18 June 2015 - Case #355
All cases are archived on our website. To view them sorted by case number, diagnosis or category, visit our main Case of the Month page. To subscribe or unsubscribe to Case of the Month or our other email lists, click here.
Thanks to Dr. Huda Jamsheer, Ministry of Health (Kingdom of Bahrain), for contributing this case and the discussion.
Advertisement
Case #355
Clinical history:
A 16 year old girl presented with a tender, firm, non-fluctuant swelling in the right, mid-parotid region, gradually increasing in size over the past 3 years. The swelling measured 2.4 x 2.1 x 0.5 cm, and was adherent to the facial nerve by MRI. Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) was performed followed by a total parotidectomy.
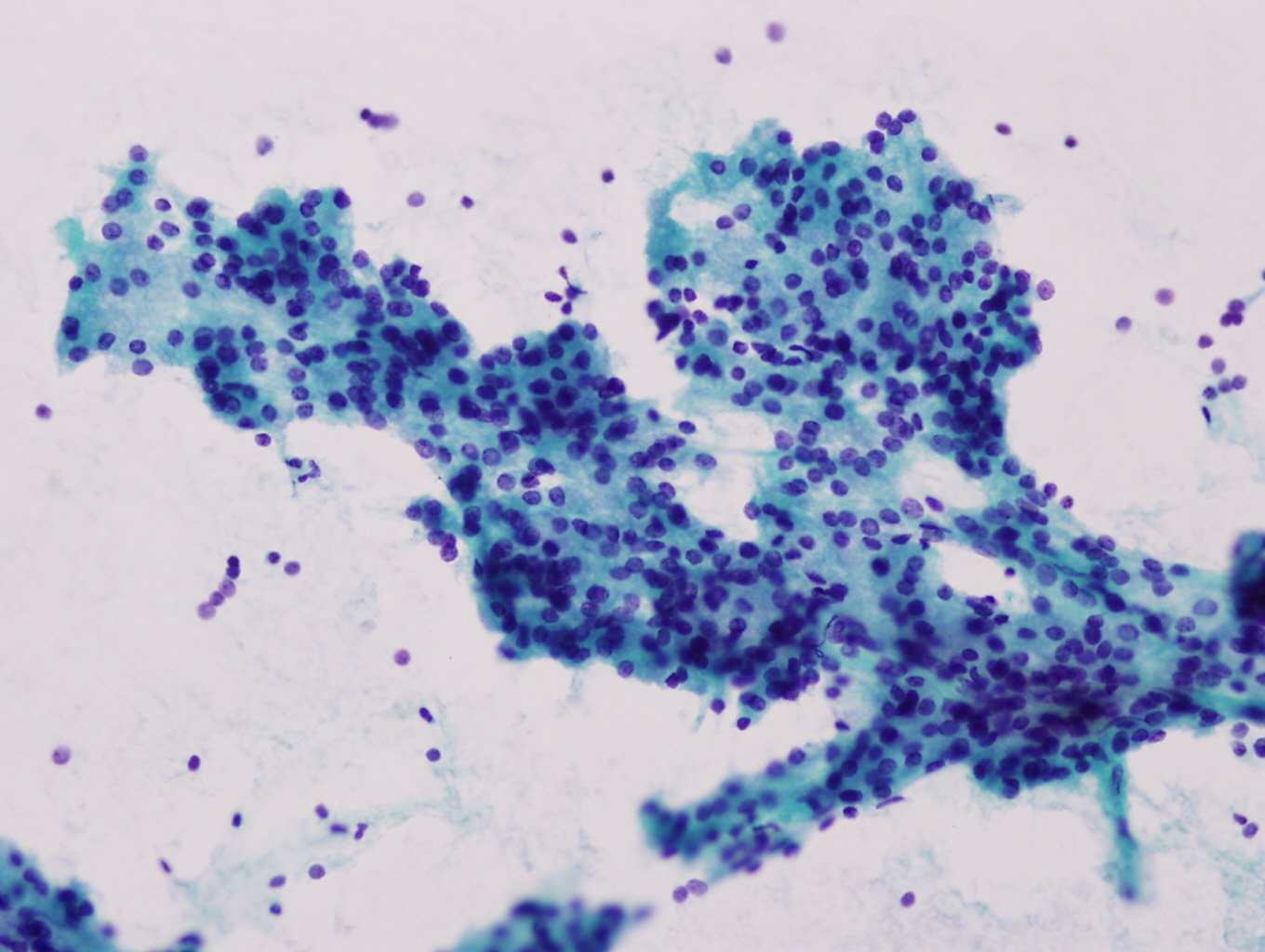
Cytology images:
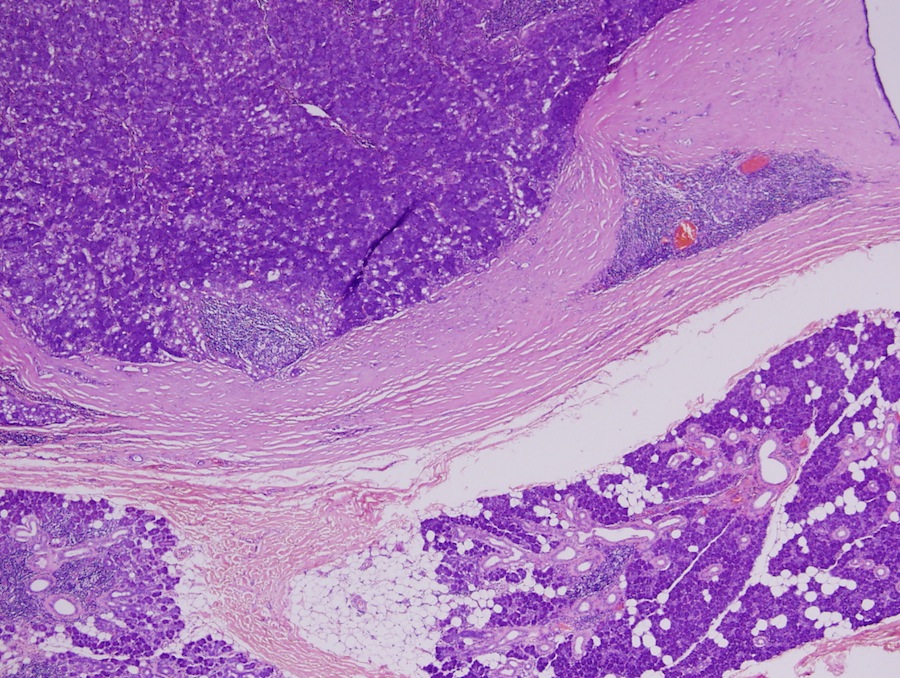
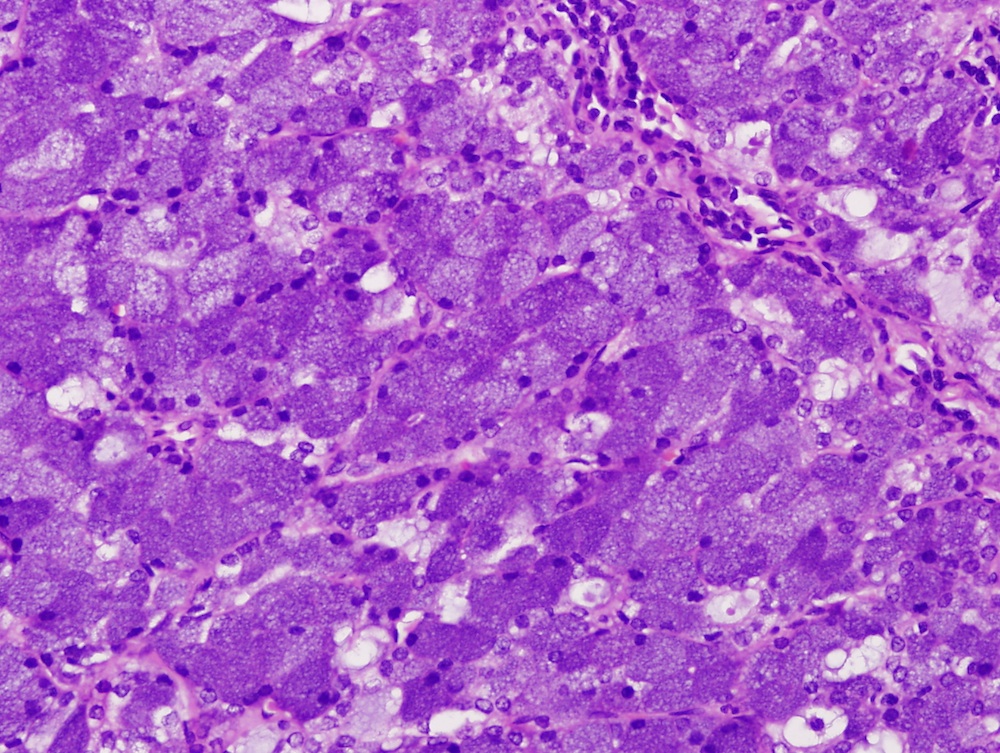
Microscopic images:
What is your diagnosis?
