Table of Contents
Definition / general | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Pernick N Metastases. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bonemetstobone.html. Accessed December 20th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Most common malignant bone tumor is metastatic carcinoma
- In adults, 80% from prostate, breast, kidney, lung or thyroid
- In children, from neuroblastoma, Wilm tumor, osteosarcoma, Ewing / PNET or rhabdomyosarcoma
- Intraspinal seeding may occur along Batson’s plexus of veins
- Positive isotope bone scans (versus myeloma)
- Sarcomatoid carcinoma: consider if patient 60+ years with spindling bone malignancy; cells usually plumper than bone sarcomas and accompanied by carcinoma; renal cell carcinoma is most common primary site
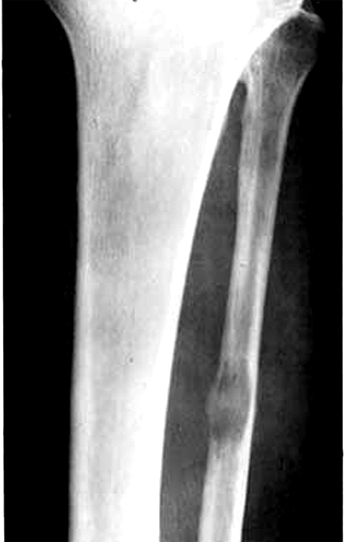
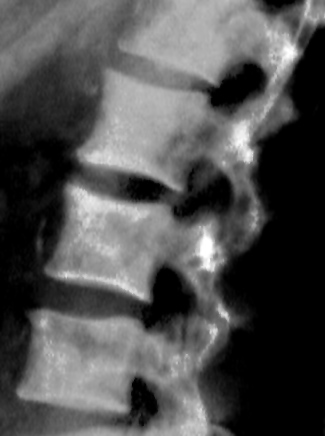
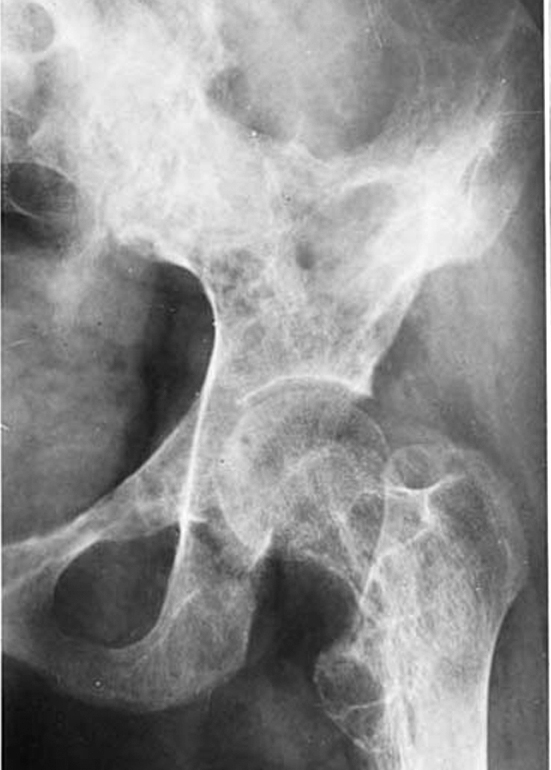
