Table of Contents
Definition / general | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy images | Additional referencesCite this page: Luca DC. Megakaryocytes. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bonemarrowmegakaryocytematuration.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
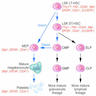
- Progresses from myeloid stem cell (pluripotential hematopoietic stem cell) to megakaryoblast to promegakaryocyte to megakaryocyte to proplatelets (released into circulation) to platelets (J Thromb Haemost 2003;1:1580, Front Biosci 2007;12:2050)
- Two groups of factors influencing megakaryopoiesis are early acting multilineage cytokines (stem cell factor, GM-CSF, IL3, IL6) and cytokines that are more megakaryocyte specific (thrombopoietin)
- Thrombopoietin: produced by bone marrow stromal cells, hepatocytes and proximal renal tubular epithelial cells; poorly understood regulation
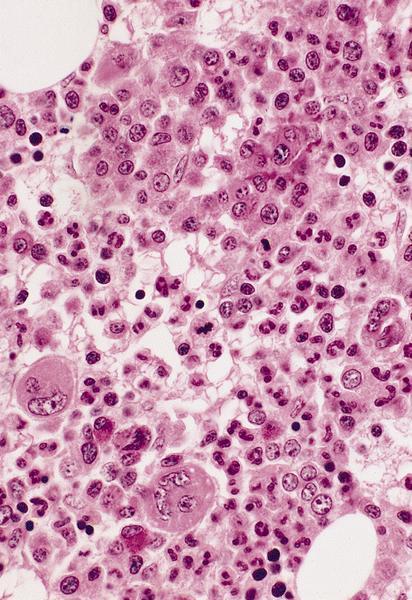
- Maturation is characterized by an increase in size and lobulation of nuclei and is controlled by thrombopoietin (J Clin Invest 2005;115:3339)
- Endomitosis: unique property of megakaryocytes characterized by ongoing DNA synthesis, without mitosis resulting in progressive nuclear lobulation with increasing DNA content (nuclear lobes remain connected)
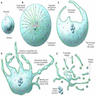
