
Home
Case
of Week Home
Jobs
Conferences
Fellowships
Books
21 February 2013 - Case of the Week #267
All cases are archived on our website. To view them sorted by number, diagnosis or category, visit our Home Page and click on the Case of the Week button on the left hand side. To subscribe or unsubscribe to the Case of the Week or our other email lists, click here.
Thanks to Dr. David Cohen, Herzliya Medical Center (Israel), for contributing this case and the discussion. To contribute a Case of the Week, follow the guidelines on our Case of the Week page.

Advertisement
Website news:
(1) We have updated the following chapters:
(2) The most popular book sold through our Books pages for 2012 was Montgomery: Biopsy Interpretation of the Gastrointestinal Tract Mucosa: Volume 1: Non-Neoplastic. Check out the complete list at our updated Top Books page.
Case of the Week #267
Clinical History:
A 75 year old woman had a broad-based, 2 x 1 cm, centrally ulcerated mass of the distal ureter, which was excised.
Micro images:
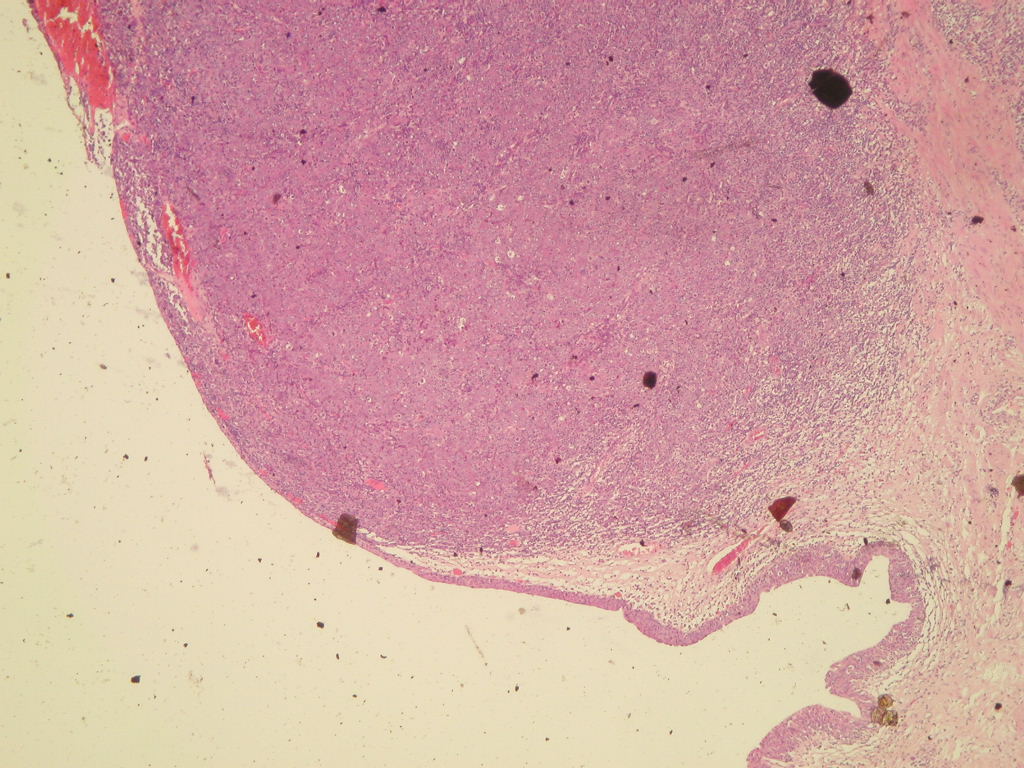
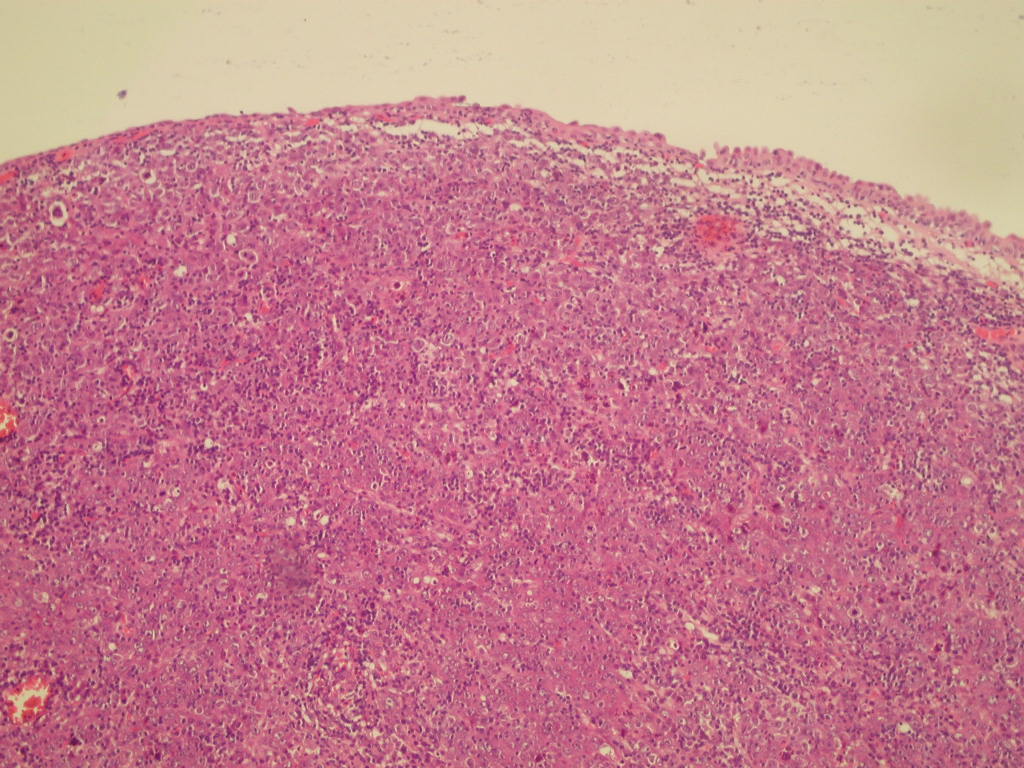

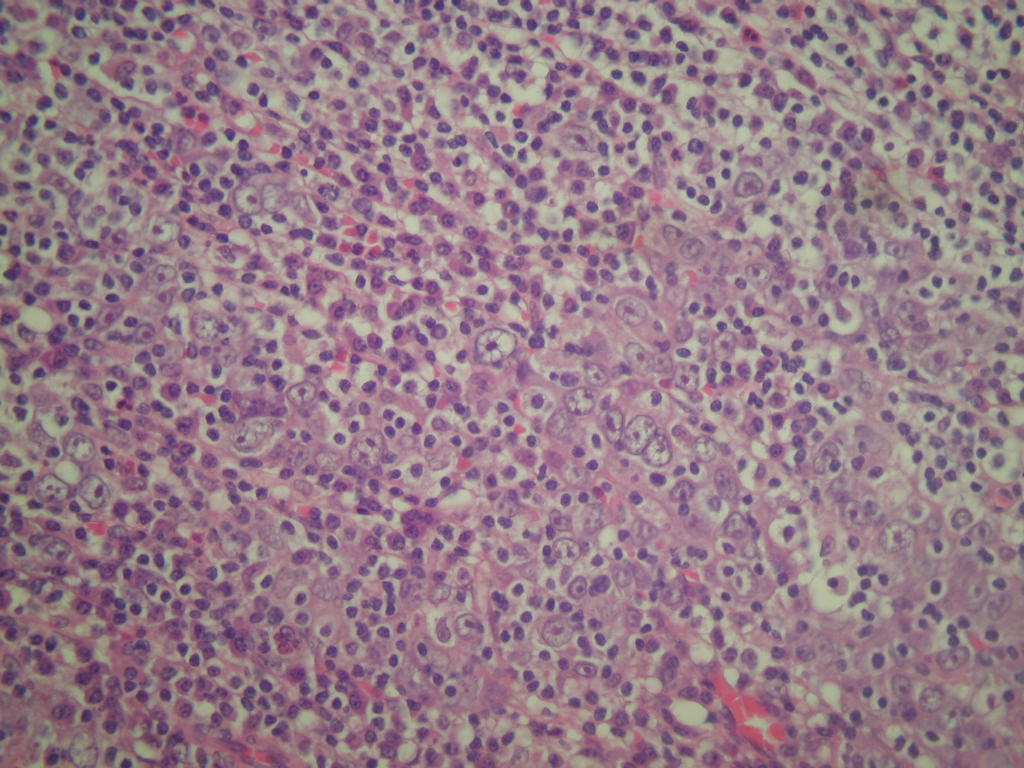
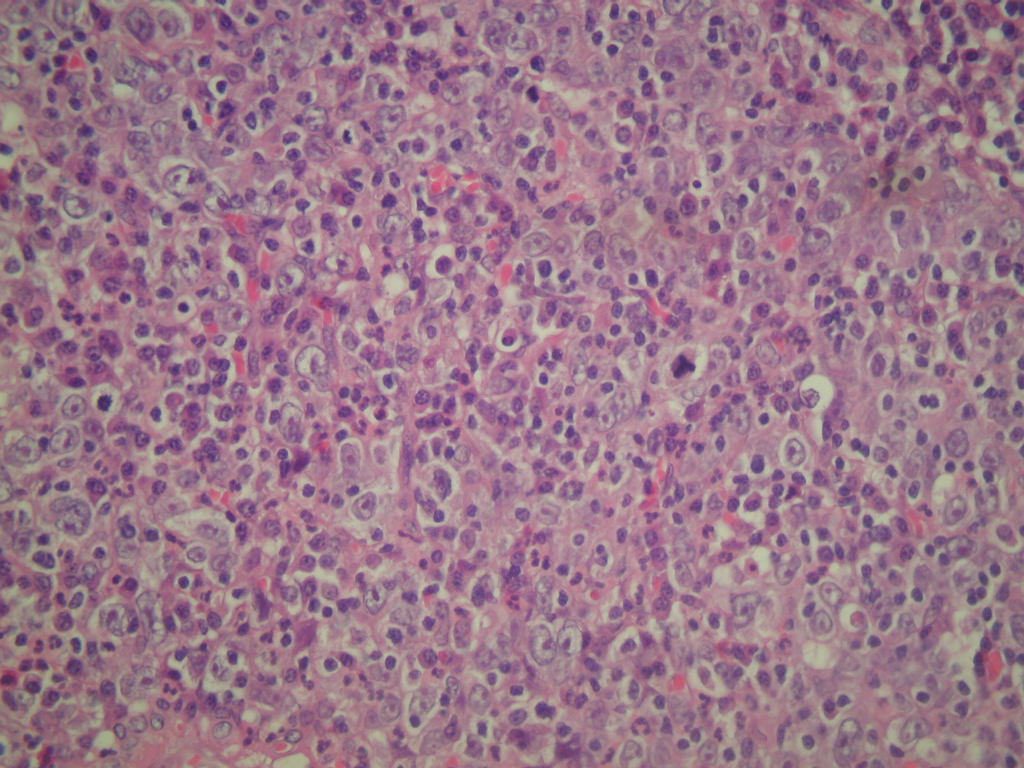
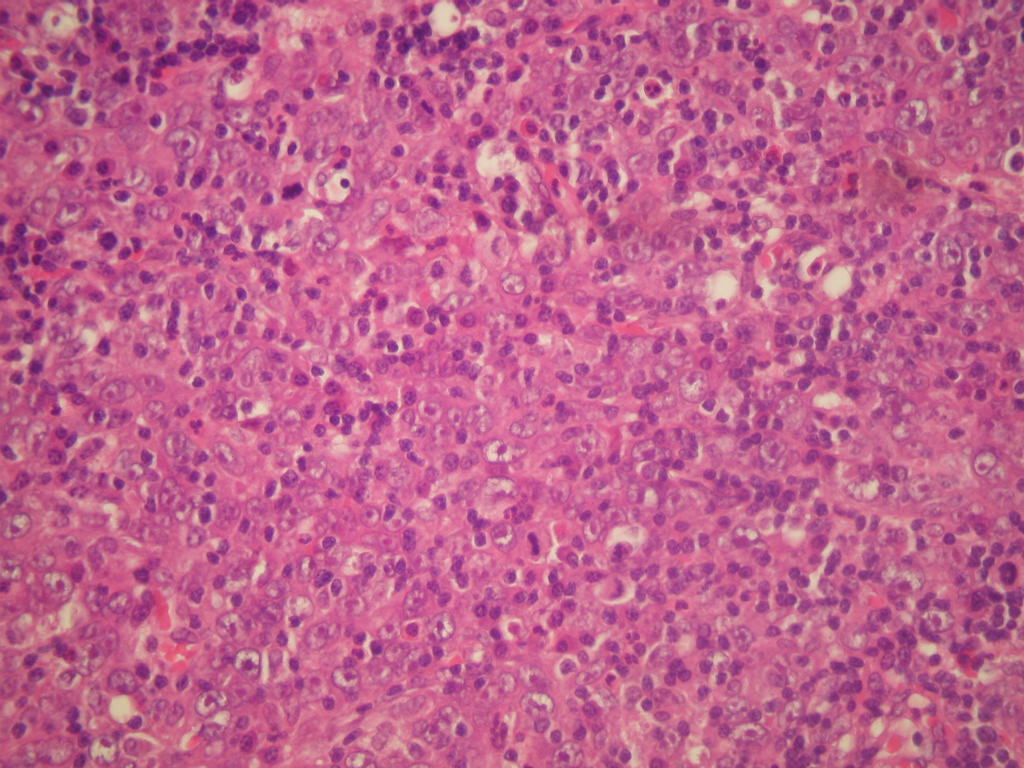
What is your diagnosis?
Diagnosis:
Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the ureter
Discussion:
Immunostains highlighted the lymphocytic component (CD45+) and the carcinoma component (AE1-AE3+):
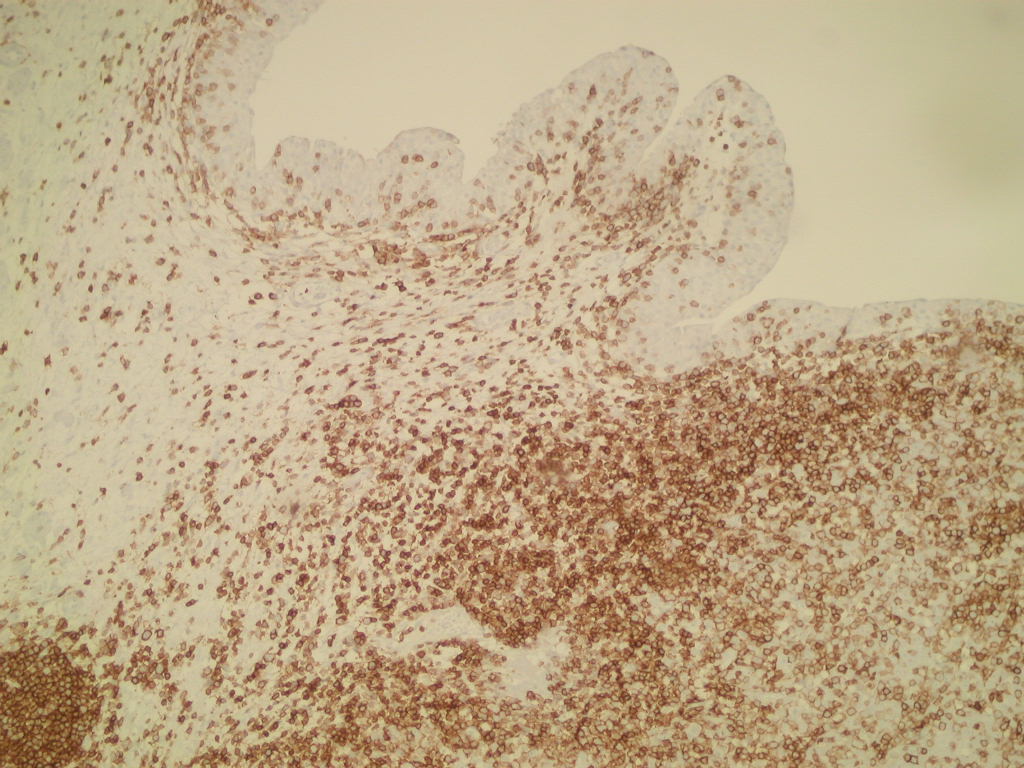
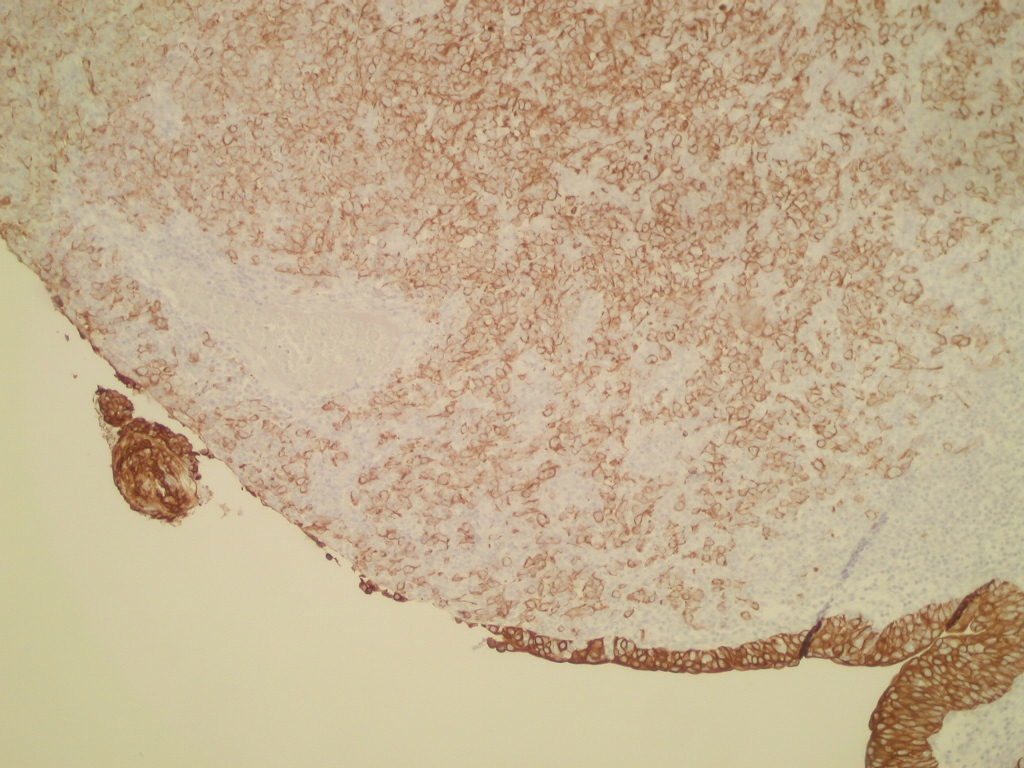

Left to right: CD45, AE1-AE3 (two images)
Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma is a rare GU tumor resembling undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma (lymphoepithelioma), but EBV negative. For that reason, the "-like" is typically added to the name for GU tumors. In the ureter, less than 15 cases have been reported (Kaohsiung J Med Sci 2012;28:509, Ann Diagn Pathol 2010;14:209).
Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma is much more common in the Bladder, with similar features at both sites. Undifferentiated keratin+ carcinoma cells are present in syncytial sheets with minimal cytoplasm, prominent nucleoli, numerous mitoses and lymphocytes. Non-neoplastic inflammatory cells are a mixture of CD45+ polyclonal B and T lymphocytes, histiocytes, eosinophils and plasma cells. As noted, the tumor cells are EBV negative.
The differential diagnosis includes:
- Florid inflammatory infiltrate: no carcinoma component, although keratin stains or multiple sections may be necessary to confirm their absence
- Large cell undifferentiated carcinoma: tumor cells have distinct cell borders, no prominent lymphocytic component
- Lymphoma: no malignant epithelial component, lymphocytes are clonal
Excision with negative margins appears to be adequate treatment, with a good prognosis, in the limited number of cases reported in the ureter (Urology 2005;66:1109).
Nat Pernick, M.D., President
and Palak Thakore, Associate Medical Editor
PathologyOutlines.com, Inc.
30100 Telegraph Road, Suite 408
Bingham Farms, Michigan (USA) 48025
Telephone: 248/646-0325
Email:
NatPernick@Hotmail.com
Alternate email: NatPernick@gmail.com