- Common sites: axial skeleton, proximal femur, proximal humerus; usually marrow; very rare to be distal to elbow or knee
- Solitary metastases: kidney, thyroid
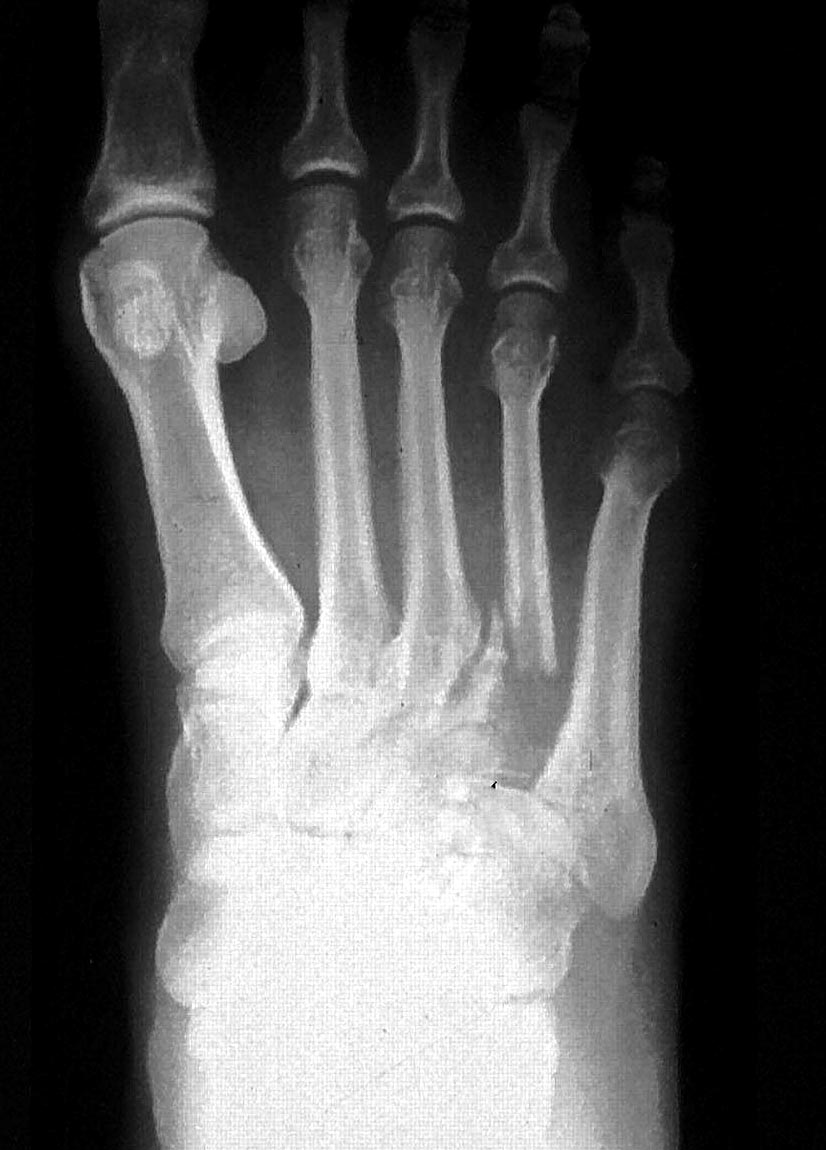
- Small bones of hands and feet: colon, lung, kidney
- Blastic lesions: prostate, carcinoid tumor, neuroendocrine tumors
