Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Ud Din N. Simple bone cyst. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bonesolitarybonecyst.html. Accessed December 22nd, 2024.
Definition / general
- A benign, intramedullary, mostly unilocular cystic lesion with a fibrous tissue wall containing serous or serosanguineous fluid
Essential features
- Cystic bone lesion with compatible radiological features
- Cyst lacks epithelial lining
- Fibrin-like deposits in the cyst wall, which organize and mineralize, forming immature and mature bone as well as cementum-like structures
Terminology
- Solitary bone cyst
- Unicameral bone cyst (no longer recommended for use by WHO)
ICD coding
- ICD-11: FB80.5 - solitary bone cyst
Epidemiology
- 85% occur during first 2 decades (J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2000;8:217)
- M > F (3:1)
Sites
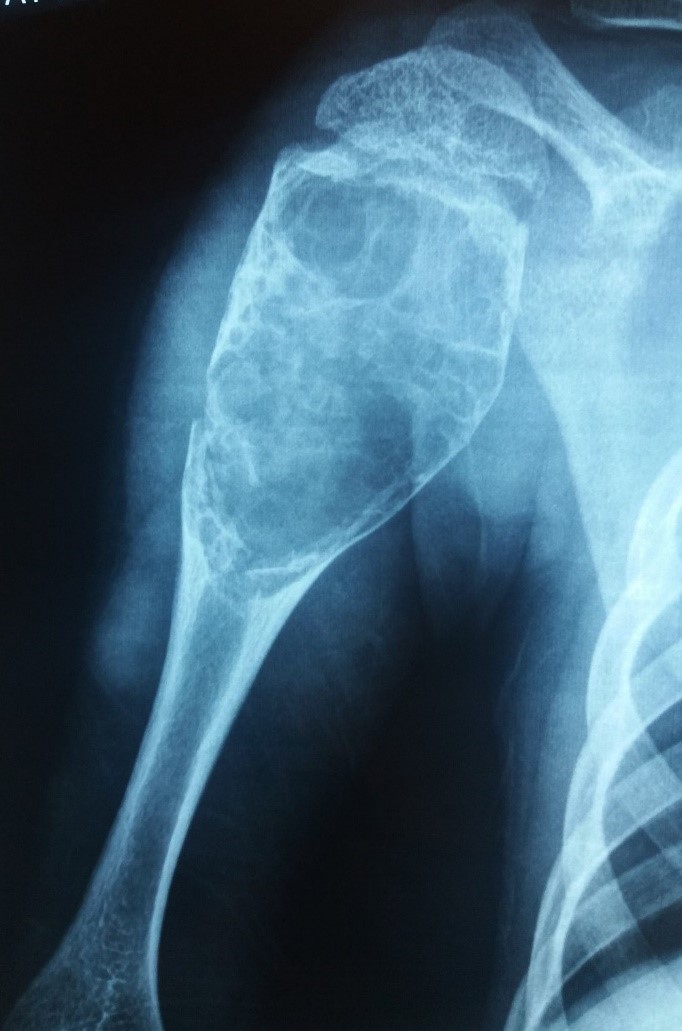
