Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Peripheral smear description | Peripheral smear images | Positive stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Marks E. AML with FLT3. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bonemarrowneoplasticAMLFLT3.html. Accessed December 22nd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Not a specific WHO designated entity but has specific prognostic and treatment ramifications
- FLT3 (FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3) gene encodes a membrane bound receptor tyrosine kinase and is located on chromosome 13q12
- 2 mutation types in leukemia: internal tandem duplication (ITD), usually within the juxtamembrane domain, and a missense point mutation on the tyrosine kinase domain (TKD)
Essential features
- Can be found in ~30% of cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia (AML) (Br J Haematol 2017;179:530)
- Up to 40% of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) patients have FLT3 mutations
- ~20% of AML cases with t(9;11)(p21.3;q23.3) have point mutations in FLT3
- High percentage (~70%) of AML with t(6;9)(p23;q34.1) have FLT3 mutations (Leukemia 2006;20:1295)
- Higher prevalence in younger patients with AML (< 60 years old) (Ann Hematol 2017;96:1993)
- There are several new FLT3 targeted drugs that show promising results, which necessitate rapid analysis of the FLT3 status in patients with AML
Terminology
- FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- More prevalent in patients < 60 years old
- Found in ~31% of patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia (22% FLT3-ITD mutation and 9% FLT3 D835) (Haematologica 2011;96:1470)
- Can be found in about 30% (28 - 34% FLT3-ITD and 11 - 14% FLT3-TKD) of cytogenetically normal AML (Br J Haematol 2017;179:530)
Clinical features
- White blood cell count is increased compared with AML without FLT3 mutation (Dis Markers 2013;35:581)
Diagnosis
- FLT3 mutations are generally detected in the clinical laboratory by PCR and electrophoresis based product sizing as well as using next generation sequencing (NGS) platforms
Prognostic factors
- FLT3-ITD is an independent adverse prognostic indicator in AML