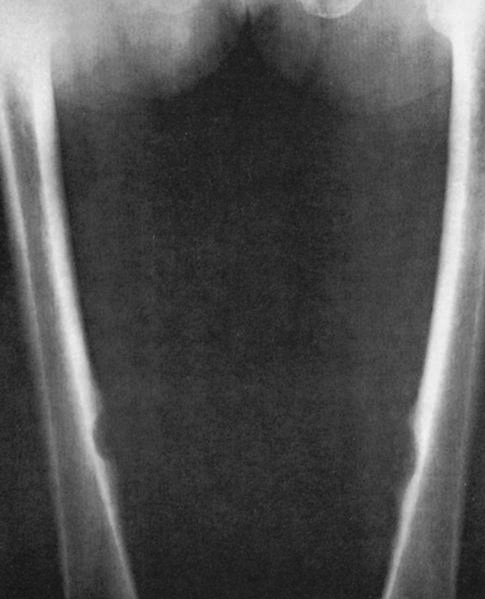
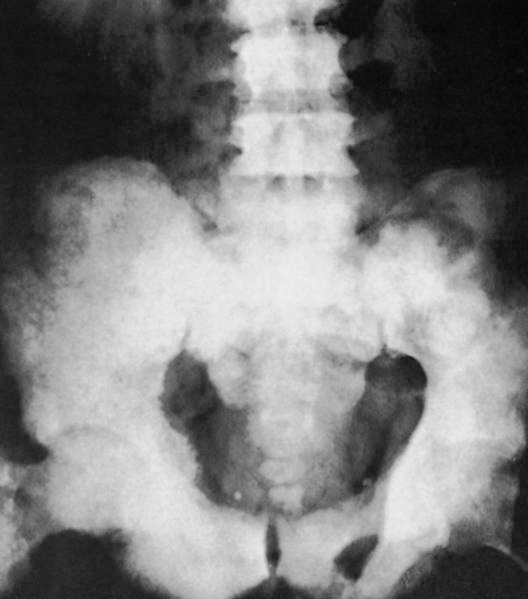
Radiology images
Case reports
- 37 year old man with spinal cord compression (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:887)
- 63 year old woman with metastatic basal cell carcinoma to vertebrae in nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:819)