- Mostly involves appendicular skeleton, metaphysis of proximal humerus and proximal femur (Ann Diagn Pathol 2014;18:1)
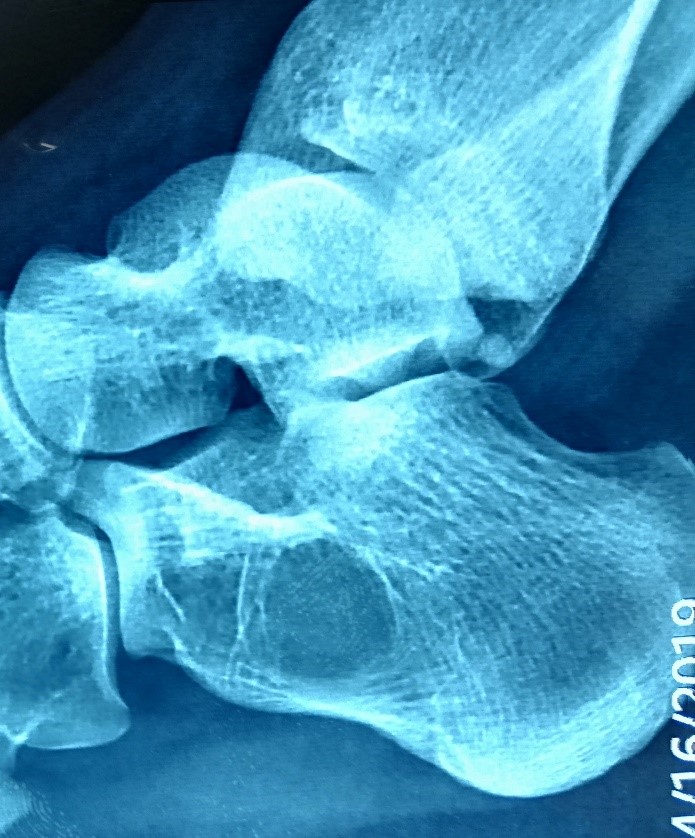
- Calcaneum, talus and pelvic bones (iliac wings) are less frequently involved and occur in older patients
- May also involve radius, sacrum, spine and jaw bones
Pathophysiology
- The exact pathogenesis is unknown; thought to be reactive or developmental in nature, probably related to a disturbance in growth at the epiphyseal plate
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Most are asymptomatic
- Others are diagnosed after pathological fracture (J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2014;22:295)
- Local pain and swelling due to fracture
Diagnosis
- Requires correlation of plain Xray findings with histological features
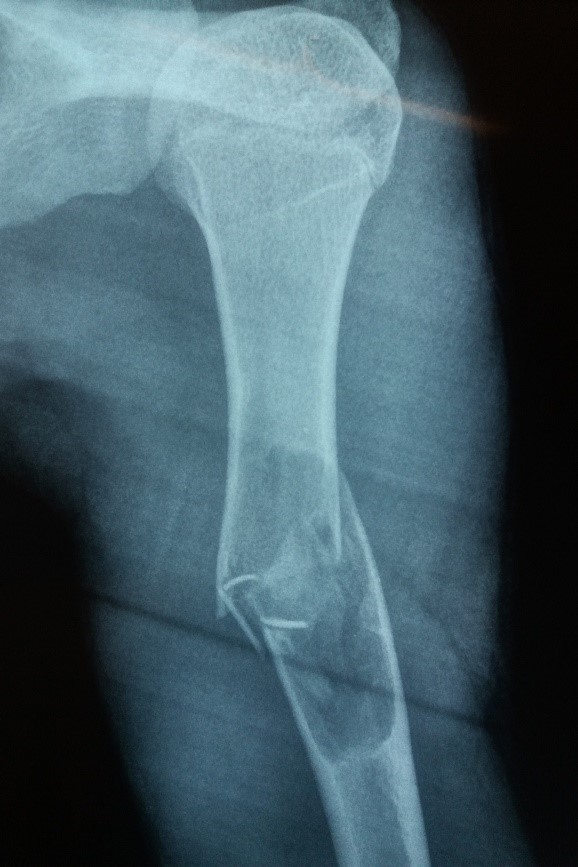
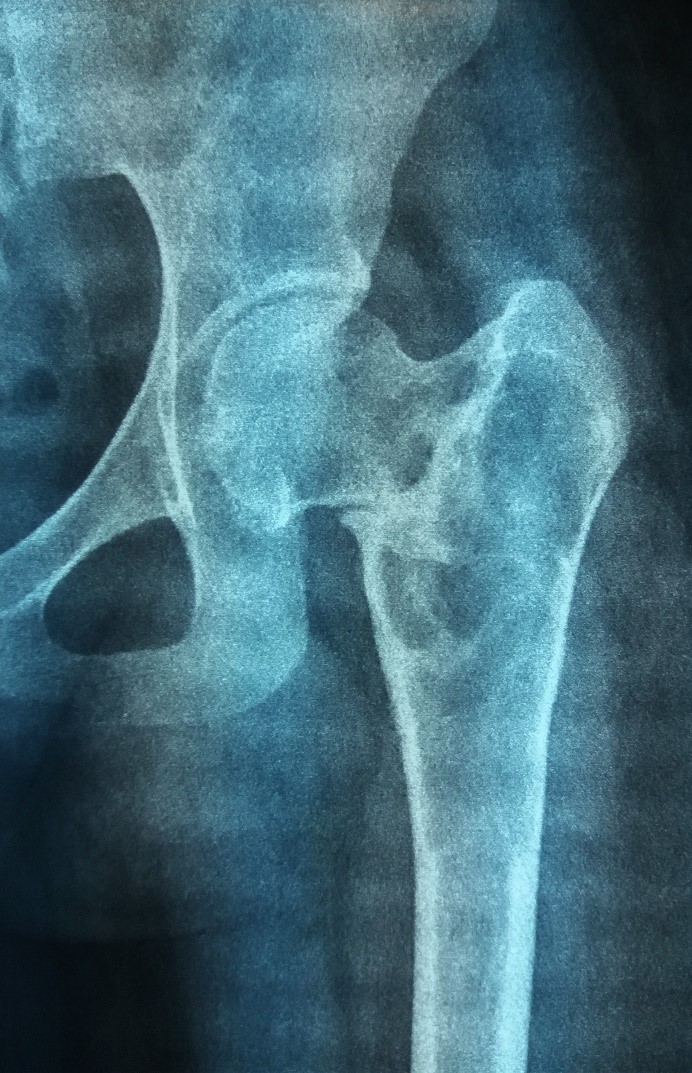
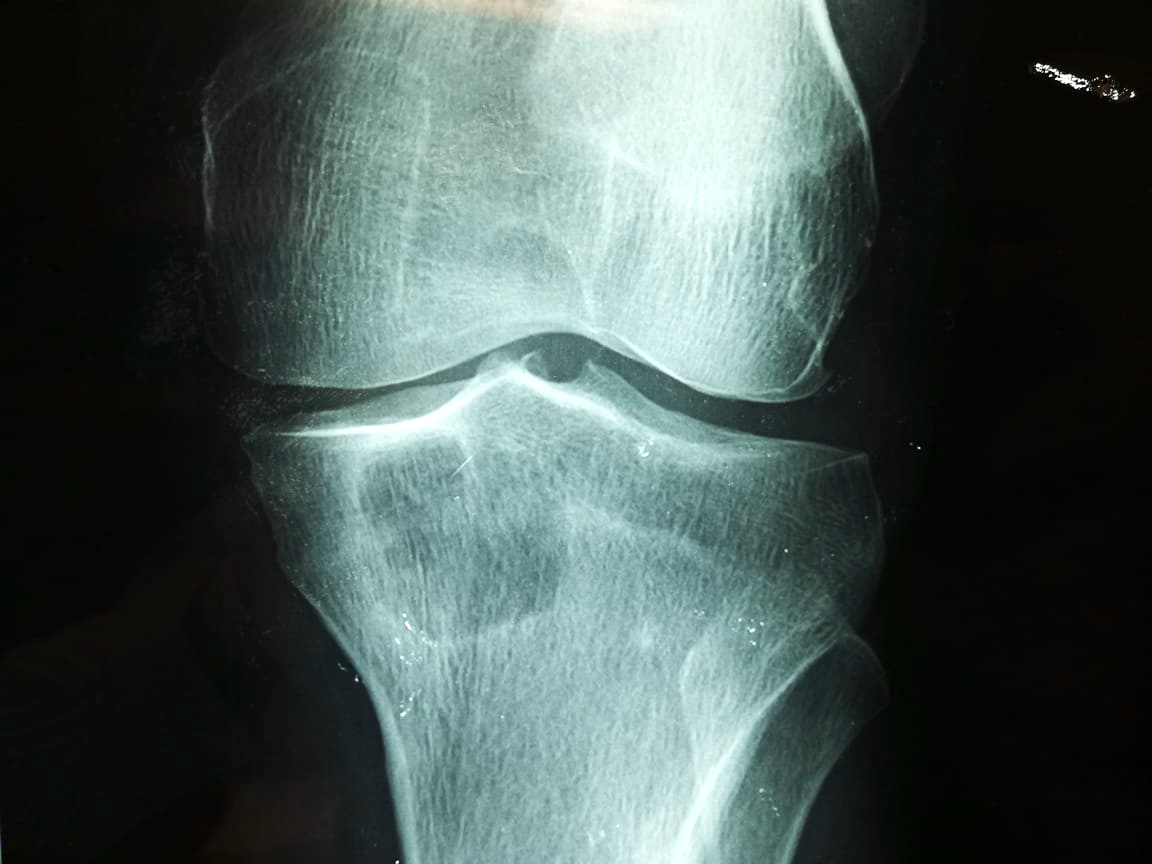
Radiology description
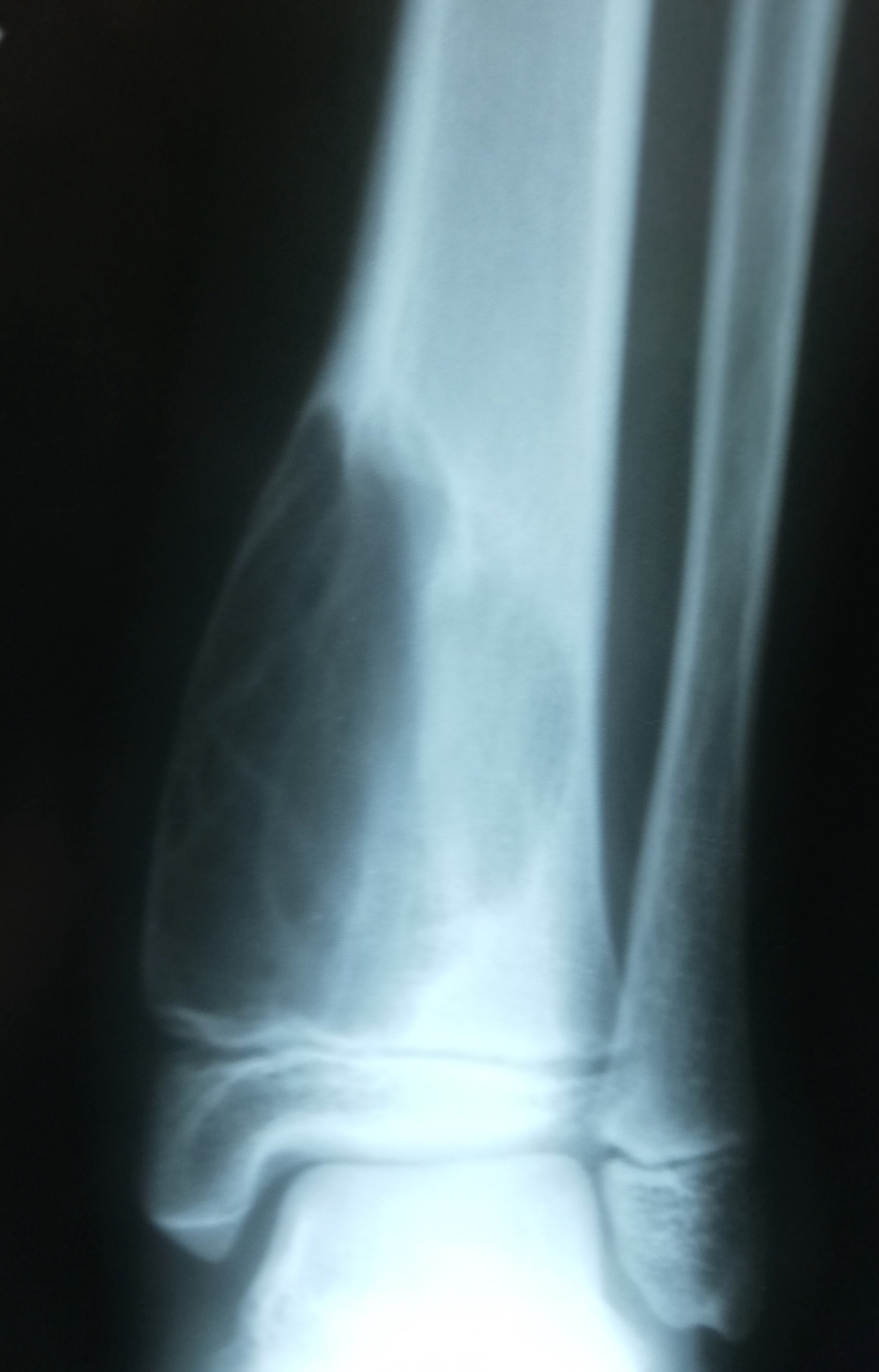