- Favorable outcome if mutated nucleophosmin (NPM1) without FLT3-ITD or with FLT3-ITDlow (allelic ratio < 0.5)
- Intermediate outcome if mutated NPM1 and FLT3-ITDhigh (allelic ratio ≥ 0.5) or wild type NPM1 without FLT3-ITD or with FLT3-ITDlow (without adverse risk genetic lesions)
- Adverse outcome if wild type NPM1 and FLT3-ITDhigh
- Prognostic impact of FLT3-TKD mutations is uncertain (Leukemia 2019;33:299)
- Acute promyelocytic leukemia with FLT3 mutations appear to represent a subset of APL patients who have a higher risk of relapse (Am J Hematol 2010;85:956)
Case reports
- 4 and 9 month old boys, previously healthy, born at full term (Case Rep Oncol 2020;13:266)
- 26 year old man developed GVHD after treatment (Case Rep Oncol Med 2020;2020:4936846)
- 28 year old woman in the 26th week of gestation (BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019;19:394)
- 60 year old man diagnosed with FLT3-ITD positive AML in second remission (Clin Case Rep 2019;7:2579)
- 73 year old woman with FLT3 and NPM1 mutations (Case Rep Hematol 2016;2016:1259759)
Treatment
- FLT3 targeted therapies including lestaurtinib, sorafenib, midostaurin, quizartinib, crenolanib and gilteritinib (Ther Adv Hematol 2019;10:2040620719827310)