Diagnosis: Acinic cell carcinoma
Discussion:
Histologic examination revealed a solid growth pattern of cells exhibiting serous acinar differentiation with cytoplasmic basophilic granules. The diagnosis was acinic cell carcinoma with no metastasis in the 10 lymph nodes found within the specimen. No facial nerve involvement was seen.
Epithelial salivary gland neoplasms are rare in children and adolescents, and represent only 1 - 5% of childhood salivary gland tumors (Pediatr Surg Int 2005;21:377). The clinical evaluation of a parotid mass can be difficult in children. Clinically, these lesions manifest as painless, enlarging lesions and grow slowly, without symptoms.
Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is safe, rapid and helpful to evaluate a parotid mass, with a 91% specificity and 96% sensitivity when sufficient cells are present (Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2000;126:177). The diagnosis of acinic cell carcinoma by FNA can be particularly challenging. A College of American Pathologists (CAP) Interlaboratory Comparison Program revealed that 49% were called benign, the most likely malignant salivary gland neoplasm to be misdiagnosed as benign (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:26). The tumor can resemble normal salivary gland tissue but its aspirate smears are very cellular. The cells have abundant cytoplasm, uniform round nuclei with evenly dispersed chromatin and a small nucleolus. Absence of well formed acini and salivary ducts are diagnostic (Diagn Cytopathol 1997;17:347, Diagn Cytopathol 1997;17:8, Acta Cytol 2000;44:1073). The differential diagnosis includes chronic sialadenitis and Warthin tumor, if background lymphocytes or cellular debris are seen.
Treatment includes surgery, radiotherapy and brachytherapy (Strahlenther Onkol 2014;190:1008). 5 year survival is up to 97% (Laryngoscope 2014;124:172, Acta Otolaryngol 2005;125:207, Head Neck 1999;21:297). Continued careful follow up of patients is required due to case reports of recurrence up to 10 years after diagnosis (J Med Invest 1999;46:213).
All cases are archived on our website. To view them sorted by case number, diagnosis or category, visit our main Case of the Month page. To subscribe or unsubscribe to Case of the Month or our other email lists, click here.
Thanks to Dr. Huda Jamsheer, Ministry of Health (Kingdom of Bahrain), for contributing this case and the discussion.
- Silverberg's Principles and Practice of Surgical Pathology and Cytopathology (2015) by Mark R. Wick, Virginia A. LiVolsi, John D. Pfeifer, Edward B. Stelow and Paul E. Wakely Jr. Silverberg's Principles and Practice of Surgical Pathology and Cytopathology is one of the most durable reference texts in pathology. Thoroughly revised and updated, this state-of-the-art new edition encompasses the entire fields of surgical pathology and cytopathology in a single source. Its practice-oriented format uniquely integrates these disciplines to present all the relevant features of a particular lesion, side by side. Over 3500 color images depict clinical features, morphological attributes, histochemical and immunohistochemical findings, and molecular characteristics of all lesions included. This edition features new highly experienced and academically accomplished editors, while chapters are written by the leading experts in the field (several new to this edition, bringing a fresh approach).