- Xray
- Intramedullary unilocular radiolucent lesion with symmetric expansion of cortex
- When a pathological fracture occurs, cortical bone fragments float within cyst fluid (called fallen leaf sign); this phenomenon is pathognomonic of simple bone cyst (Skeletal Radiol 1989;18:261)
- Another pathognomonic sign is presence of a gas bubble in most nondependent area of simple bone cyst called rising bubble sign (Skeletal Radiol 2009;38:597)
- Multilocular appearance during healing of repeated fractures by multiple septation
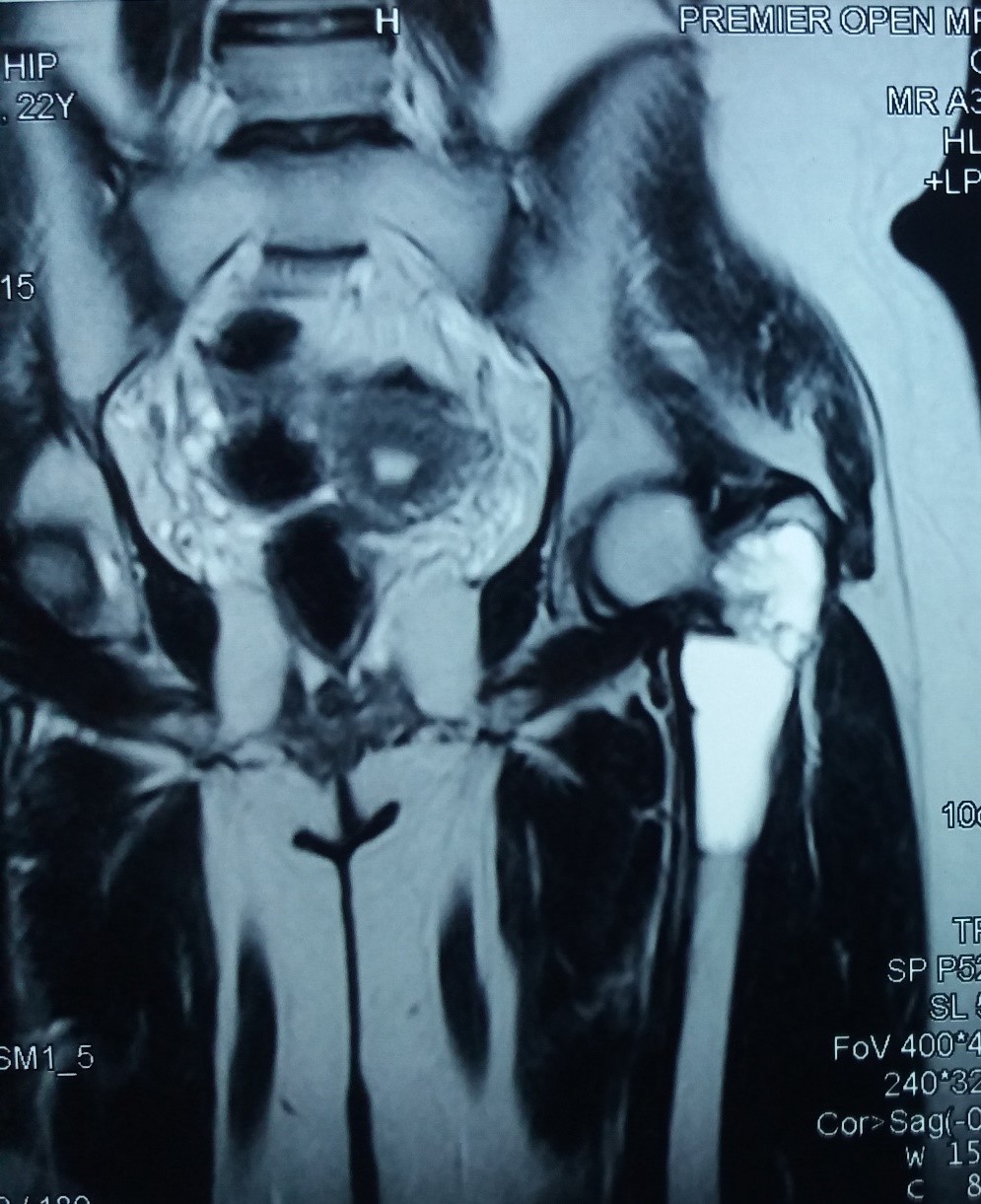
- CT and MRI
- Cystic lesion with well circumscribed borders and homogenous fluid attenuation are CT findings
- MRI shows high signal intensity on T2 weighted imaging, thus confirming increased fluid content and low signal intensity on T1 weighted images (Clin Orthop Relat Res 1999;366:186)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Overall prognosis is good
