Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Diagnosis | Case reports | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Treatment | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Andeen NK Lipid-rich. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladderlipidcell.html. Accessed December 22nd, 2024.
Definition / general
- An uncommon WHO recognized variant of invasive urothelial carcinoma
- First described by Mostofi et al in 1999
Terminology
- Lipid cell, lipoid cell
Epidemiology
- Median age 74 years
- Primarily seen in men, who present with hematuria (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:371)
Sites
- Predominantly in bladder
- Rare cases in the ureter and renal pelvis (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:371, Case Rep Oncol 2015;8:515, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:770, Pathology 2016;48:388, Journal of Clinical Oncology 2018;36:487)
Etiology
- Coexists with high grade conventional and papillary UC
- May coexist with other variants, particularly micropapillary or plasmacytoid (Case Rep Oncol 2015;8:515, Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:371, Journal of Clinical Oncology 2018;36:487)
Diagnosis
- Presence of cytokeratin and CK7 positive lipoblast-like cells and conventional urothelial carcinoma
- Consistently negative for mucin (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:371)
- Has areas of conventional UC, distinguishing it from a metastasis
- May have heterologous liposarcomatous elements but lacks the prominent high grade spindled features of sarcomatoid carcinoma
- Does not usually coexist with the sarcomatoid variant
Case reports
- 70 year old woman with bladder tumor resection (TURBT) (Case of the Week #466)
- 78 year old man with gross hematuria (Pathol Int 2013;63:183)
Gross description
- Distinct macroscopic features are not well documented
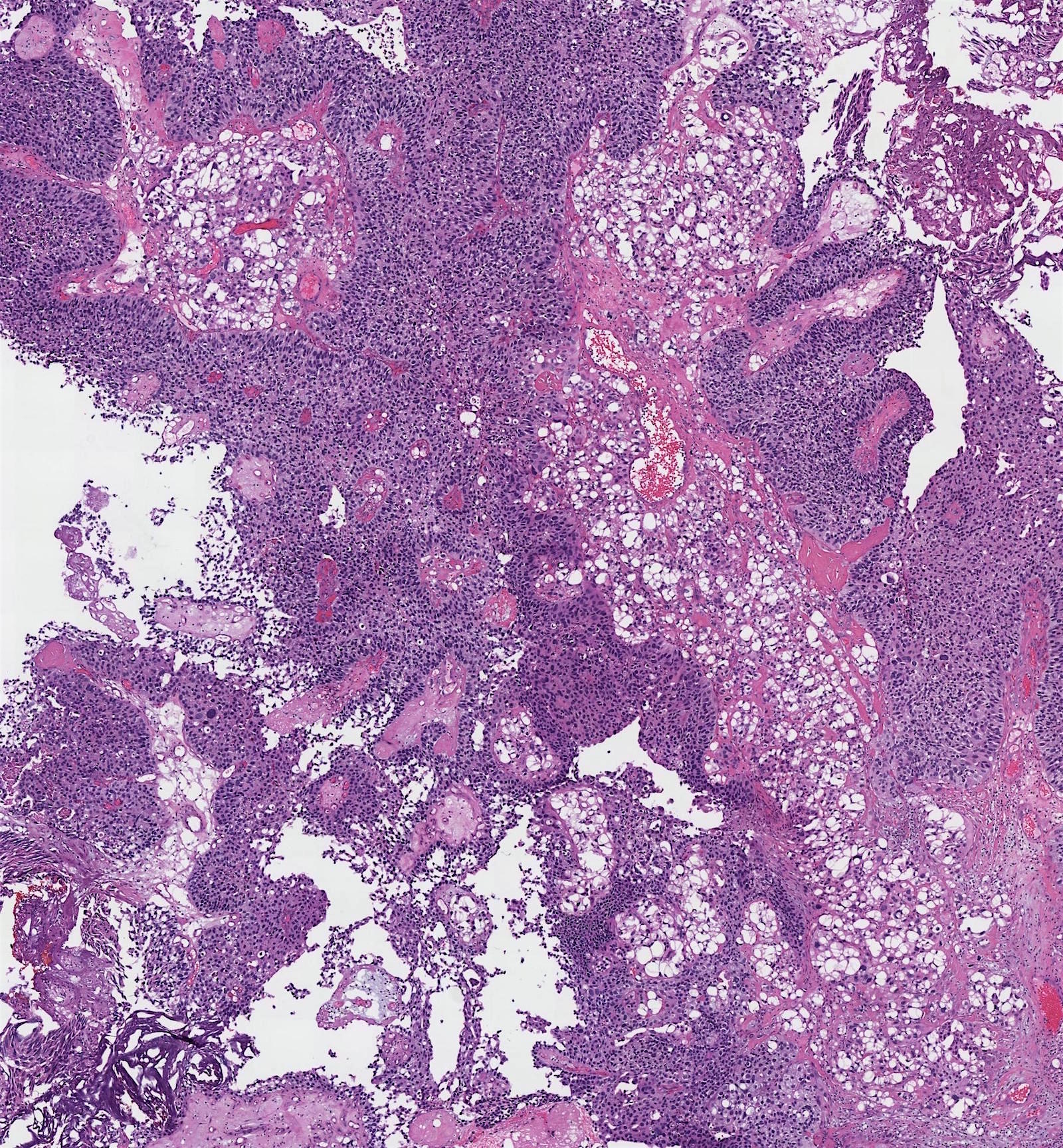
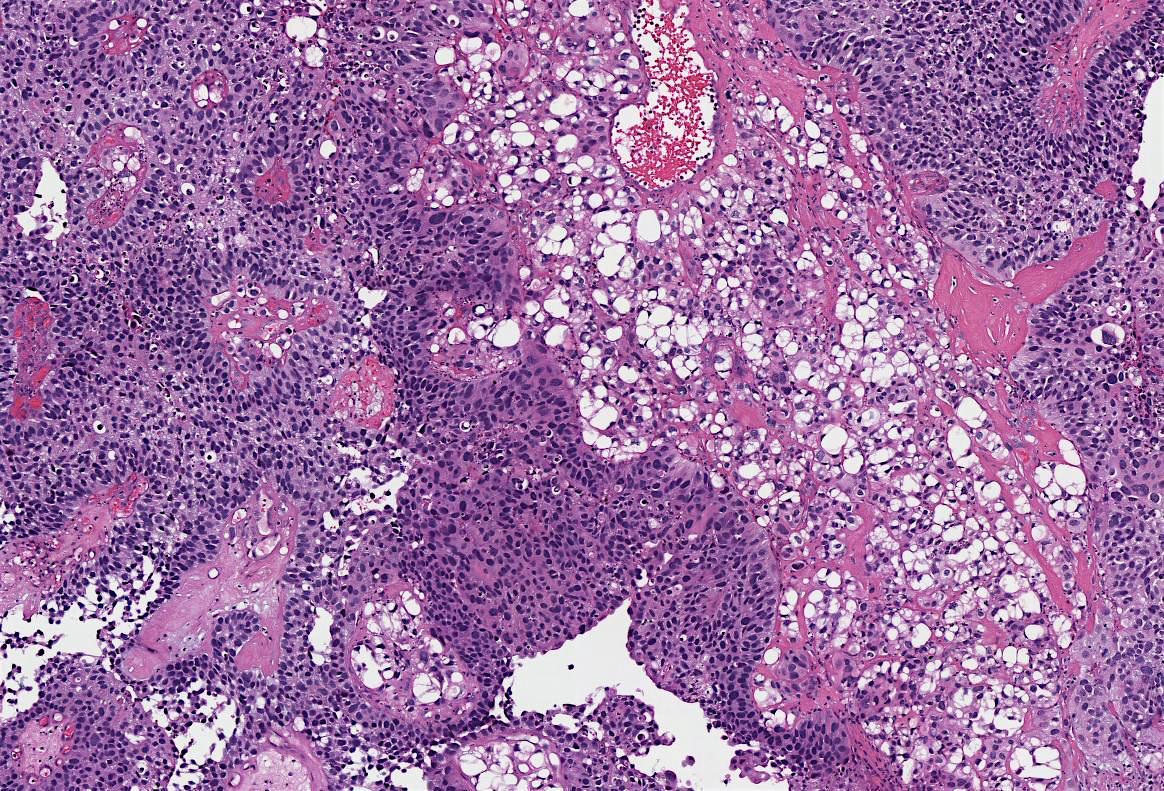
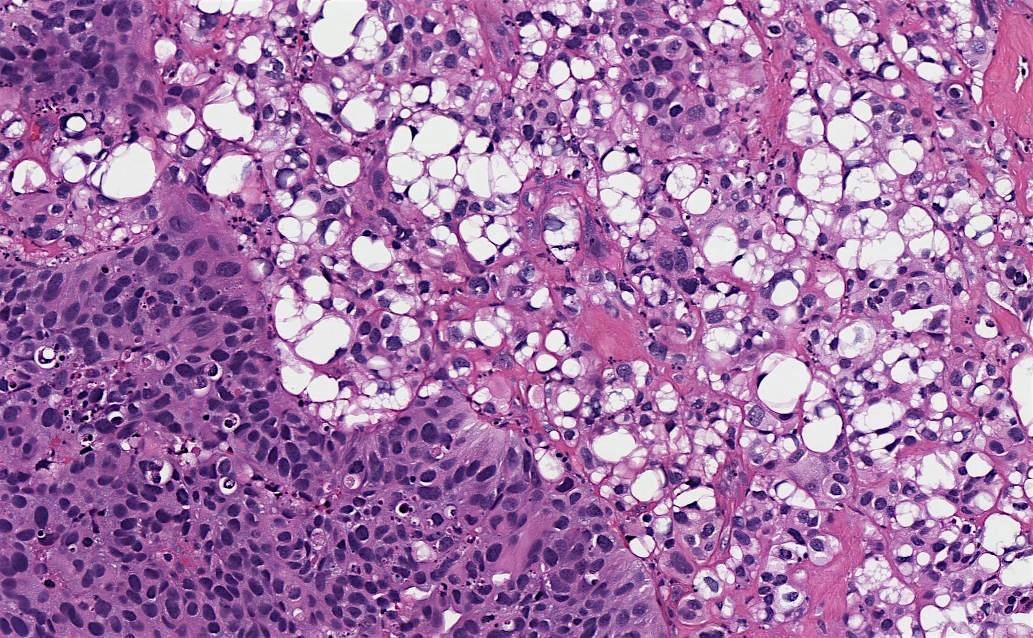
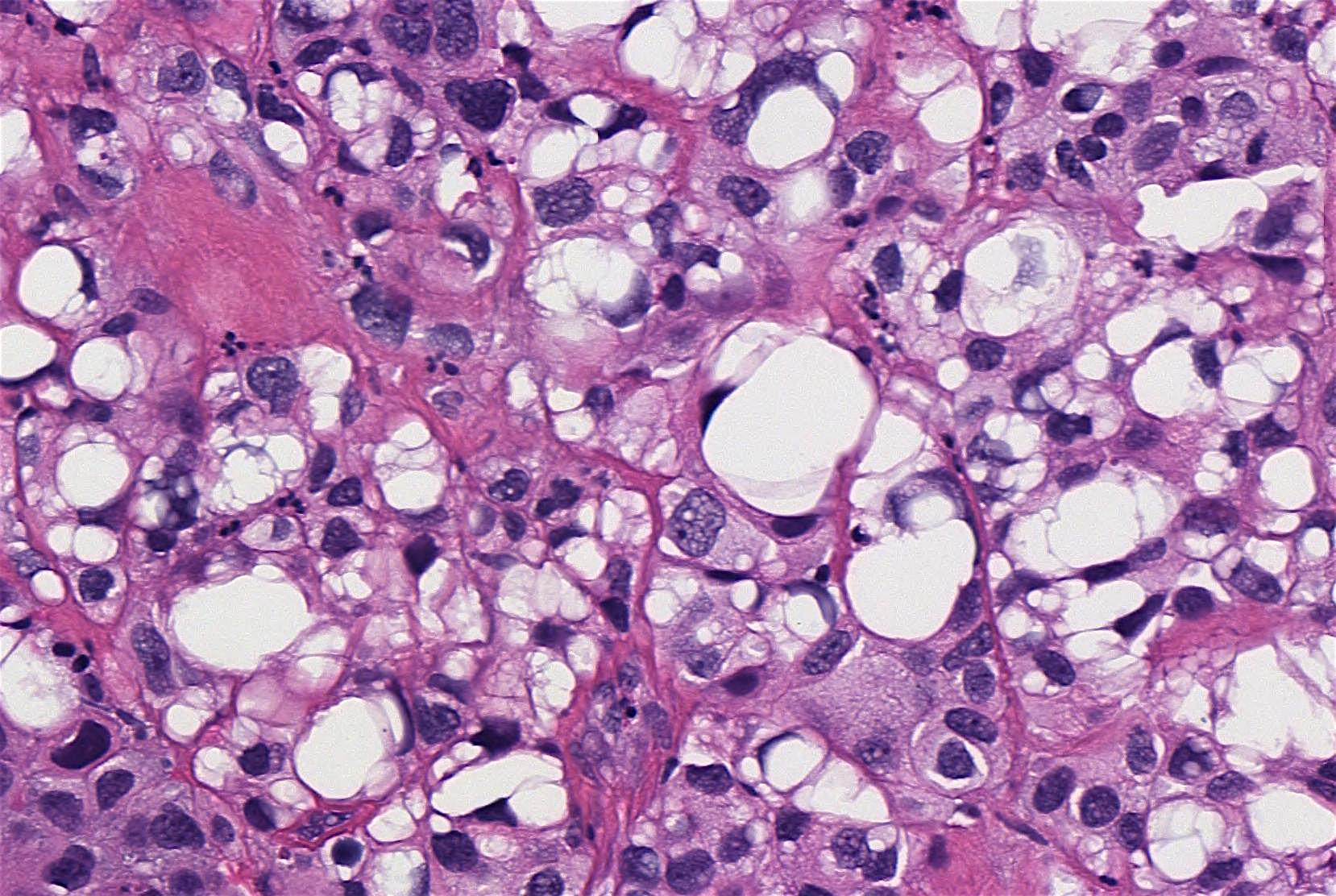
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Large signet ring lipoblast-like cells with single or multiple clear cytoplasmic vacuoles indenting the nucleus (Eur Urol 2016;70:93)