For more information, visit our New Books page.
Website news:
(1) We have now listed several new webinars from American Society of Clinical Pathology on our Webinars page. Also, don't forget to check out Ventana's new product announcement on our New Products and Services page!
(2) We have posted six new CME lectures from ARUP Laboratories on our CME / Apps / Board Review for Pathology or Laboratory Medicine page. In addition, we have now categorized all of our CME listings by subspecialty for your convenience. Click here to see.
(3) You don't want to miss any of our blog posts, so subscribe and get our posts emailed to you! Simply go to our Blog Homepage and on the right hand side put your email address in the field under "Follow by Email". You will receive an email asking you to confirm. It's that easy! You will only get one email per day (at most) and only on the days which we post a new entry.
Visit and follow our Blog to see recent updates to the website.
(1) We have now listed several new webinars from American Society of Clinical Pathology on our Webinars page. Also, don't forget to check out Ventana's new product announcement on our New Products and Services page!
(2) We have posted six new CME lectures from ARUP Laboratories on our CME / Apps / Board Review for Pathology or Laboratory Medicine page. In addition, we have now categorized all of our CME listings by subspecialty for your convenience. Click here to see.
(3) You don't want to miss any of our blog posts, so subscribe and get our posts emailed to you! Simply go to our Blog Homepage and on the right hand side put your email address in the field under "Follow by Email". You will receive an email asking you to confirm. It's that easy! You will only get one email per day (at most) and only on the days which we post a new entry.
Visit and follow our Blog to see recent updates to the website.
Case #355
Clinical history:
A 16 year old girl presented with a tender, firm, non-fluctuant swelling in the right, mid-parotid region, gradually increasing in size over the past 3 years. The swelling measured 2.4 x 2.1 x 0.5 cm, and was adherent to the facial nerve by MRI. Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) was performed followed by a total parotidectomy.
Cytology images:
Microscopic images:
What is your diagnosis?
Click here for diagnosis and discussion:
Diagnosis: Acinic cell carcinoma
Discussion:
Histologic examination revealed a solid growth pattern of cells exhibiting serous acinar differentiation with cytoplasmic basophilic granules. The diagnosis was acinic cell carcinoma with no metastasis in the 10 lymph nodes found within the specimen. No facial nerve involvement was seen.
Epithelial salivary gland neoplasms are rare in children and adolescents, and represent only 1 - 5% of childhood salivary gland tumors (Pediatr Surg Int 2005;21:377). The clinical evaluation of a parotid mass can be difficult in children. Clinically, these lesions manifest as painless, enlarging lesions and grow slowly, without symptoms.
Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is safe, rapid and helpful to evaluate a parotid mass, with a 91% specificity and 96% sensitivity when sufficient cells are present (Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2000;126:177). The diagnosis of acinic cell carcinoma by FNA can be particularly challenging. A College of American Pathologists (CAP) Interlaboratory Comparison Program revealed that 49% were called benign, the most likely malignant salivary gland neoplasm to be misdiagnosed as benign (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:26). The tumor can resemble normal salivary gland tissue but its aspirate smears are very cellular. The cells have abundant cytoplasm, uniform round nuclei with evenly dispersed chromatin and a small nucleolus. Absence of well formed acini and salivary ducts are diagnostic (Diagn Cytopathol 1997;17:347, Diagn Cytopathol 1997;17:8, Acta Cytol 2000;44:1073). The differential diagnosis includes chronic sialadenitis and Warthin tumor, if background lymphocytes or cellular debris are seen.
Treatment includes surgery, radiotherapy and brachytherapy (Strahlenther Onkol 2014;190:1008). 5 year survival is up to 97% (Laryngoscope 2014;124:172, Acta Otolaryngol 2005;125:207, Head Neck 1999;21:297). Continued careful follow up of patients is required due to case reports of recurrence up to 10 years after diagnosis (J Med Invest 1999;46:213).