- Local recurrence seen in 10 - 20% (Clin Orthop Relat Res 2005;439:136)
- Unfavorable prognostic factors include (J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2010;18:215):
- Age ≤ 5 years
- Large cyst size
- Pathological fracture
- Poorer prognosis if cyst near epiphysis
Case reports
- 12 year old boy with simple bone cyst of mandible (BMJ Case Rep 2014;2014:bcr2013200945)
- 12 year old girl with simple bone cyst of iliac bone (Hip Pelvis 2014;26:202)
- 20 year old man with simple bone cyst of calcaneum (Rom J Morphol Embryol 2017;58:689)
- 25 year old man with simple bone cyst of distal radius (BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2014;15:202)
- 26 year old man with simple bone cyst of humerus (World J Surg Oncol 2017;15:102)
Treatment
- Curettage with bone graft
- Cyst fluid aspiration and then injecting steroids
Gross description
- If an intact cyst is removed
- Straw or clear fluid filled large intramedullary cavity
- Usually unilocular but may be multilocular
- Thin and smooth cyst membrane
- In curettage specimens
- Multiple thin greyish or reddish membranes admixed with blood clots and bony fragments
Frozen section description
- Frozen section is seldom done
- Fragments of fibrous cyst wall, along with bony fragments with or without fibrin-like material in cyst wall
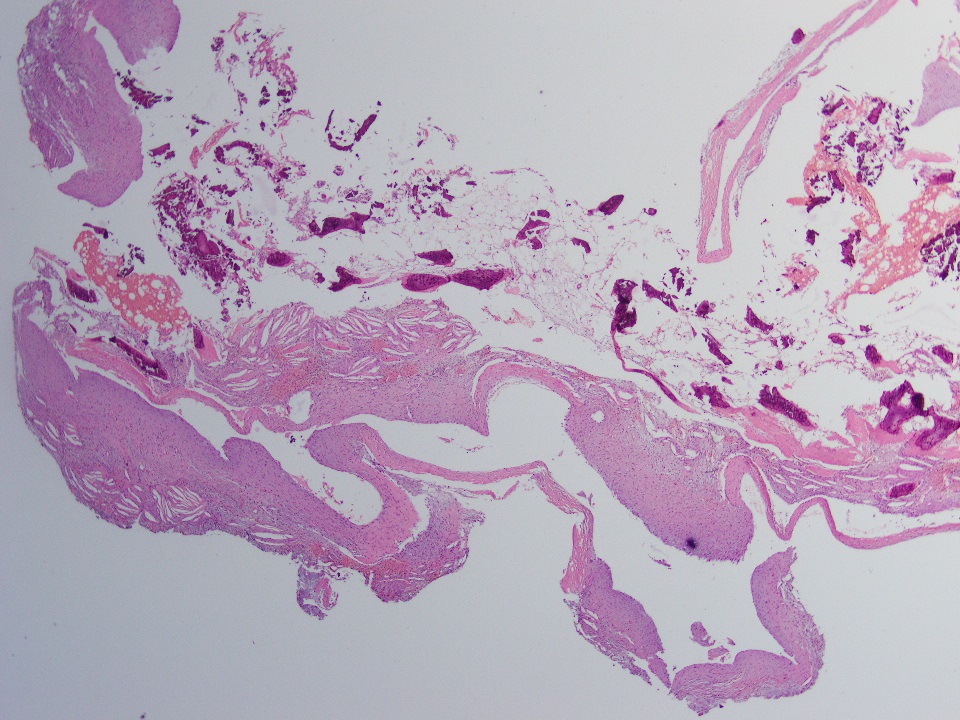
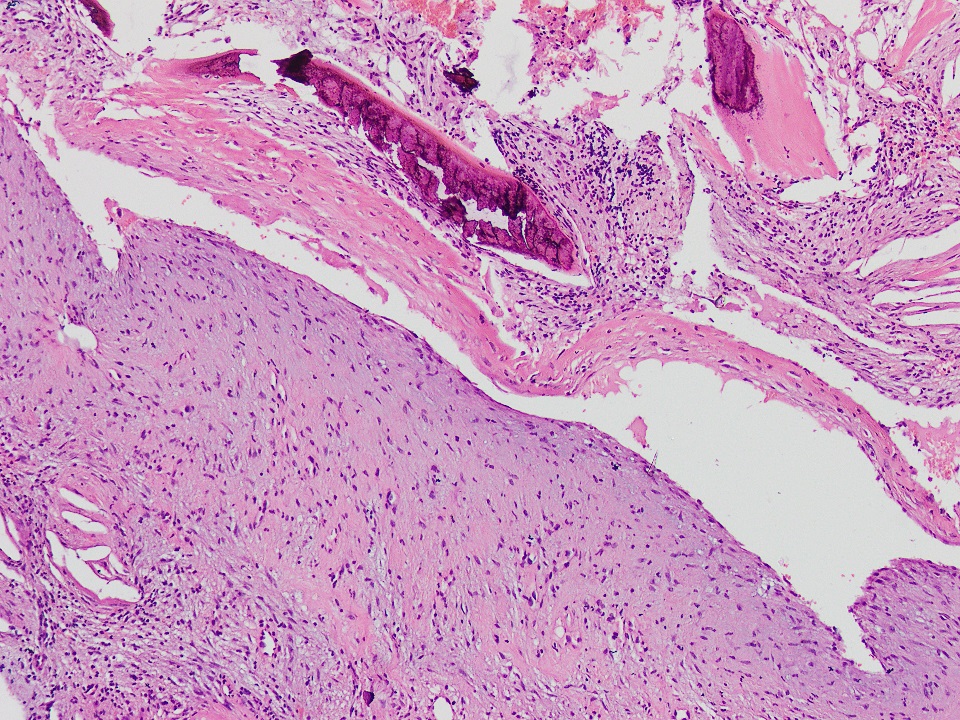
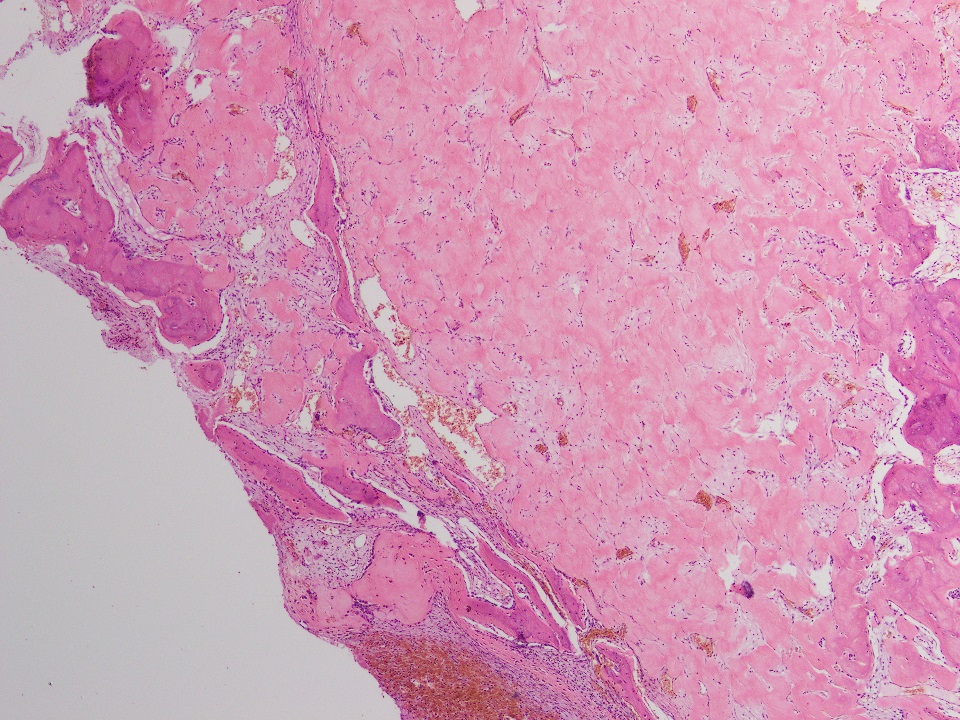
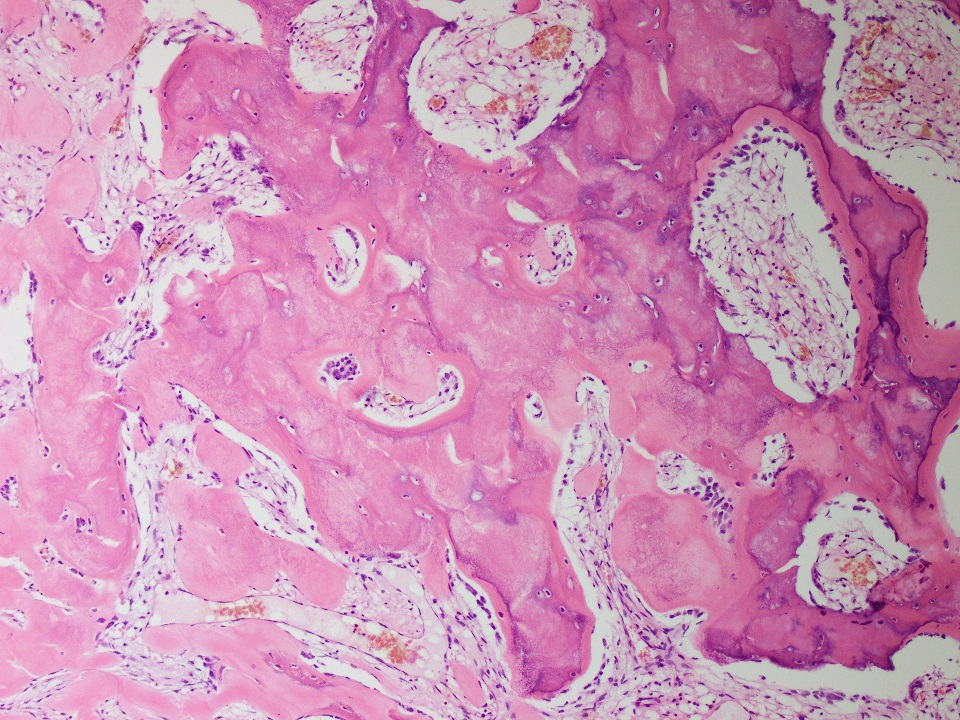
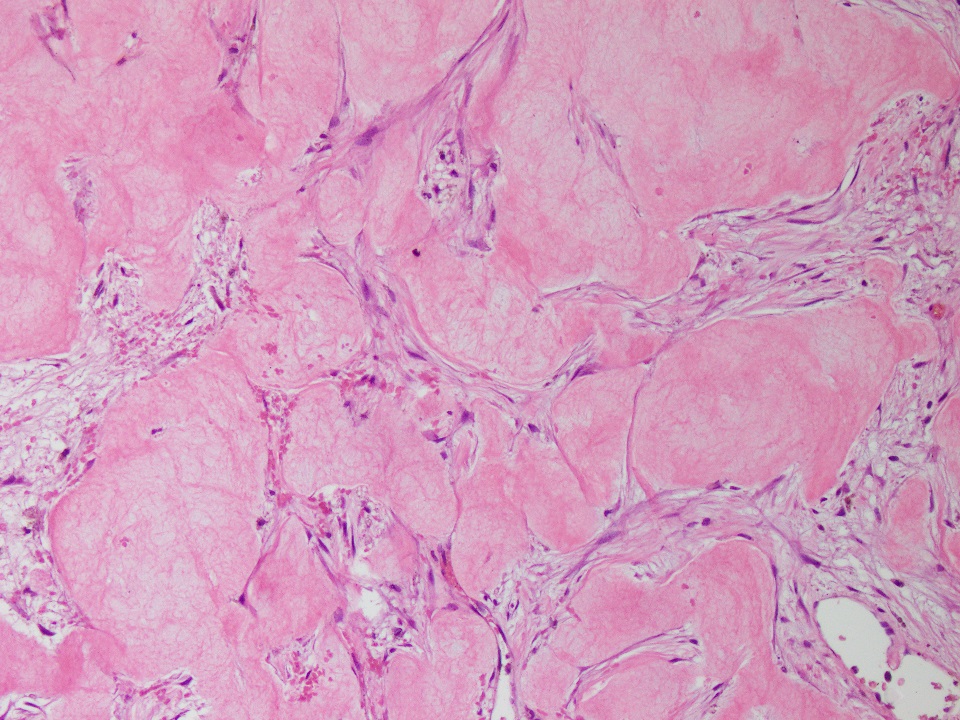
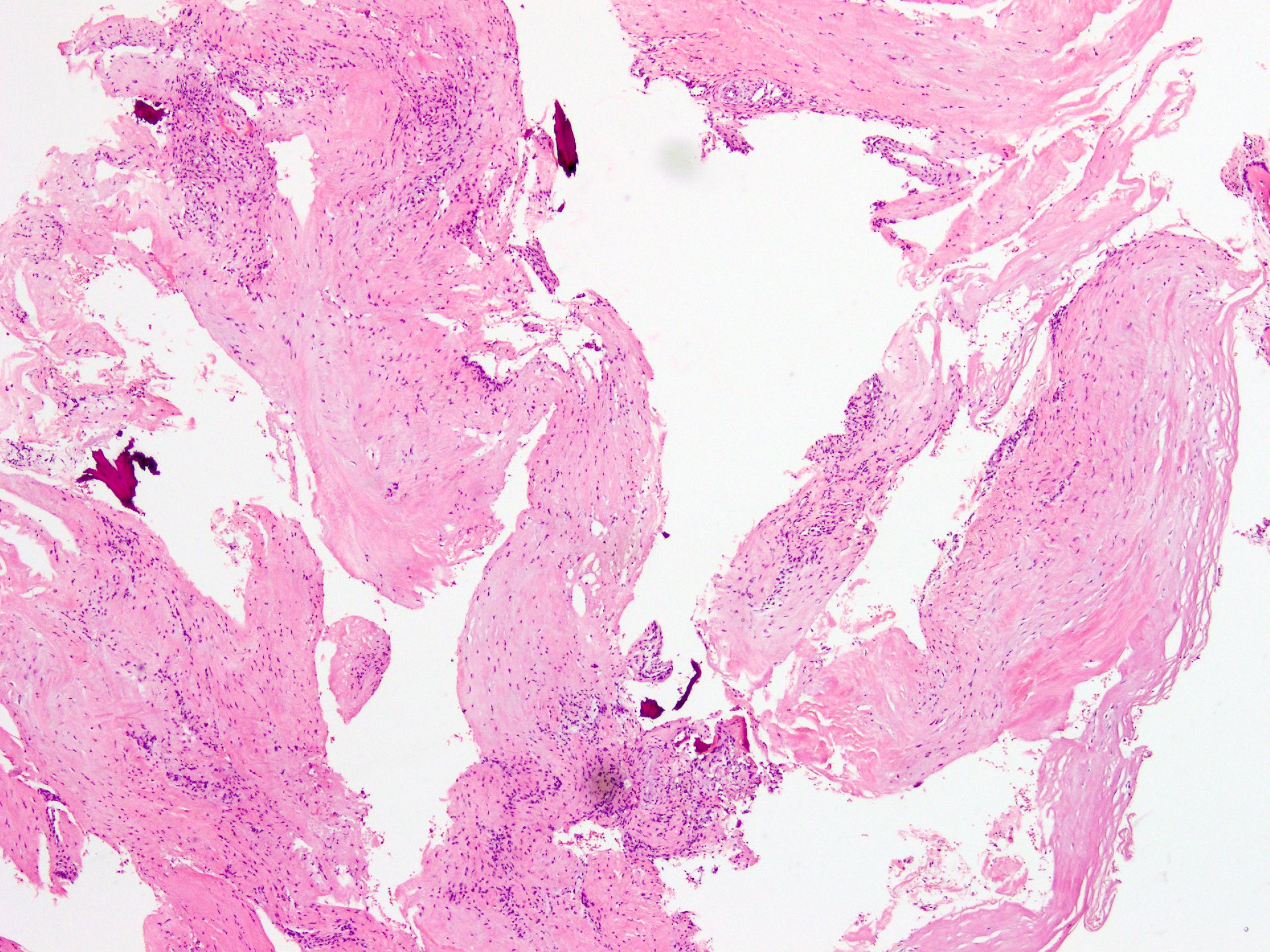
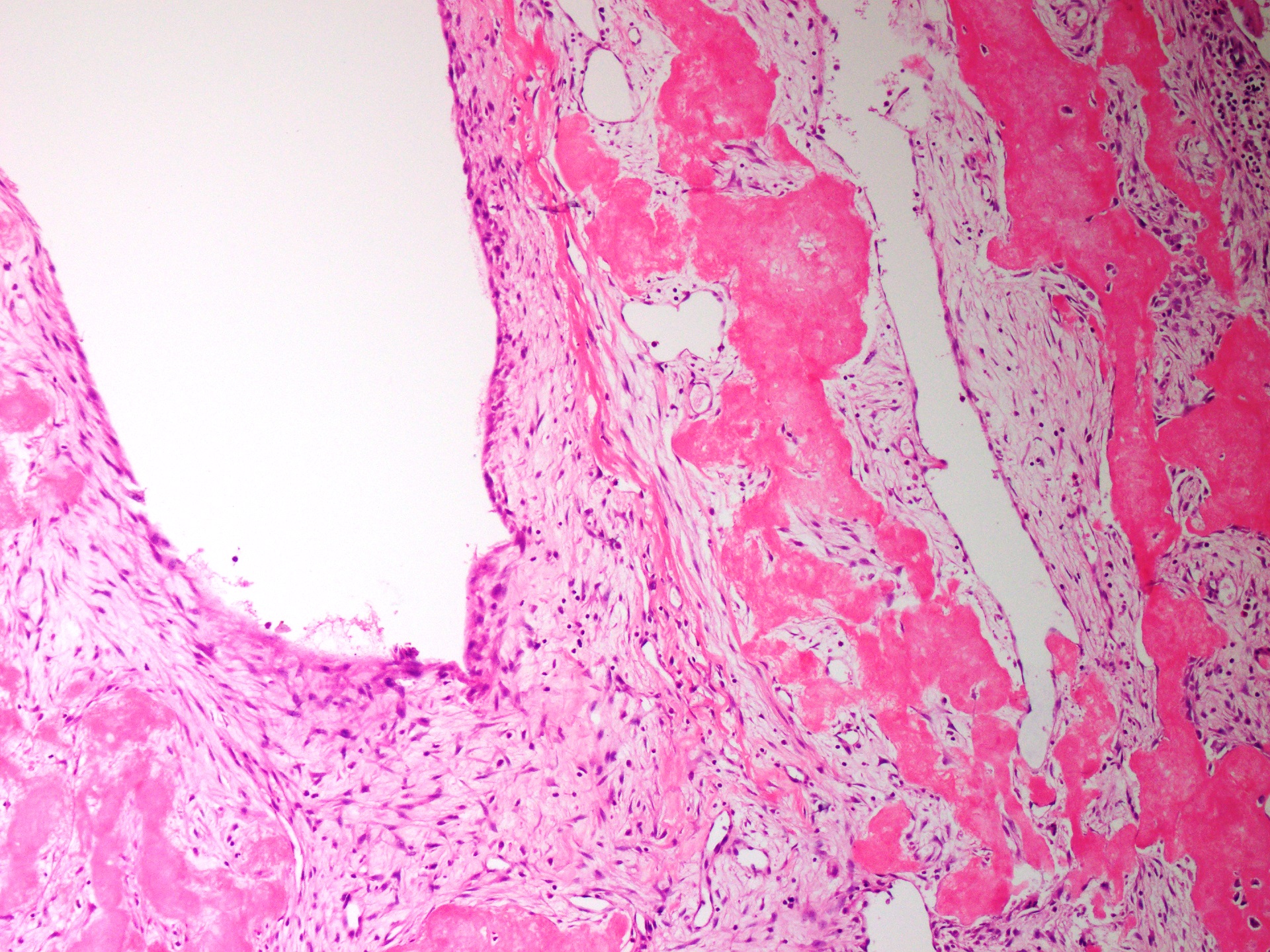
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Thin fibrous cyst wall lacking an epithelial lining and composed of fibroblasts
- Irregular bands of fibrin-like, often calcified material in cyst wall mimicking odontogenic cement (Histopathology 2011;59:390)