- Megakaryocytes form demarcation membrane within cytosol, which leads to production of platelets
- Maturation is associated with acquisition of surface GP Ib, GP IIb and von Willebrand factor
- Four types of cytoplasmic granules are alpha, delta, gamma and peroxisomes
- Megakaryocytes reside next to the bone marrow sinuses and project pseudopodia through the sinus walls, releasing platelets directly into the circulation
Clinical features
- Megakaryocytes are smaller in fetuses and infants and show less nuclear segmentation when compared to older children
- Platelet production appears to be dependent on megakaryocyte ploidy
- Platelet production rate under homeostatic conditions: 2 - 4 x 109/kg/day; may increase 8 - 10x if needed; 10 day survival time in peripheral blood
- Emperipolesis: other cells, especially neutrophils, pass through megakaryoctye tubular system (due to its location) to enter the circulation
- Thrombocytopenia with normal / increased megakaryocytes: congenital (Bernard-Soulier, May-Hegglin, gray platelet syndrome) or acquired (ITP, DIC, TTP, HUS, hypersplenism, megaloblastic anemia)
- Thrombocytopenia with decreased megakaryocytes: congenital (Fanconi, thrombocytopenia with absent radii, X linked amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia, dyskeratosis congenita, Shwachman-Diamond) or acquired (aplastic anemia, bone marrow infiltration, infections, toxins, immune disorders)