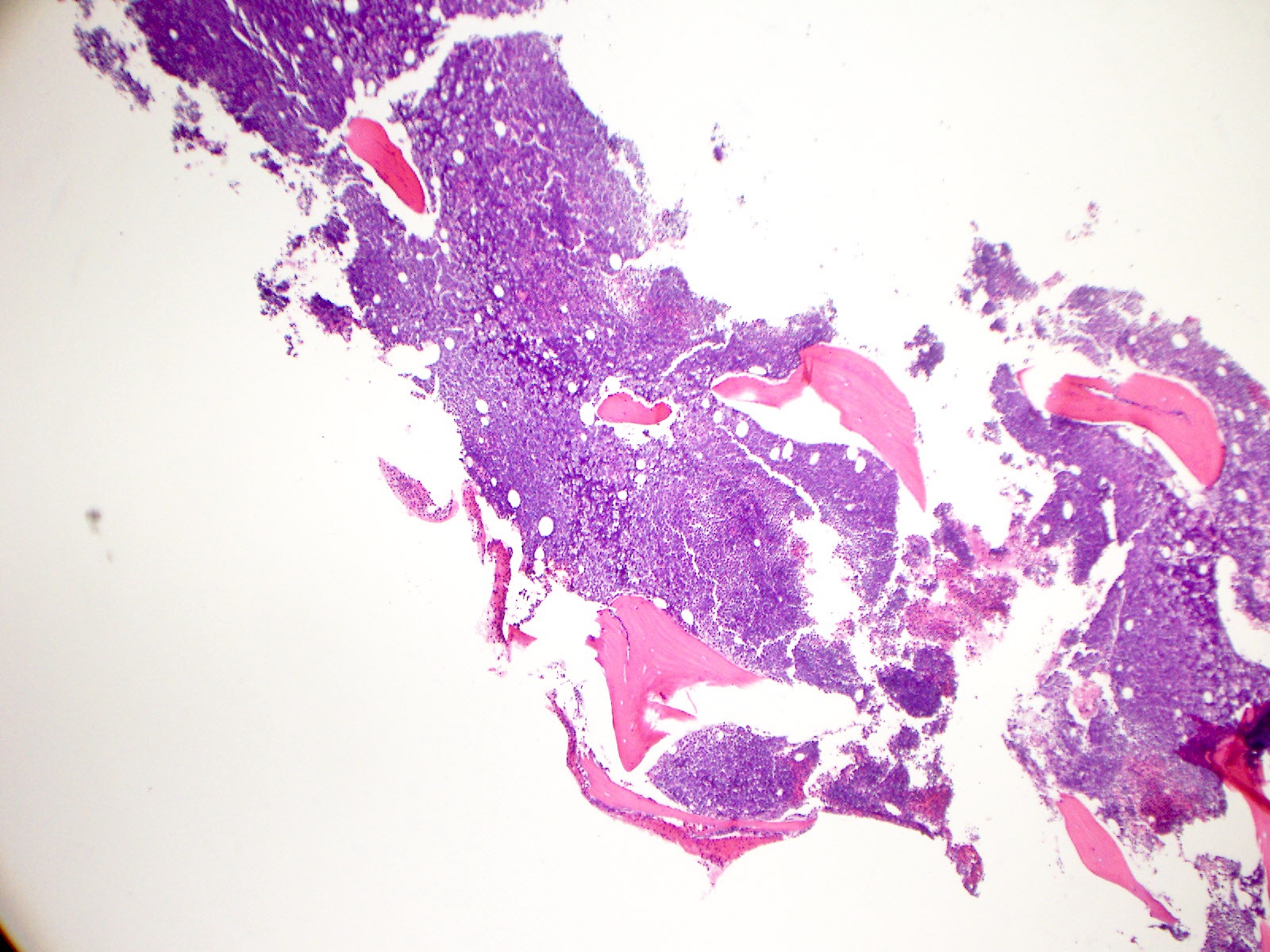
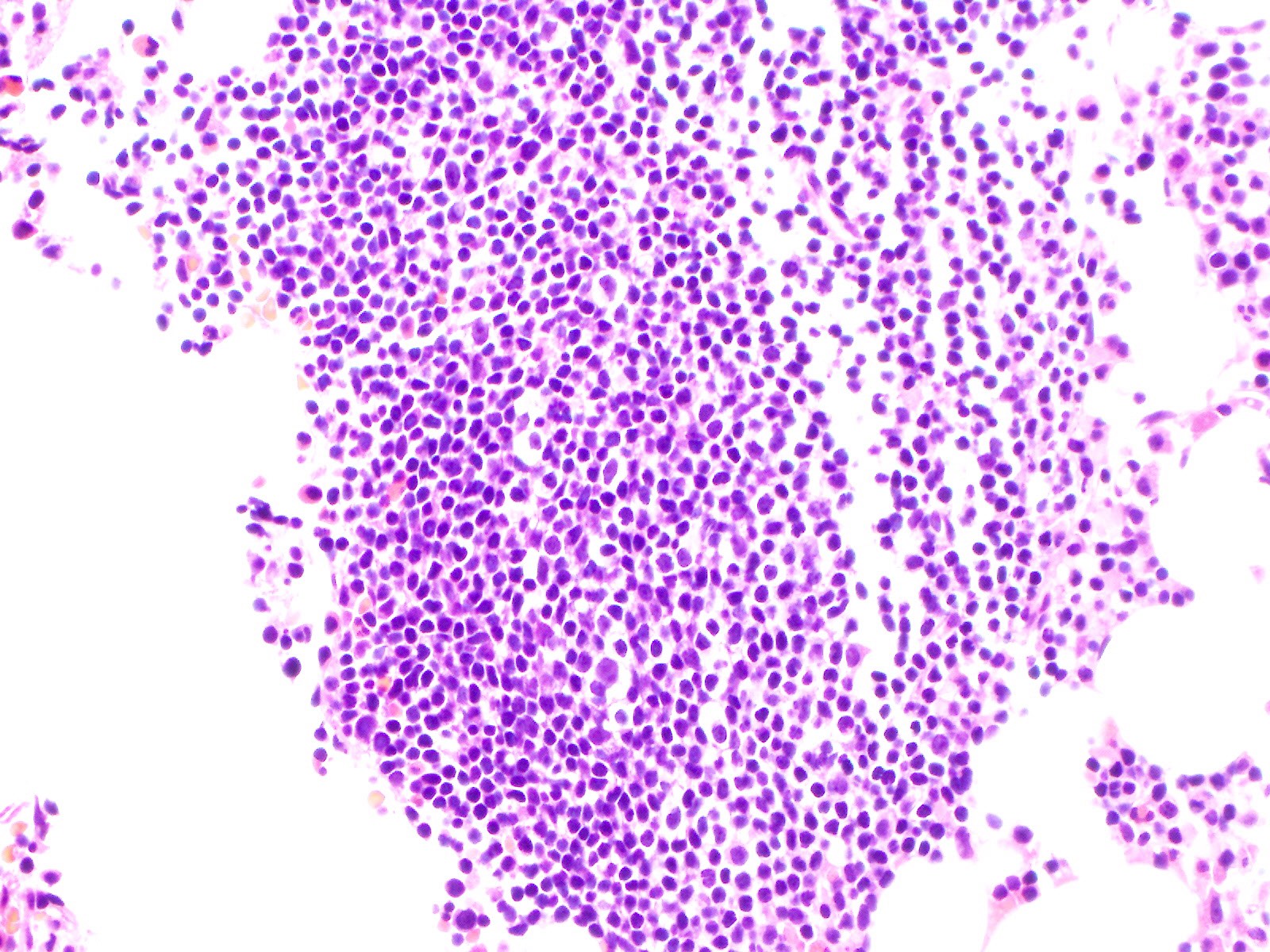
Microscopic (histologic) description
- No specific microscopic findings associated with FLT3 mutation
- No correlation with a single, specific French-American-British (FAB) subtype was found (Blood 2002;100:59)
- When FLT3 occurs with other mutations or cytogenetic abnormalities, the characteristic microscopic features seen with those abnormalities are usually present
Microscopic (histologic) images
Peripheral smear description
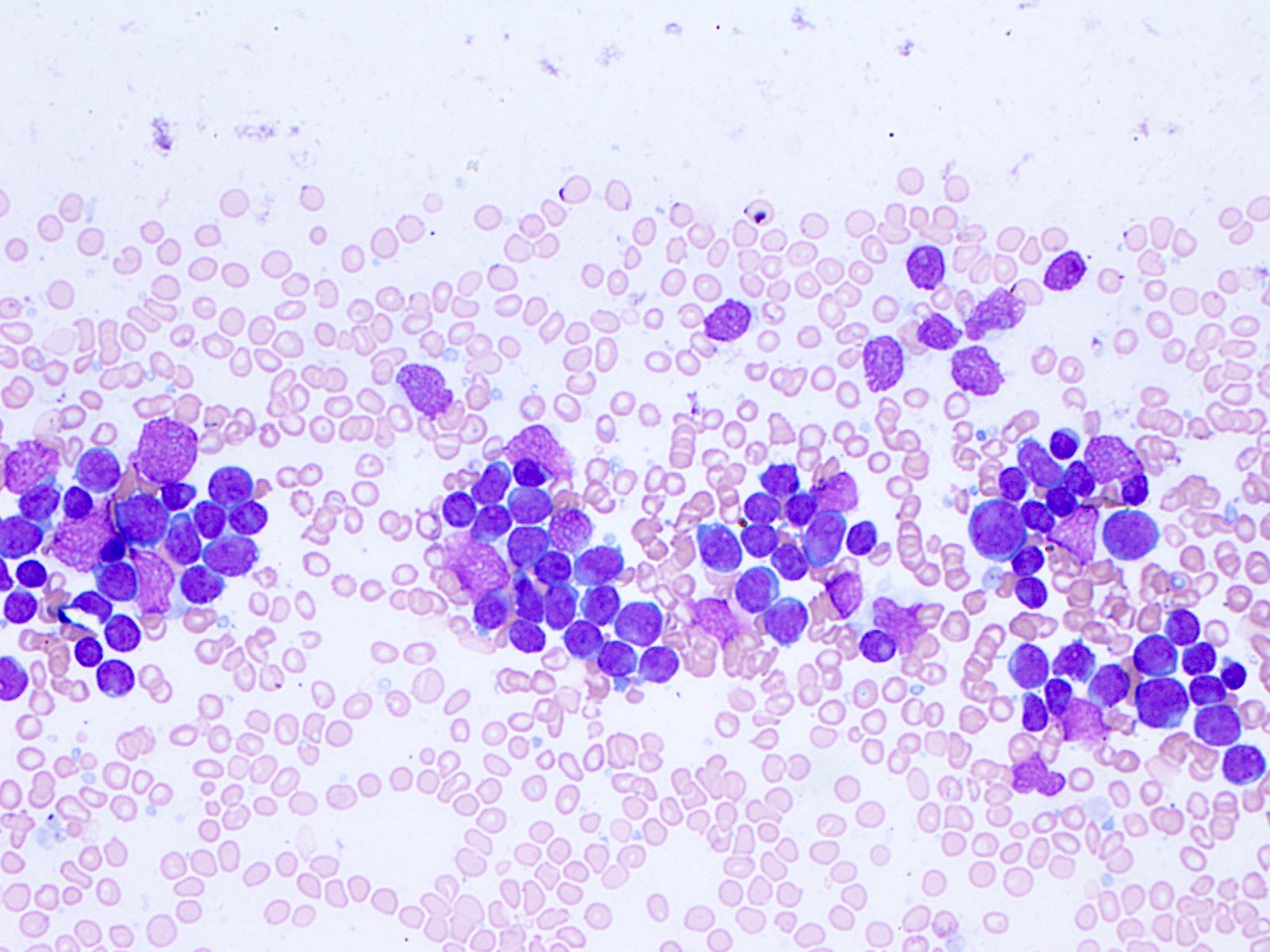
- Similar to other acute myeloid leukemias with ≥ 20% myeloblasts or ≥ 20% promyelocytes
Peripheral smear images
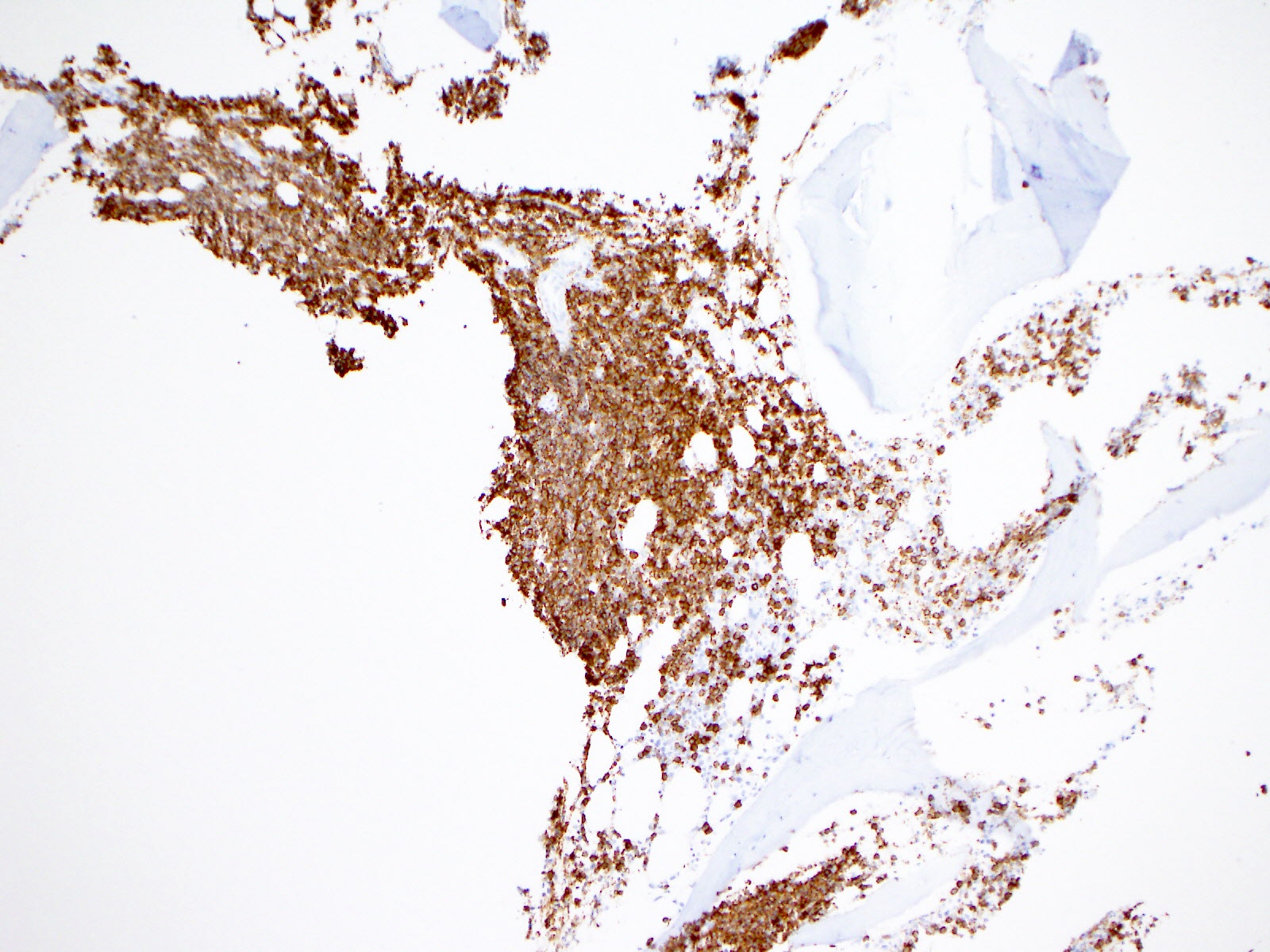
Positive stains
- Aberrant expression of CD2 has been associated with FLT3-ITD mutations in acute promyelocytic leukemia (Haematologica 2011;96:1470)
- CD135 is the receptor for the cytokine Flt3 ligand (Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2013;84:390)
- CD34 is often positive but can be negative
- CD117