Treatment
- Radiation therapy for pain relief and to prevent fracture of weight bearing bones
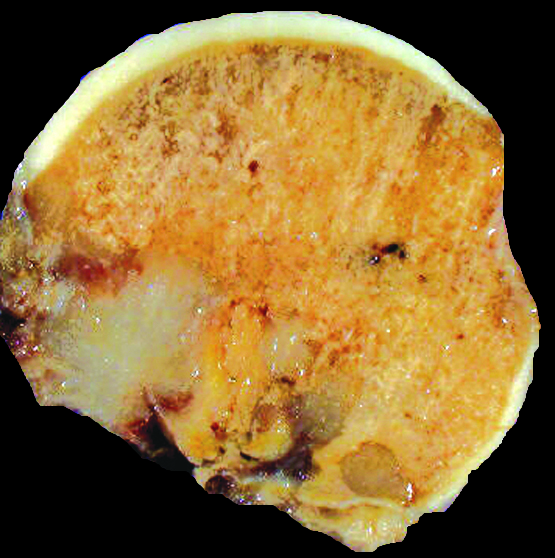
Gross images
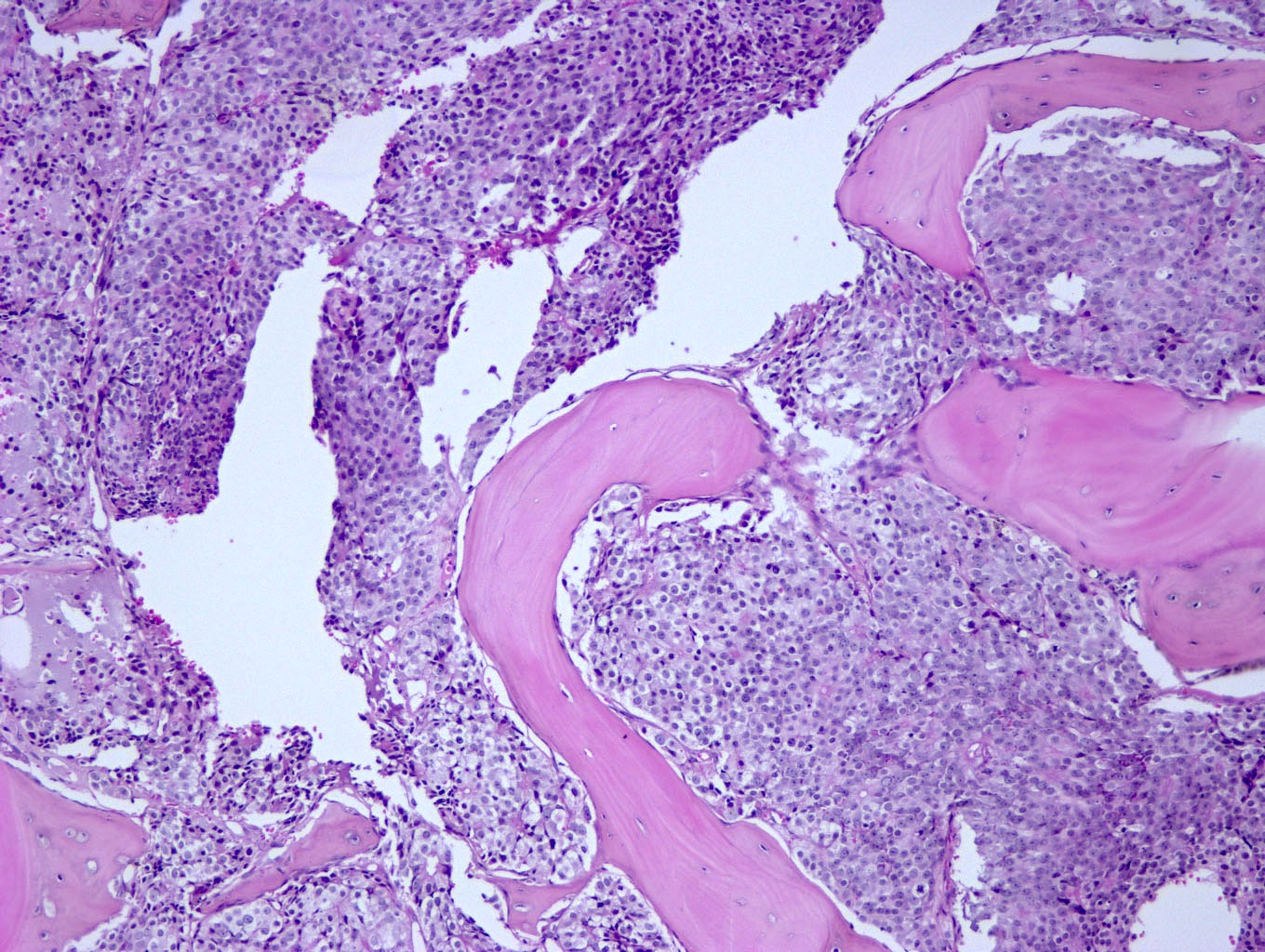
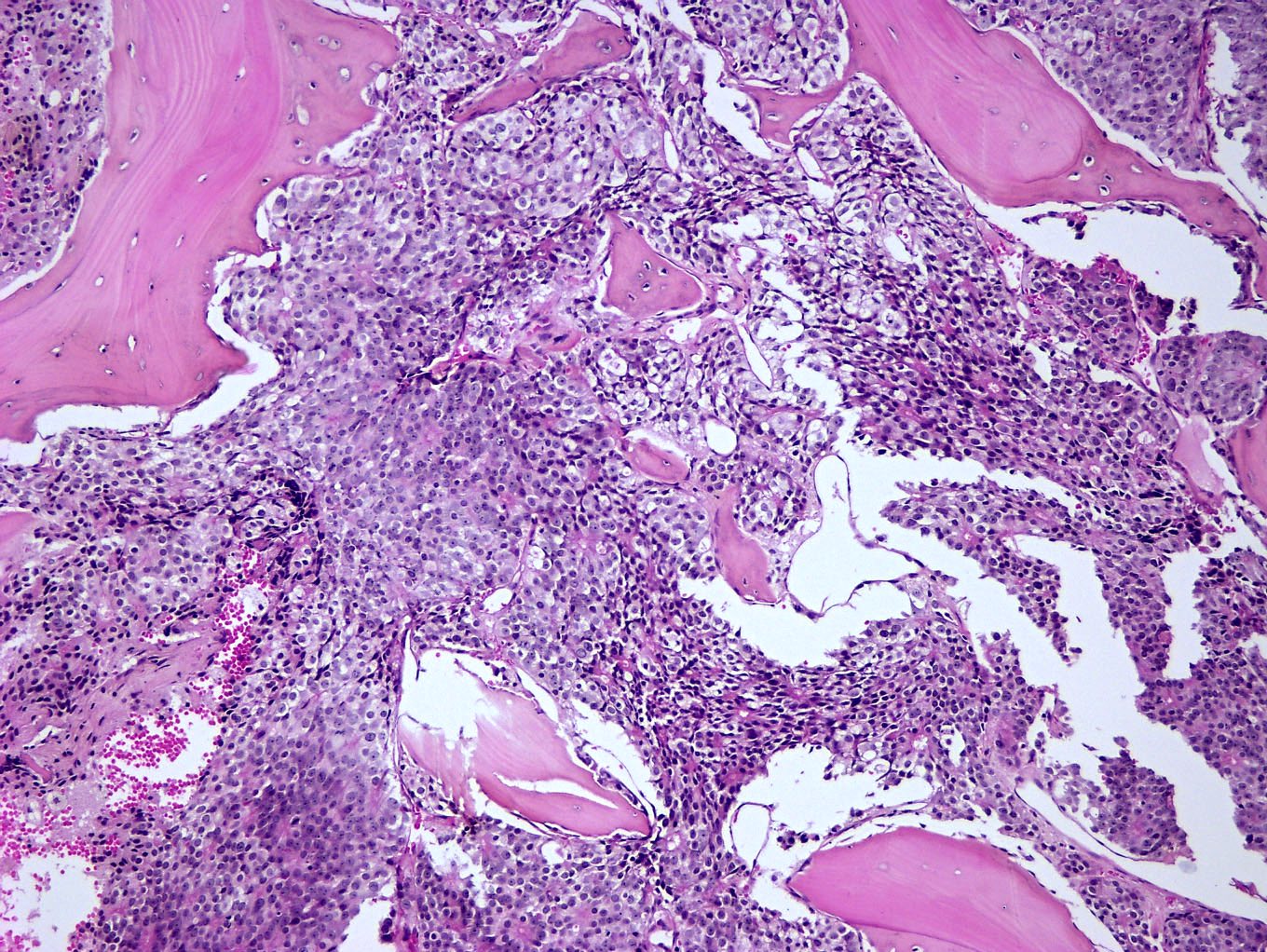
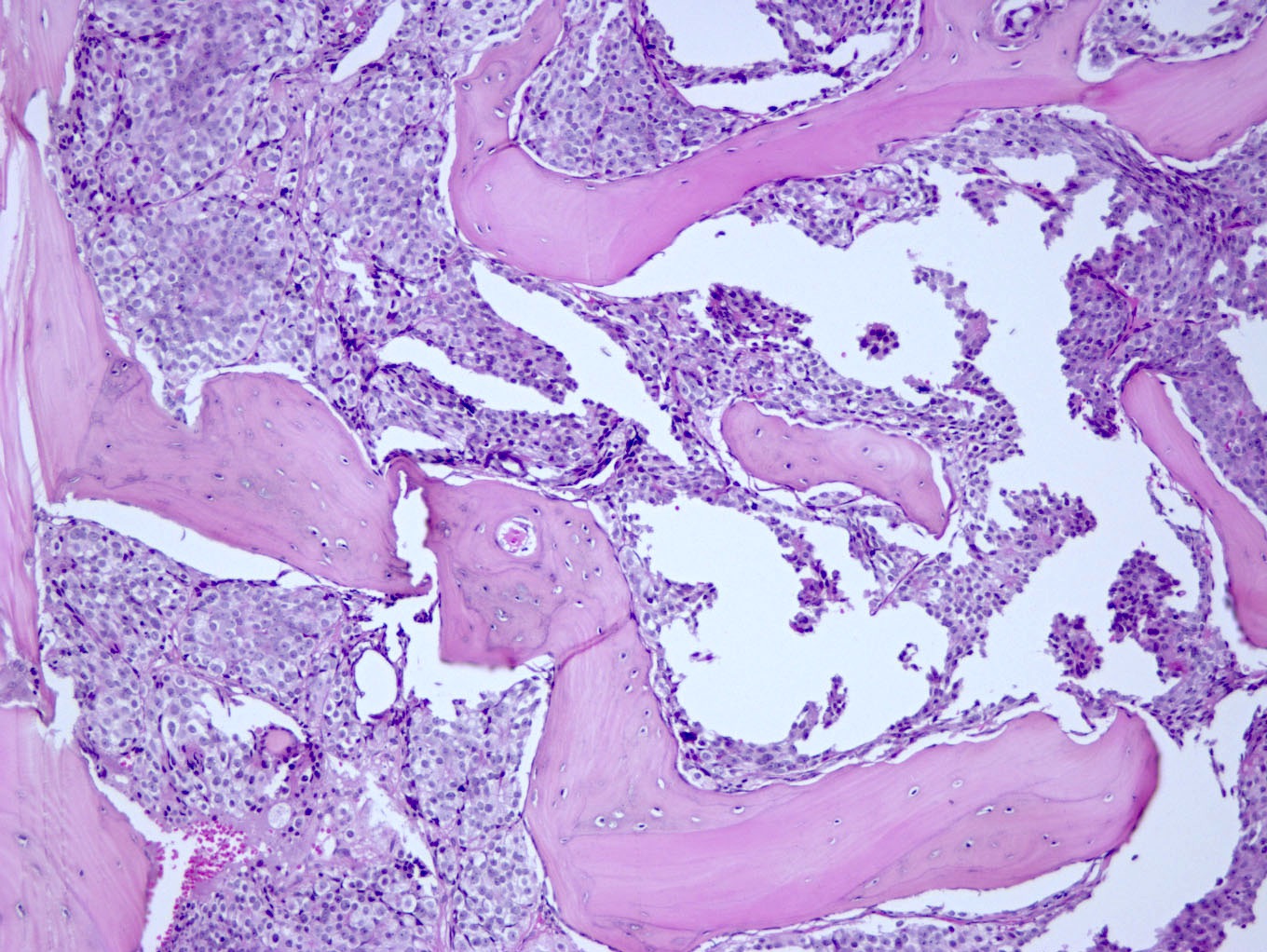