- Lipid component comprises 10 - 50% of the tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:371)
Treatment
- Similar to conventional high grade invasive urothelial carcinoma
Positive stains
- PanCK, CK7, CK20 (variable), EMA, thrombomodulin (variable)
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Shows identical loss of heterozygosity (LOH) patterns with the coexistent conventional UC, supporting a shared clonal origin (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:371)
Differential diagnosis
- Clear cell (glycogen rich)
urothelial carcinoma:
- Has intracytoplasmic PAS+ and diastase sensitive glycogen, rather than lipid
- Lacks lipoblast-like nuclear indentations
- Adenocarcinoma with signet ring features:
- Positive for mucin in contrast to lipid rich variant
- Sarcomatoid carcinoma:
- May have heterologous liposarcomatous elements
- Lipid rich variant lacks the prominent high grade spindled features of sarcomatoid carcinoma
- Liposarcoma:
- Cytokeratin negative
- In contrast, lipid rich variant has cytokeratin and CK7 positive lipoblast-like cells and conventional urothelial carcinoma
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true about lipid-rich variant of urothelial carcinoma?
- It is S100 and vimentin positive
- The lipid cell component usually comprises greater than 50% of the urothelial carcinoma
- The lipid cells are negative for panCK and CK7, contributing to diagnostic challenges with lipoblasts and liposarcoma
- The lipid cells express panCK and CK7 and are negative for mucin, distinguishing this entity from others in the differential diagnosis
Board review style answer #1
D. The lipid cells express panCK and CK7 and are negative for mucin, distinguishing this entity from others in the differential diagnosis.
This and the presence of conventional high grade urothelial carcinoma are helpful diagnostic features in the differential diagnoses of lipid-rich variant of urothelial carcinoma with adenocarcinomas with signet ring features, sarcomatoid carcinoma and liposarcoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Lipid-rich urothelial carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Lipid-rich urothelial carcinoma