5 August 2015 - Case #360
All cases are archived on our website. To view them sorted by case number, diagnosis or category, visit our main Case of the Month page. To subscribe or unsubscribe to Case of the Month or our other email lists, click here.
Thanks to Dr. Roopa Arora, Dr. S. George, Dr. Eman Juffairi, Dr. Rawia Mubarak and Dr. Safa Sheikh, Salmaniya Medical Complex (Kingdom of Bahrain) for contributing this case and the discussion.
Advertisement
Case #360
Clinical history:
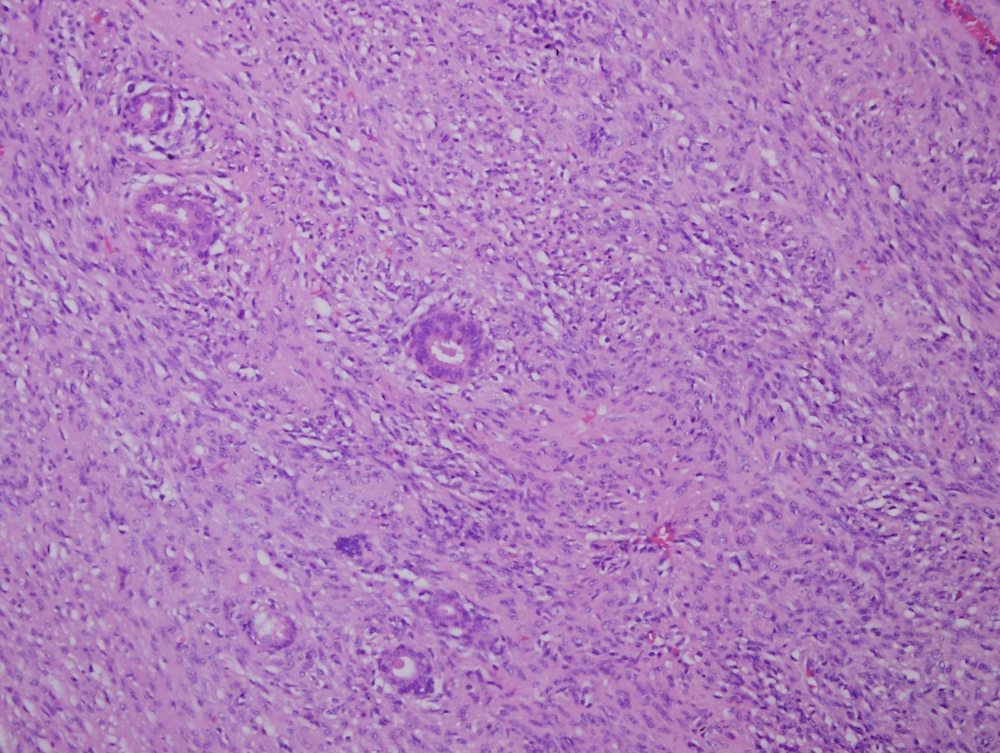
A 36 year old man presented with a history of right parotid swelling for five months, gradually increasing in size. Examination revealed a 10 x 5 x 4 cm irregular, firm to hard, non-expansile, non-translucent multinodular mass with irregular edges in the region of the parotid gland. USG, MRI and CT scan revealed a well defined soft tissue mass with an irregular outline involving the superficial and deep parotid gland, extending into the right retro-auricular space. No lymph node enlargement was seen. Frozen section revealed morphology of a spindle cell neoplasm. A total parotidectomy was performed.
Gross examination showed tan, firm tissue fragments weighing 77 g. The largest fragment measured 6 x 5 x 4 cm. They showed a vaguely lobulated appearance and no foci of necrosis were seen.
Microscopic images:
What is your diagnosis?
Diagnosis: Deep benign fibrous histiocytoma
Immunostain images:
Discussion:
Microscopically, a rim of normal parotid tissue surrounded an ill defined, encapsulated spindled cell tumor with a well marked storiform pattern and scattered mild lymphocytic infiltrate. No ramifying vessels with thickened or hyalinized walls were seen. The tumor showed pushing margins, entrapping normal salivary epithelium. The mitotic count was 4 - 5/10 HPF.