- Osteoclast type giant cells, foamy histiocytes and hemosiderin pigment and cholesterol clefts in cyst wall
- Reactive bone in case of fracture
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Scanty aspirates containing histiocytes, lymphocytes and osteoclast giant cells (Cytopathology 2005;16:59)
Positive stains
- Immunohistochemical stains are of no diagnostic utility; in one study, the following IHC
was performed (Histopathology 2011;59:390):
- Elastic van Geison (EVG) stain, strong fuscinophilic appearance was noted
- Procollagen I, collagen I, collagen III and bone proteoglycan (decorin) were positive
- Transcription factors RUNX2 and osterix were positive in osteoblasts
Negative stains
- Fibrin and other noncollagenous proteins (Histopathology 2011;59:390)
Electron microscopy description
- Collagen fibers and numerous matrix vesicles in cementum-like material (Clin Orthop Relat Res 1978;135:295)
- 2 cell types, which showed features identical to those described for type A and type B synovial cells, were noted in cyst lining (Clin Orthop Relat Res 1978;135:295)
Sample pathology report
- Right proximal humerus, cystic lesion, curettage:
- Simple bone cyst (see comment)
- Comment: Radiological and histological features are consistent with simple bone cyst.
Differential diagnosis
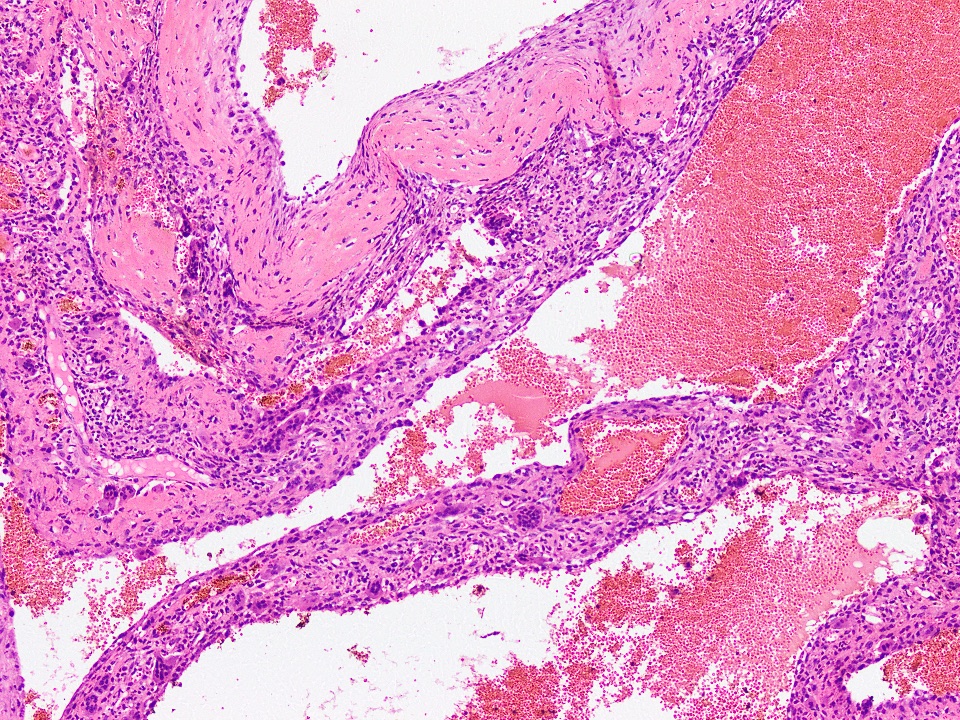
- Aneurysmal bone cyst:
- More expansile and eccentrically located
- Septations are more pronounced than in simple bone cyst
- Cystic spaces contain blood
- More osteoclast type giant cells and reactive woven bone in cyst wall
- Calcified, basophilic material (blue reticulated chondroid-like material)
- Intraosseous ganglion cyst:
- Usually found incidentally in the subchondral region
- Found in skeletally mature individuals
- Appears as a small radiolucent lesion
- Histologically, like soft tissue ganglion cyst
- No fibrin-like material or giant cells are seen
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 12 year old boy presented with pain and swelling of right upper arm. Xray and histology image of the cystic lesion are shown above. Which of the following is true regarding this lesion?
- Commonly involves small bones of hand and feet
- Commonly occurs in third to fourth decade of life
- Cyst frequently contains hemorrhagic fluid
- More common in females
- Proximal humerus is most common location
Board review style answer #1
E. Proximal humerus is most common location. This is a simple bone cyst.
Comment Here
Reference: Simple bone cyst
Comment Here
Reference: Simple bone cyst
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is the most important diagnostic feature of simple bone cyst?
- Blood filled cystic spaces
- Calcified basophilic material
- Fibrin-like eosinophilic material
- Osteoclast like giant cells
- USP6 gene rearrangement
Board review style answer #2