- Thrombocytosis: congenital (familial essential thrombocythemia, other familial myeloproliferative disorders) or acquired (reactive or neoplastic)
Microscopic (histologic) description
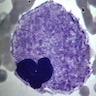
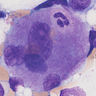
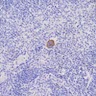
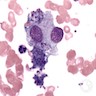
- Megakaryoblast: variable size (7 - 35 microns); may be designated micromegakaryoblast if < 15 microns; round / ovoid cells with scanty blue agranular cytoplasm that often forms a rim around nucleus and may have a few small budding protrusions at periphery; nuclei are round / oval with coarse granular chromatin, one or more nucleoli
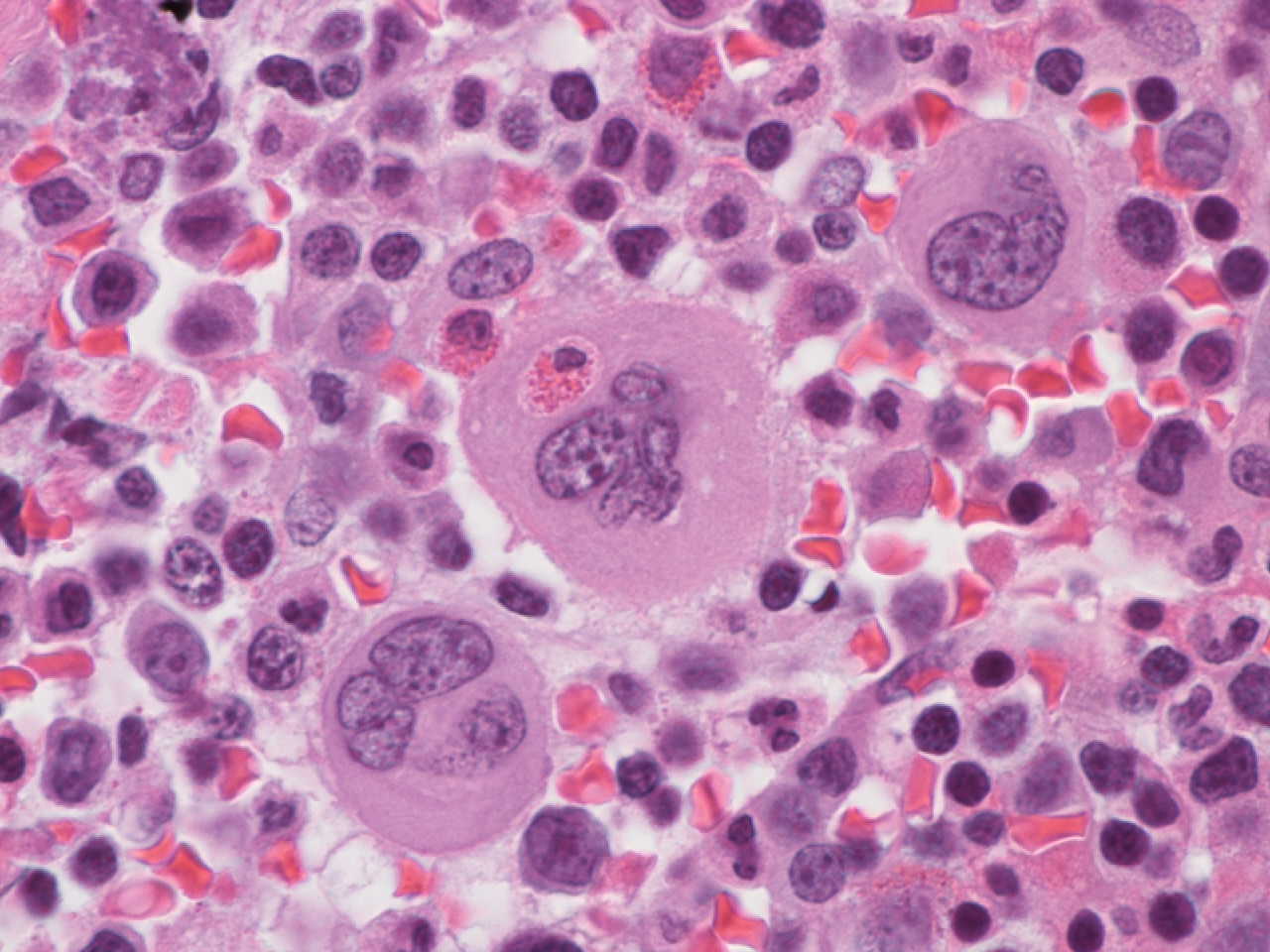
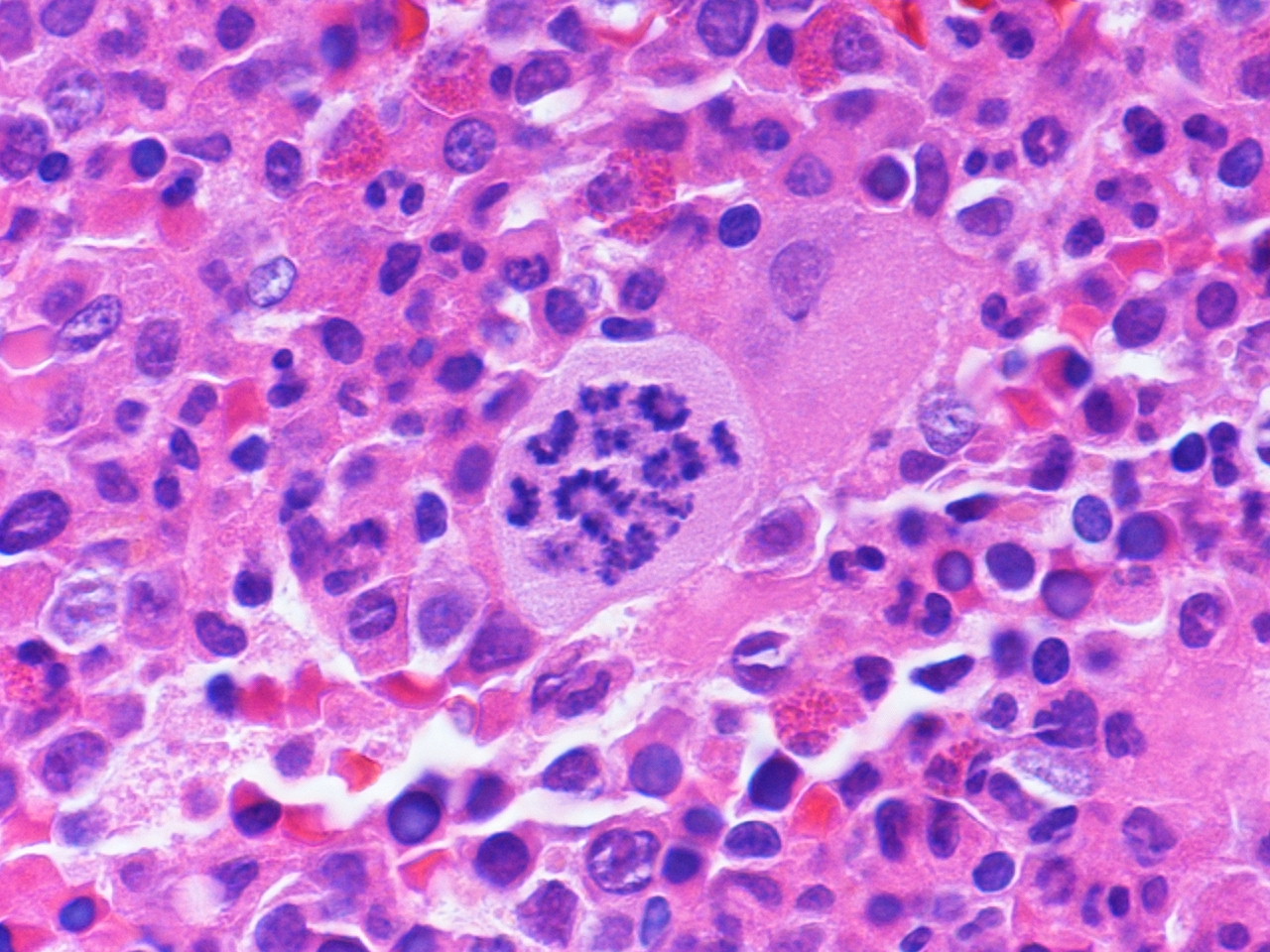
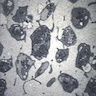
- Megakaryocyte: randomly disbursed throughout bone marrow; 50 - 150 microns (largest normal nucleated cell in marrow); micromegakaryocytes measure 15 - 30 microns; abundant light blue to pink cytoplasm with numerous purple red or pink granules; nucleus has 8, 16 or 32 overlapping lobes; no nucleolus; megakaryocytes producing platelets may have demarcated granular clumps of platelets streaming from the margins
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Additional references