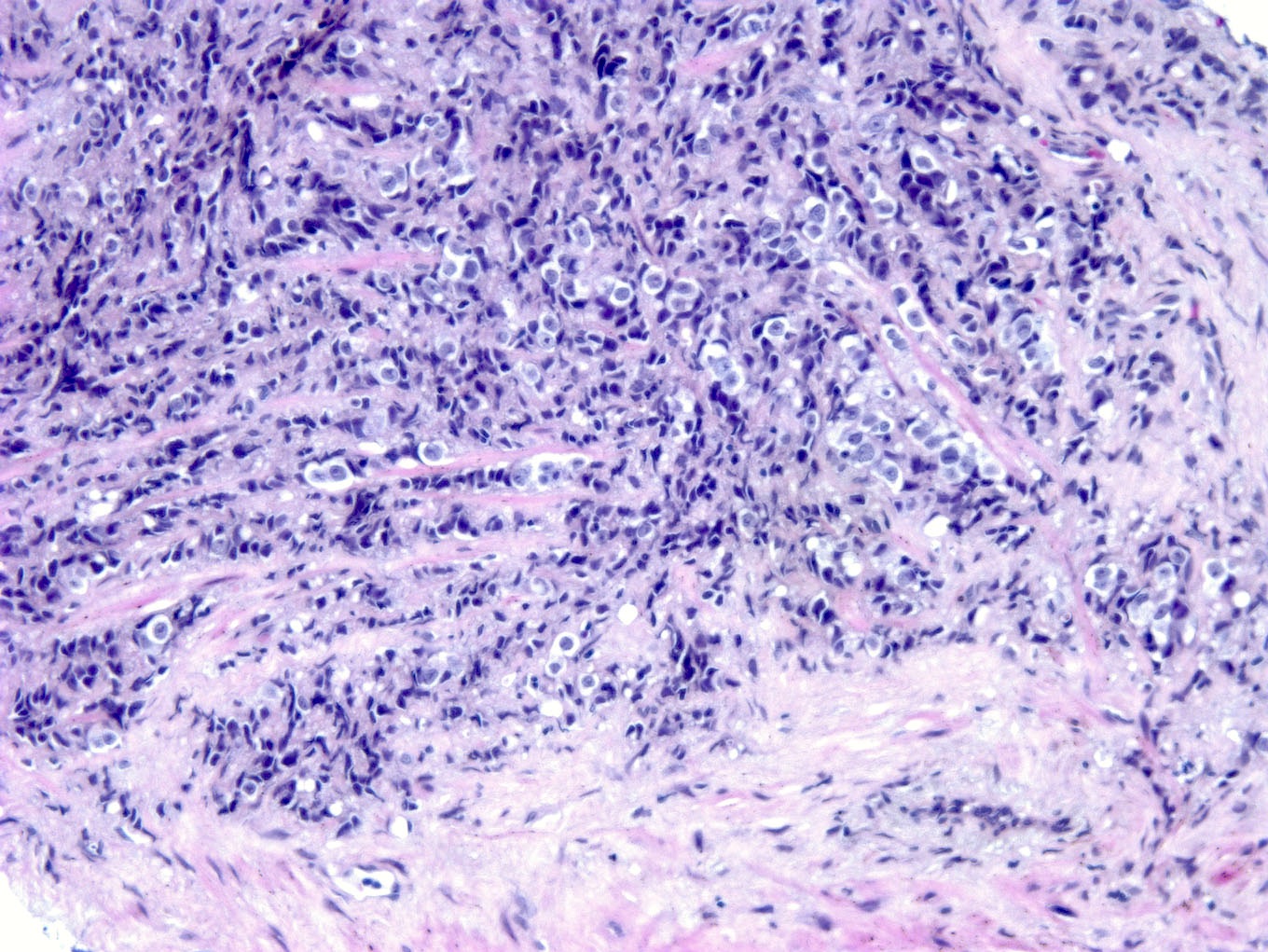
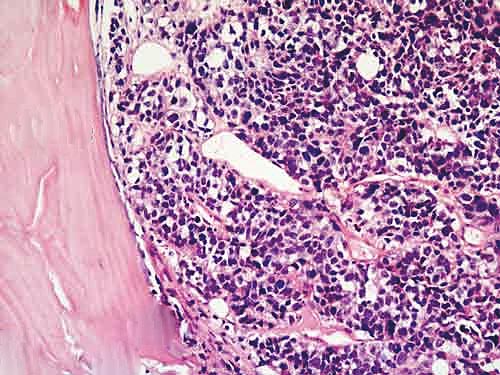
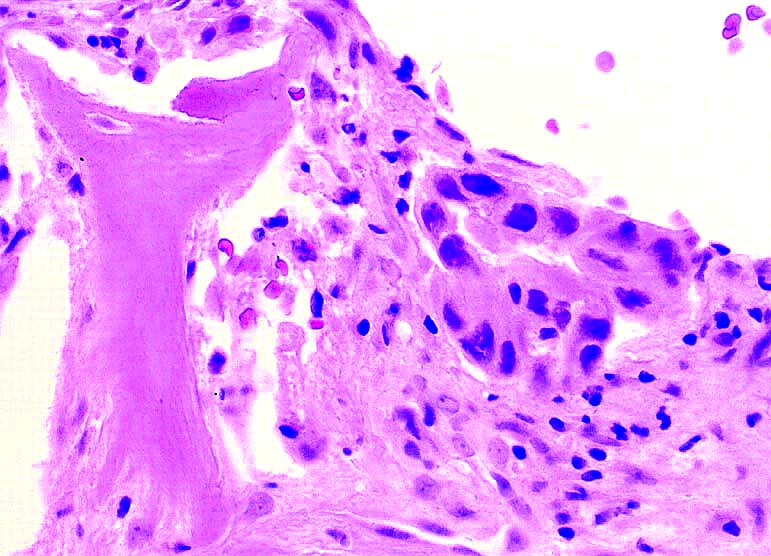
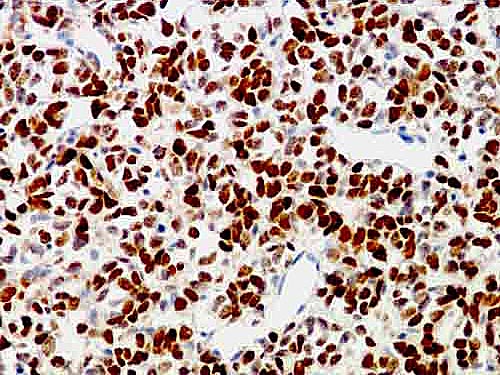
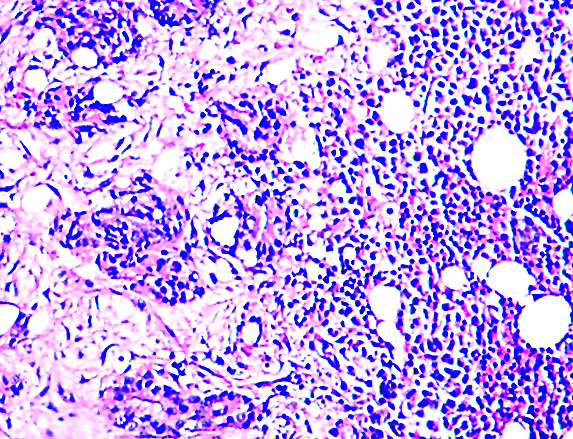
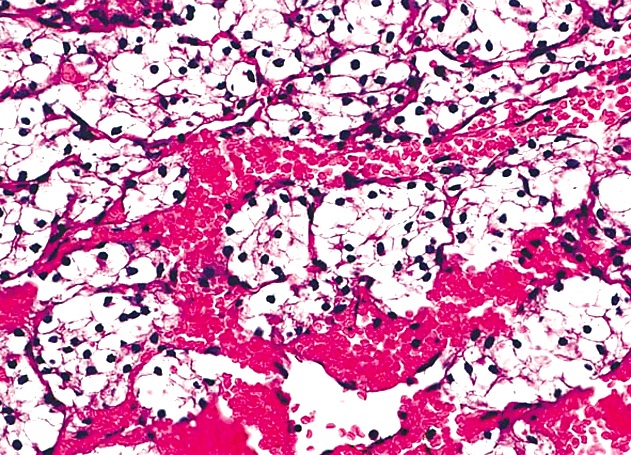
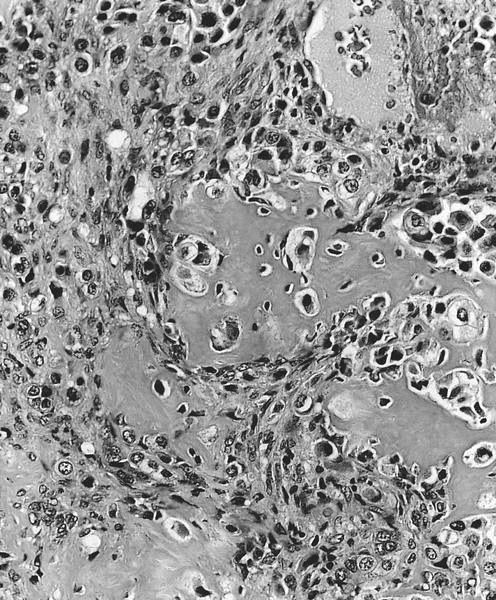
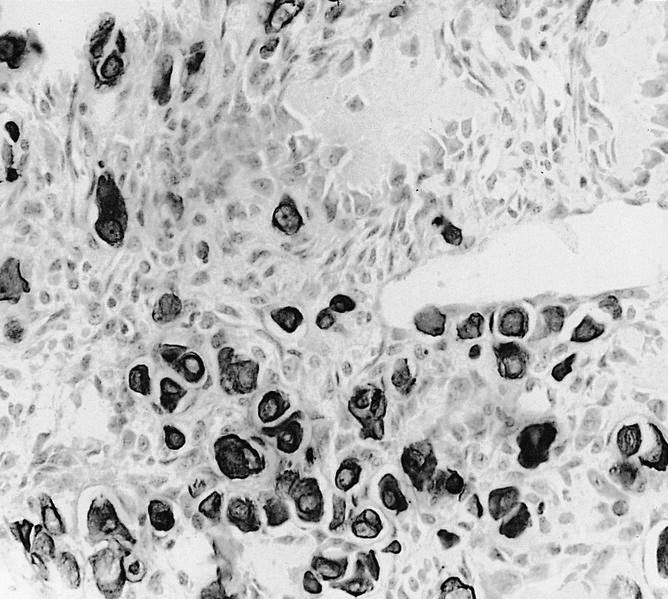