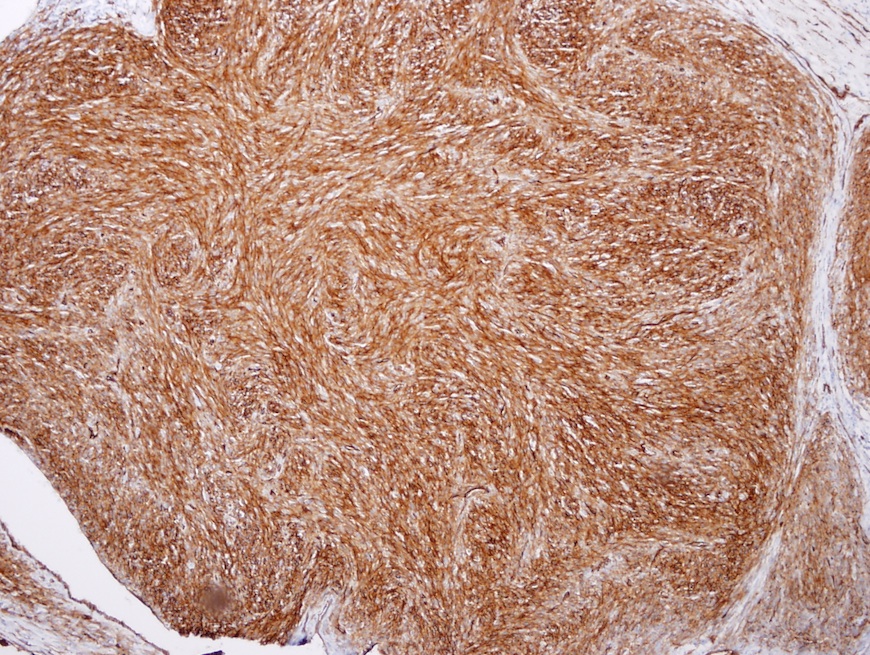
Immunostains included were vimentin (positive), CD34 (positive), CD99 and BCL2 (focally positive). No reactivity for keratin, desmin, alpha smooth muscle actin, EMA, S100 protein or CD117 was observed.
Very few cases of benign and malignant fibrous histiocytoma involving the salivary glands have been reported. Deep benign fibrous histiocytoma is an uncommon and poorly recognized clinical subtype that arises in subcutaneous or deep soft tissue. Only a single series of these neoplasms have been published and their clinical behavior is not well characterized. In this series, 22% arose in the head and neck region, ranging in size from 0.5 to 25 cm. Their morphology and immunostaining was as described in this case.
Differential diagnosis includes solitary fibrous tumor, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and soft tissue perineuroma. Solitary fibrous tumor has patternless sheets of cells with alternating hypo and hypercelluar areas, although it has an overlapping immunostaining profile with deep benign fibrous histiocytoma. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans have a dermal origin with infiltrative extension into the subcutis. Nuclei are small and slender. A lymphocytic infiltrate is usually absent. Soft tissue perineuroma has a whorled architecture. Cells have bipolar processes and very thin nuclei. EMA is positive, highlighting the cell processes.
To conclude, this neoplasm is a very rare in this site and must be distinguished from other spindle cell tumors of the parotid gland. A combination of light microscopy and immunostaining helps to differentiate it from other tumors. Recurrence is common after incomplete excision. Rarely, metastasis occurs. A careful follow up is advised.
References: Laryngoscope 1979;89:1808, J Clin Pathol 1982;35:946, Am J Clin Pathol 1992;97:512, Auris Nasus Larynx 2003;30:315, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354, Semin Cutan Med Surg 1999;18:91, Am J Surg Pathol 1994;18:677
All cases are archived on our website. To view them sorted by case number, diagnosis or category, visit our main Case of the Month page. To subscribe or unsubscribe to Case of the Month or our other email lists, click here.