- HLA-DR is often positive, unless it is found in a case of acute promyelocytic leukemia
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- FLT3-ITD mutations consist of a duplicated coding sequence usually derived from the juxtamembrane domain inserted in tandem (ITD) (Haematologica 2011;96:1470, Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2013;84:390)
- These in frame insertion mutations range from 3 to > 200 bp in length and result in disruption of the autoinhibitory function
- FLT3-TKD point mutations occur in the activation loop of the kinase domain, most commonly at residue aspartate 835 (D835)
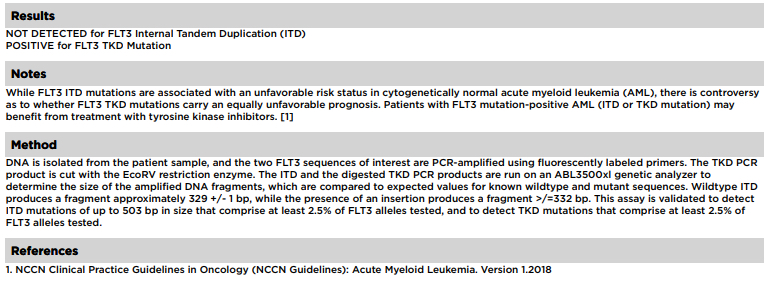
Sample pathology report
Differential diagnosis
- Same as other AMLs
- Growth factor related increased myeloblasts
- Myelodysplastic syndrome with increased blasts
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which mutational combination carries with it the worst overall prognosis in AML?
- 5q deleted AML
- Mutated FLT3 and wild type NPM1
- Wild type FLT3 and mutated NPM1
- Wild type NPM1 and biallelic mutated CEBPA
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2