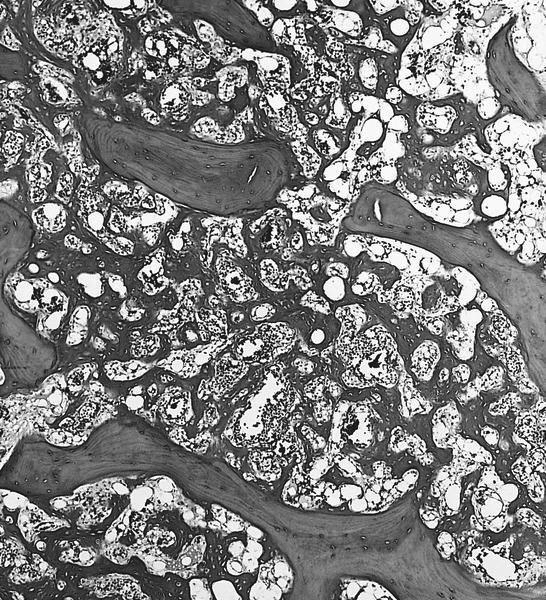
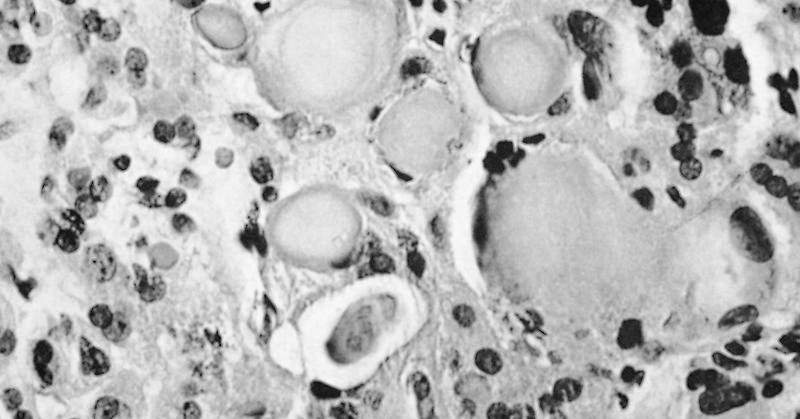
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Semir Vranić, M.D., Ph.D., Mark R. Wick, M.D. and AFIP images
Differential diagnosis
- Myeloma:
- Negative isotope bone scan, monoclonal protein in serum or urine