Thanks to Dr. Roopa Arora, Dr. S. George, Dr. Eman Juffairi, Dr. Rawia Mubarak and Dr. Safa Sheikh, Salmaniya Medical Complex (Kingdom of Bahrain) for contributing this case and the discussion.
- Neoplastic Gastrointestinal Pathology (1st ed) by Laura Lamps, Andrew Bellizzi, Wendy Frankel, Scott Owens and Rhonda Yantiss. 2015, 408 pages, 600+ illus, $133 list.
- Clinical Diagnostic Tests (1st ed) by Michael Laposata. 2015, 310 pages, $55 list.
For more information, visit our New Books page.
Website news:
(1) We now have the 2016 version of How to be a Lab Director on our website. To buy the printed version for a nominal price from Amazon, click here.
Visit and follow our Blog to see recent updates to the website.
(1) We now have the 2016 version of How to be a Lab Director on our website. To buy the printed version for a nominal price from Amazon, click here.
Visit and follow our Blog to see recent updates to the website.
Case #360
Clinical history:
A 36 year old man presented with a history of right parotid swelling for five months, gradually increasing in size. Examination revealed a 10 x 5 x 4 cm irregular, firm to hard, non-expansile, non-translucent multinodular mass with irregular edges in the region of the parotid gland. USG, MRI and CT scan revealed a well defined soft tissue mass with an irregular outline involving the superficial and deep parotid gland, extending into the right retro-auricular space. No lymph node enlargement was seen. Frozen section revealed morphology of a spindle cell neoplasm. A total parotidectomy was performed.
Gross examination showed tan, firm tissue fragments weighing 77 g. The largest fragment measured 6 x 5 x 4 cm. They showed a vaguely lobulated appearance and no foci of necrosis were seen.
Microscopic images:
What is your diagnosis?
Click here for diagnosis and discussion:
Diagnosis: Deep benign fibrous histiocytoma
Immunostain images:
Discussion:
Microscopically, a rim of normal parotid tissue surrounded an ill defined, encapsulated spindled cell tumor with a well marked storiform pattern and scattered mild lymphocytic infiltrate. No ramifying vessels with thickened or hyalinized walls were seen. The tumor showed pushing margins, entrapping normal salivary epithelium. The mitotic count was 4 - 5/10 HPF.
Immunostains included were vimentin (positive), CD34 (positive), CD99 and BCL2 (focally positive). No reactivity for keratin, desmin, alpha smooth muscle actin, EMA, S100 protein or CD117 was observed.
Very few cases of benign and malignant fibrous histiocytoma involving the salivary glands have been reported. Deep benign fibrous histiocytoma is an uncommon and poorly recognized clinical subtype that arises in subcutaneous or deep soft tissue. Only a single series of these neoplasms have been published and their clinical behavior is not well characterized. In this series, 22% arose in the head and neck region, ranging in size from 0.5 to 25 cm. Their morphology and immunostaining was as described in this case.
Differential diagnosis includes solitary fibrous tumor, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and soft tissue perineuroma. Solitary fibrous tumor has patternless sheets of cells with alternating hypo and hypercelluar areas, although it has an overlapping immunostaining profile with deep benign fibrous histiocytoma. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans have a dermal origin with infiltrative extension into the subcutis. Nuclei are small and slender. A lymphocytic infiltrate is usually absent. Soft tissue perineuroma has a whorled architecture. Cells have bipolar processes and very thin nuclei. EMA is positive, highlighting the cell processes.
To conclude, this neoplasm is a very rare in this site and must be distinguished from other spindle cell tumors of the parotid gland. A combination of light microscopy and immunostaining helps to differentiate it from other tumors. Recurrence is common after incomplete excision. Rarely, metastasis occurs. A careful follow up is advised.
References: Laryngoscope 1979;89:1808, J Clin Pathol 1982;35:946, Am J Clin Pathol 1992;97:512, Auris Nasus Larynx 2003;30:315, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:354, Semin Cutan Med Surg 1999;18:91, Am J Surg Pathol 1994;18:677