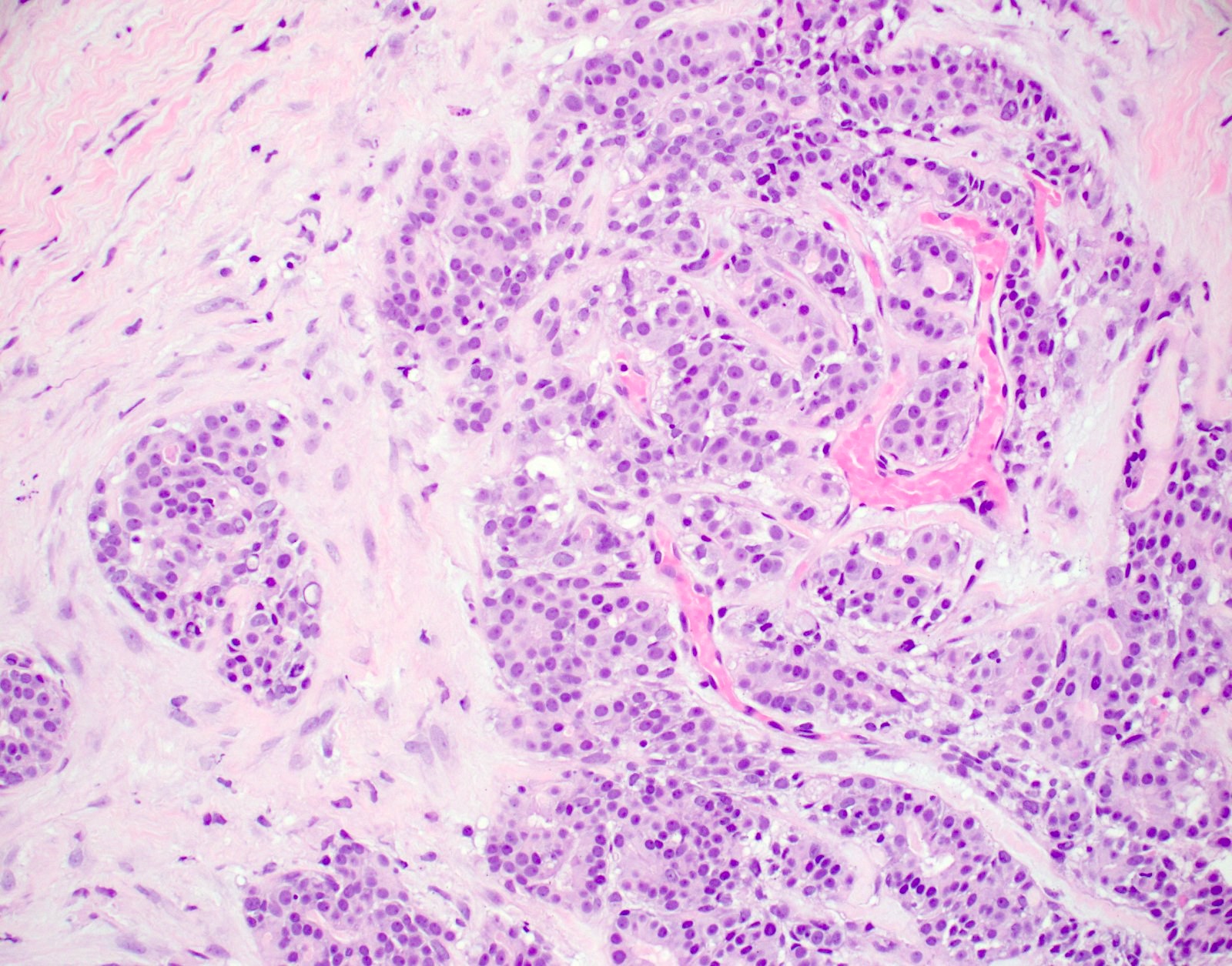
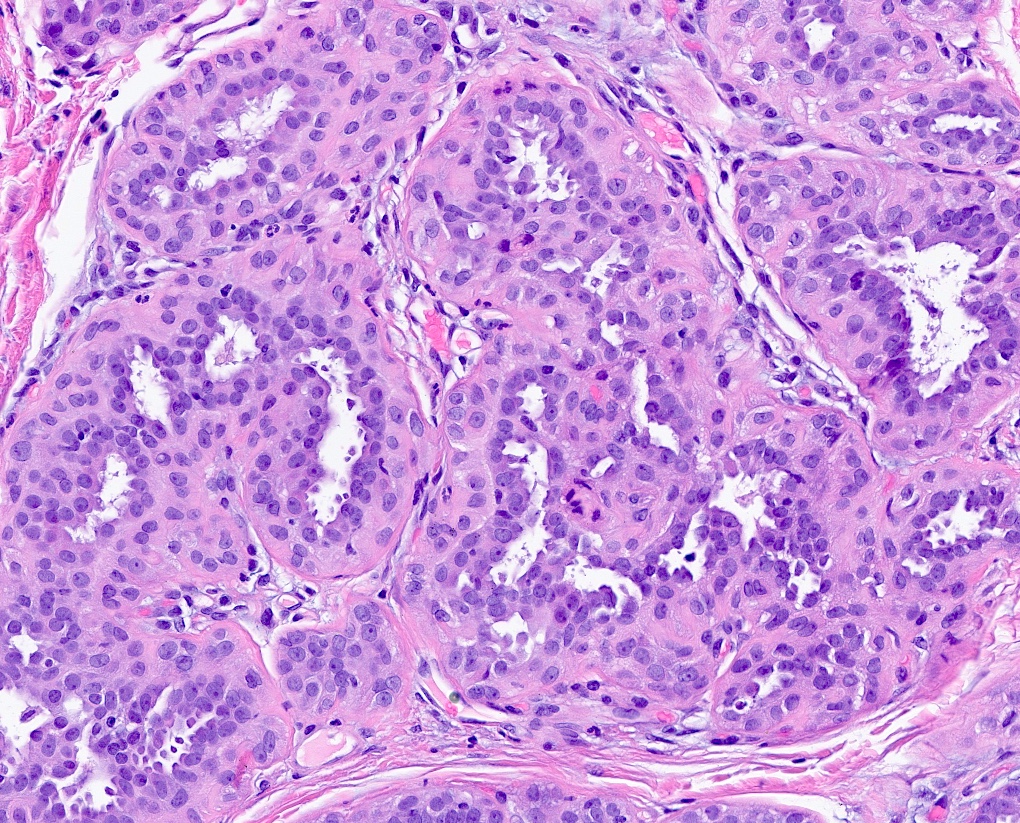
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Multiple foci of haphazardly arranged ducts with eosinophilic granular secretions
- Lined by cuboidal to columnar cells surrounded by hyperplastic myoepithelial cells
- Resembles microglandular adenosis but with larger and more irregularly shaped glands, taller lining epithelial cells with eosinophilic granular cytoplasm and bland basal nuclei
- May show apocrine or squamous metaplasia (Breast Care (Basel) 2008;3:427)
- May have mild nuclear atypia
- Rare to no mitotic activity
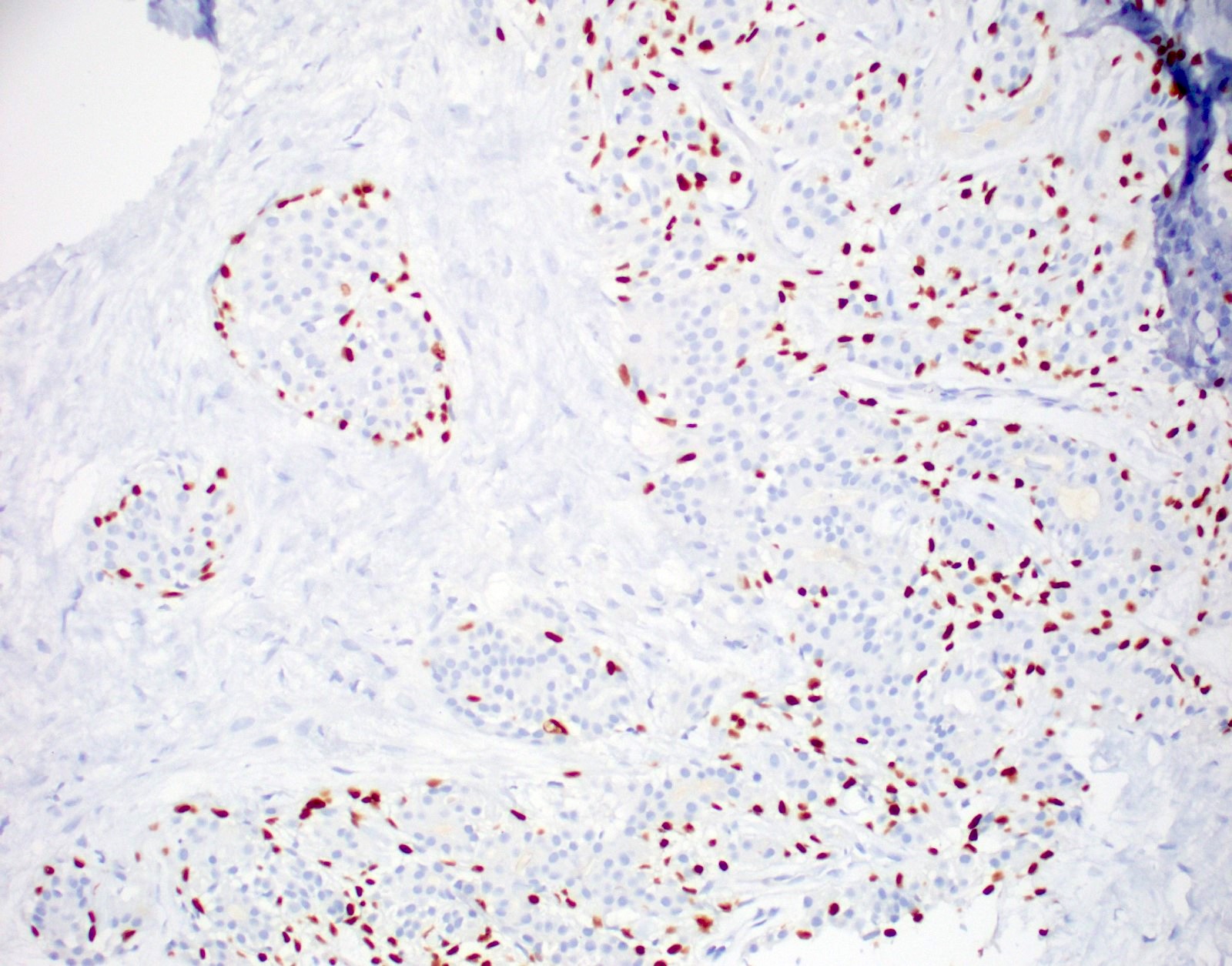
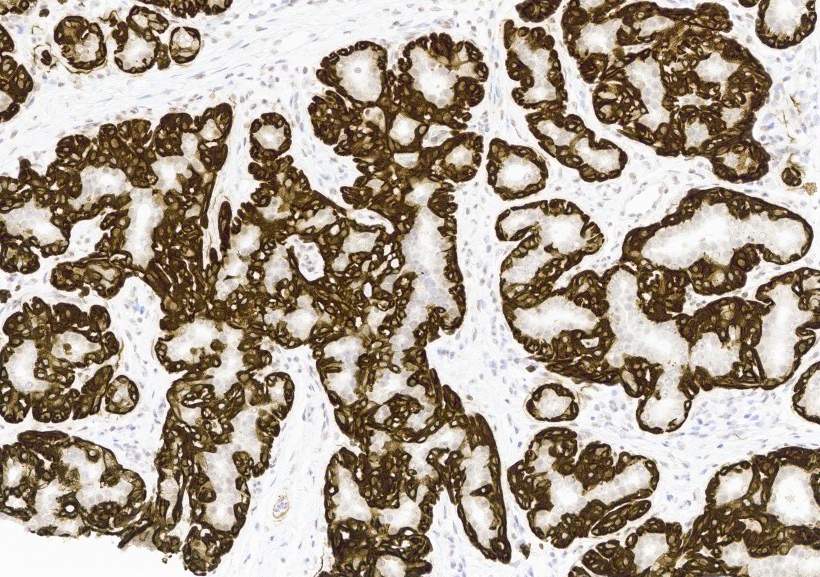
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Myoepithelial cells are positive for p63, CK5/6, S100, alpha smooth muscle actin
Sample pathology report
- Right breast, core biopsy:
- Benign breast tissue with adenomyoepithelial adenosis
Differential diagnosis
- Cannot be distinguished from a microscopic adenomyoepithelioma
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
A. Adenomyoepithelioma.
The pictured lesion is adenomyoepithelial adenosis, an uncommon variant of adenosis with a prominent myoepithelial component. This benign lesion may be difficult to distinguish from adenomyoepithelioma, which forms a circumscribed tumor but has similar microscopic features. Adenomyoepithelial adenosis, like other adenosis variants, may have similar features to microglandular adenosis or low grade invasive ductal carcinoma; however, these lesions lack myoepithelium, which is readily evident in adenomyoepithelial adenosis. Phyllodes tumor is a fibroepithelial neoplasm with dissimilar features, namely stromal proliferation with a resulting leaf-like growth pattern.
Comment Here
Reference: Adenomyoepithelial adenosis
Comment Here
Reference: Adenomyoepithelial adenosis